
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The reagent for the given conversion is to be interpreted as dilute sulfuric acid or concentrated sulfuric acid.
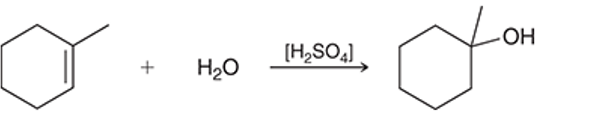
Concept introduction:
(b)
Interpretation: The reagent for the given conversion is to be interpreted as dilute sulfuric acid or concentrated sulfuric acid.
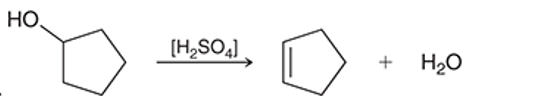
Concept introduction:
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with at least one double bond between the carbon atoms. The presence of pi bonds in these molecules makes them more reactive compared to saturated hydrocarbons; alkanes. The stability of alkenes depends on the substituted groups.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY,SOLNS...-ETEXT+BOX
- Describe concisely a chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds.(a) Propanal and propanone(b) Phenol and benzoic acid(c) Hexan-3-one and hexan-2-onearrow_forwardWrite the reagents and reaction conditions that are necessary for each of the following transformations.arrow_forwardAldehydes and ketones undergo condensation reaction with 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine. Write an equation for the reaction of 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine with any one of the pheromones. What makes 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine suitable for characterizing aldehydes and ketones?arrow_forward
- Complete the following transformationsarrow_forwardIn an advanced synthetic chemistry experiment, a researcher prepares a compound, ZY-7, by reacting a ketone (C5H10O) with hydroxylamine (NH2OH), followed by heating in the presence of an acid catalyst. The resulting compound, ZY-7, is then treated with a solution of sodium nitrite (NaNO2) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) at low temperature. Identify the class of compound that ZY-7 most likely belongs to after this series of reactions." A) Amide B) Oxime C) Nitro compound D) Diazonium salt E) Ester Don't use chatgpt please provide valuable answerarrow_forwardDraw the structure of the major organic product(s) for the following reaction between an acetylenic anion and an alkyl halide. (The reaction stoichiometry is 1:1.)arrow_forward
- You were asked to separate compounds A, B, and C extracted from a plant material through steam distillation. In your experiment, you were able to collect three distillates at different temperatures. In order to classify the compounds in each distillate, you performed several physical and chemical tests. The results are tabulated below. Based on the Results, what are the identities of the terpenoids in each distillate?arrow_forwardModify the structure of phosphoric acid to show the product of each reaction between phosphoric acid and the given number of ethanol molecules. Include all hydrogen atoms.arrow_forwardArrange these compounds in order of increasing acidity: 2,4-dichlorophenol, phenol, cyclohexanol.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

