
Concept explainers
a)
To calculate: The IRR (
Introduction:
The IRR (Internal rate of return) is a rate of discount, which makes the predictable investment’s NPV equal to zero.
The NPV (
a)
Answer to Problem 12QP
As IRR is higher in Project A when compared to Project B, Project A can be accepted. However, it is not the appropriate decision because the criterion of IRR has problem in ranking for mutually exclusive projects.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Company G has identified two mutually exclusive projects where the cash flows of Project A are$14,400, $12,300, $9,200, and $5,100 for year1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The cash flows of Project B are $4,300, $9,800, $15,200, and $16,800 for year 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The initial costs for both the projects are $29,000 respectively.
Note:
- NPV is the difference between the present values of the cash inflows from the present value of cash outflows.
- The IRR is the rate of interest, which makes the project’s NPV equal to zero. Hence, using the available information, assume that NPV is equal to zero and form an equation to compute the IRR.
Equation of NPV to compute IRR assuming that NPV is equal to zero:
Compute IRR for Project A using a spreadsheet:
Step 1:
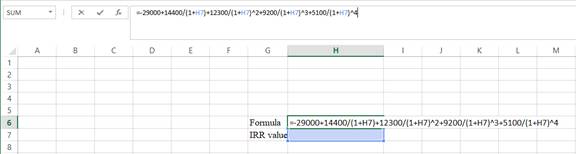
- Type the equation of NPV in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the IRR value as H7.
Step 2:
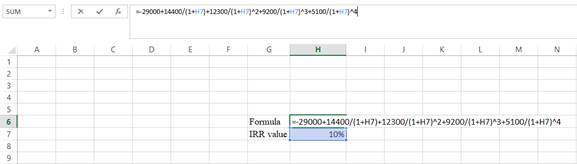
- Assume the IRRvalue as 10%.
Step 3:
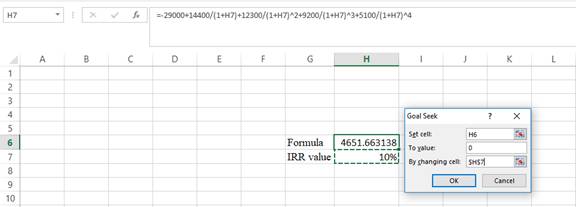
- In the spreadsheet go to data and select the what-if analysis.
- In what-if analysis select goal seek.
- In set cell select H6 (the formula).
- The “To value” is considered as 0 (the assumption value for NPV).
- The H7 cell is selected for the by changing cell.
Step 4:
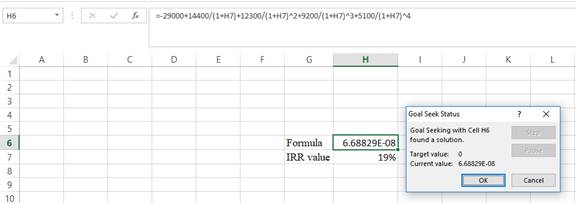
- Following the previous step click OK in the goal seek. The goal seek status appears with the IRRvalue.
Step 5:
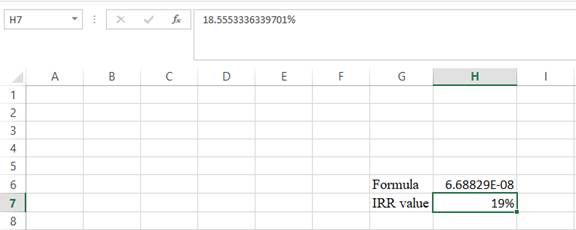
- The value appears to be 18.555336339701%.
Hence, the IRR value is 18.56%.
Compute IRR for Project B using a spreadsheet:
Step 1:
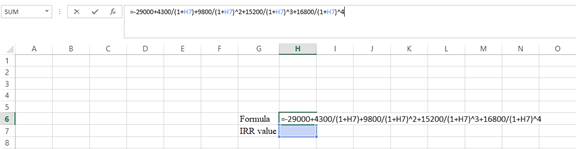
- Type the equation of NPV in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the IRR value as H7.
