
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The drug which has greater partition coefficient is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The partition coefficient is defined as the ratio of the concentration of the compound in two different solvents. The octanol-water partition coefficient is one of the most used partition coefficients which is the ratio concentration in octanol to the water.
Answer to Problem 8.54AP
The
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the two drugs is shown below.
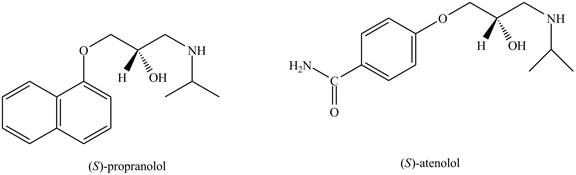
Figure 1
From the structure of two drugs, it is clear that
Therefore, the partition coefficient of
The
(b)
Interpretation:
The concentration of atenolol in each phase is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The partition coefficient is defined as the ratio of the concentration of the compound in two different solvents. The octanol-water partition coefficient is one of the most used partition coefficients which is the ratio concentration in octanol to the water.
Answer to Problem 8.54AP
The amount of atenolol is
Explanation of Solution
The given value of the logarithm of the partition coefficient is shown below.
Take antilog on both sides to find out value of
The formula of the partition coefficient is shown below.
Substitute the value of
The concentration of drug in octanol is
Since the volume of each phase is given same.
Therefore, the ratio of amount of atenolol in octanol to water is
Assume x to be the ratio constant to find out the amount in each solvent. Therefore, the amount of atenolol in water is x and in octanol is
The sum of both amounts is equal to the total amount.
Therefore the amount of atenolol is
The amount of atenolol is
(c)
Interpretation:
The relative water solubility’s of the crystalline atenolol and propranolol are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The partition coefficient is defined as the ratio of the concentration of the compound in two different solvents. The octanol-water partition coefficient is one of the most used partition coefficients which is the ratio concentration in octanol to the water.
Answer to Problem 8.54AP
The
Explanation of Solution
From the structure of two drugs, it is clear that
Therefore, the partition coefficient of
That means
The
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of the conjugated acids of the both drugs is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The drugs
Answer to Problem 8.54AP
The structure of the conjugated acids of the both drugs is shown below.
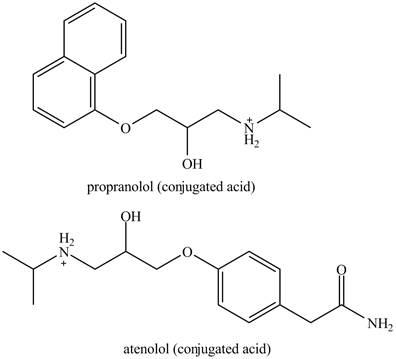
Explanation of Solution
The structure of conjugate acids of both drugs can be made by protonating the amino groups of each drug.
The structures of conjugate acids of each drug are shown below.
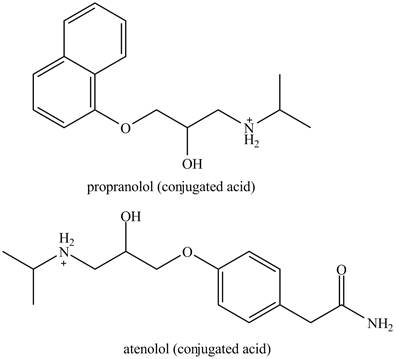
Figure 2
The structure of the conjugated acids of the both drugs is shown in Figure 2.
(e)
Interpretation:
An explanation about the change in the partition coefficient of each drug if it was determined again using water of
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 8.54AP
The value of partition coefficient for both the drugs will decrease on using water of
Explanation of Solution
The
This means the polarity of both the drugs will increase due to which their solubility in the water phase will increase. Therefore, the value of partition coefficient for both the drugs will decrease.
The value of partition coefficient for both the drugs will decrease because both the drugs will be present in the conjugated acids form and therefore their solubility in the water will increase.
(f)
Interpretation:
The reason as to why the drugs are formulated in the form of hydrogen chloride instead of using their basic form is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 8.54AP
The drugs are generally weak acids and bases and for dissolution or absorption in the body these forms are generally not ideal.
To boost their absorption and dissolution in the body, the drugs are formulated in the form of salts.
Explanation of Solution
The drugs are usually weak acids and bases but these forms are usually not optimal for the dissolution or absorption in the body. Medicines need to be water soluble as well.
The drugs are formulated in the form of the salts in order to increase their absorption and dissolution in the body. The salt forms are more optimal for the dissolution and boost its absorption in the stream of blood.
The drugs used in the form of salts in order to enhance its activity and dissolution in the body.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SAPLING ACCESS + ETEX
- Explain the differences in acidity between p-cyanobenzoic acid and m-cyanobenzoic acid. Illustrate your answer appropriately, showing the acid-base reaction that takes place with each of these and explaining in such terms as electronic (inductive or resonance) and/or steric effects.arrow_forwardAlthough benzene is normally written with three double bonds, benzene is not reactive towards many reagents that alkenes normally react with. This lack of reactivity can be explained by the unusual stability created by cyclic conjugation. (i) describe at least one of the physical properties of benzene that demonstrates how the true structure of benzene does match the way the structure is normally written (ii) explain how the unusual stability of benzenecan demonstrated by its thermodynamic properties through some form of experiment. (iii) include an appropriately labeled diagram as part of your answer (you do not have to quote any numerical values)arrow_forwardHow does bromobenzene react differently from benzyl chloride under SN1 and SN2 conditions, and why?arrow_forward
- Predict the electronic configurations of (a) the benzeneanion, (b) the benzene cation. Estimate the π-bond energy in each case.arrow_forwardA) Considering compounds 2a through 2l, identify: 1)one pair of geometric isomers 2)two pairs of enantiomers and 3)three pairs of identical molecules B) Give the names, including the configurations, of each of the geometric isomers and of each of the enantiomers identified in 1A and 1B. Draw the relevant structures. C) Sort compounds 2a, 2b, 2c, 2f and 2k in order of increasing solubility in water and briefly justify.arrow_forwardDuring Friedel Crafts Acylation , Why does AlCl3 have to be anhydrous??arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