Step 2:
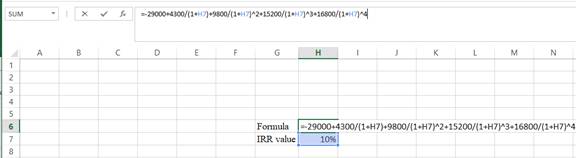
- Assume the IRRvalue as 10%.
Step 3:
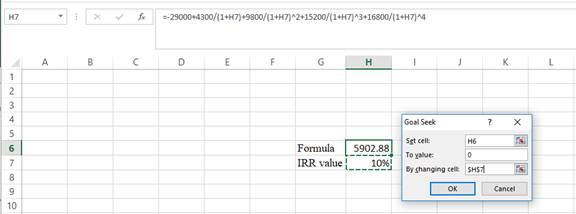
- In the spreadsheet go to data and select the what-if analysis.
- In what-if analysis select goal seek.
- In set cell select H6 (the formula).
- The “To value” is considered as 0 (the assumption value for NPV).
- The H7 cell is selected for the by changing cell.
Step 4:
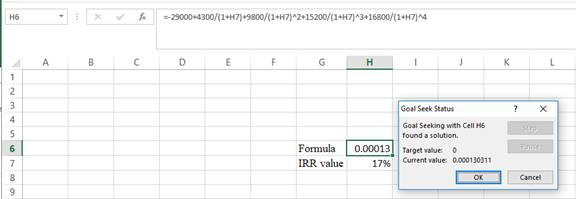
- Following the previous step click OK in the goal seek. The goal seek status appears with the IRRvalue.
Step 5:
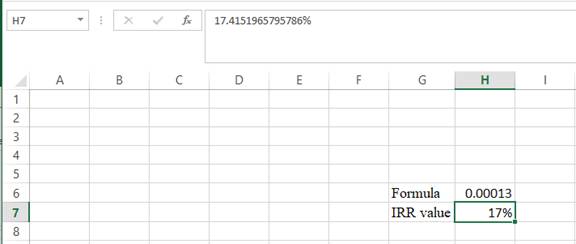
- The value appears to be 17.4151965795786%.
Hence, the IRR value is 17.42%.
b)
To calculate: The NPV for the projects to choose the best project for the company.
Introduction:
The IRR (Internal
The NPV (Net present value) is a capital budgeting technique, which is used to assess the investment that in turn, is utilized to identify the profitability in a proposed investment.
b)
Answer to Problem 12QP
As NPV is greater in Project B, the company must accept Project B.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Company G has identified two mutually exclusive projects where the cash flows of Project A are$14,400, $12,300, $9,200, and $5,100 for year1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The cash flows of Project B are $4,300, $9,800, $15,200, and $16,800 for year 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The initial costs for both the projects are $29,000 respectively.
Note:
- NPV is the difference between the present values of the cash inflows from the present value of cash outflows.
- The IRR is the rate of interest, which makes the project’s NPV equal to zero. Hence, using the available information, assume that NPV is equal to zero and form an equation to compute the IRR.
Formula to calculate the NPV:
Compute NPV for Project A:
Hence, the NPV for Project A is $4,042.42.
Compute NPV for Project B:
Note: The rate is given at 11%.
Hence, the NPV for project B is $5,008.56.
c)
To calculate: The rates of discount at which the company will select Project A and Project B and the discount rate in which the company will be indifferent in selecting between the two projects.
Introduction:
The IRR (Internal rate of return) is a rate of discount, which makes the predictable investment’s NPV equal to zero.
The NPV (Net present value) is a capital budgeting technique, which is used to assess the investment that in turn, is utilized to identify the profitability in a proposed investment.
c)
Answer to Problem 12QP
At the rate of discount above 14.83%, the company must choose Project A and for the rate below 14.83%, the company should choose Project B. Hence, it is indifferent at the discount rate of 14.83%.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Company G has identified two mutually exclusive projects where the cash flows of Project A are$14,400, $12,300, $9,200, and $5,100 for year1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The cash flows of Project B are $4,300, $9,800, $15,200, and $16,800 for year 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The initial costs for both the projects are $29,000 respectively.
Note:
- NPV is the difference between the present values of the cash inflows from the present value of cash outflows.
- The IRR is the rate of interest, which makes the project’s NPV equal to zero. Hence, using the available information, assume that NPV is equal to zero and form an equation to compute the IRR.
Equation to calculate the crossover rates:
Compute the discount rate using spreadsheet
Step 1:
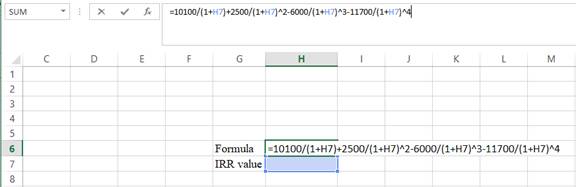
- Type the equation of NPV in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the R value as H7.
Step 2:
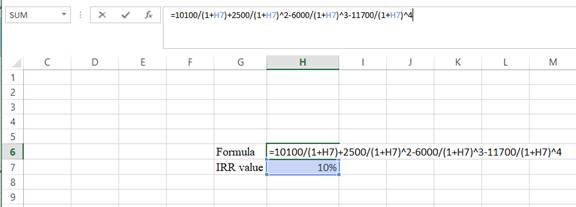
- Assume the Rvalue as 10%.
Step 3:
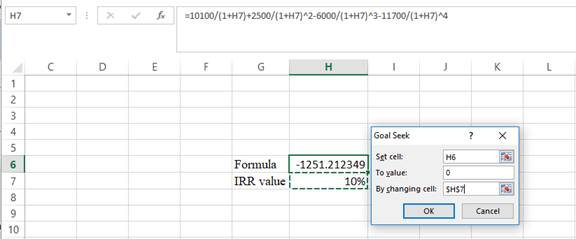
- In the spreadsheet go to data and select the what-if analysis.
- In what-if analysis select goal seek.
- In set cell select H6 (the formula).
- The “To value” is considered as 0 (the assumption value for NPV).
- The H7 cell is selected for the by changing cell.
Step 4:
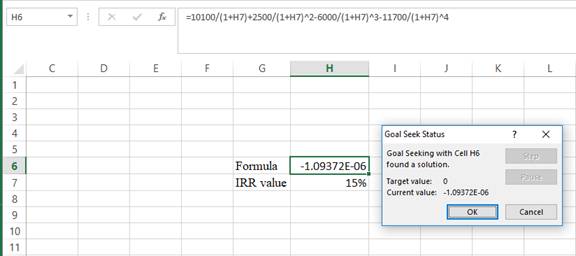
- Following the previous step click OK in the goal seek. The goal seek status appears with the Rvalue.
Step 5:
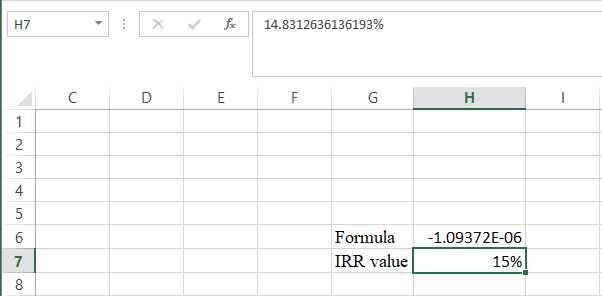
- The value appears to be 14.8312636136193%.
Hence, the R value is 14.83%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF CORPORATE FINANCE A
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





