
Concept explainers
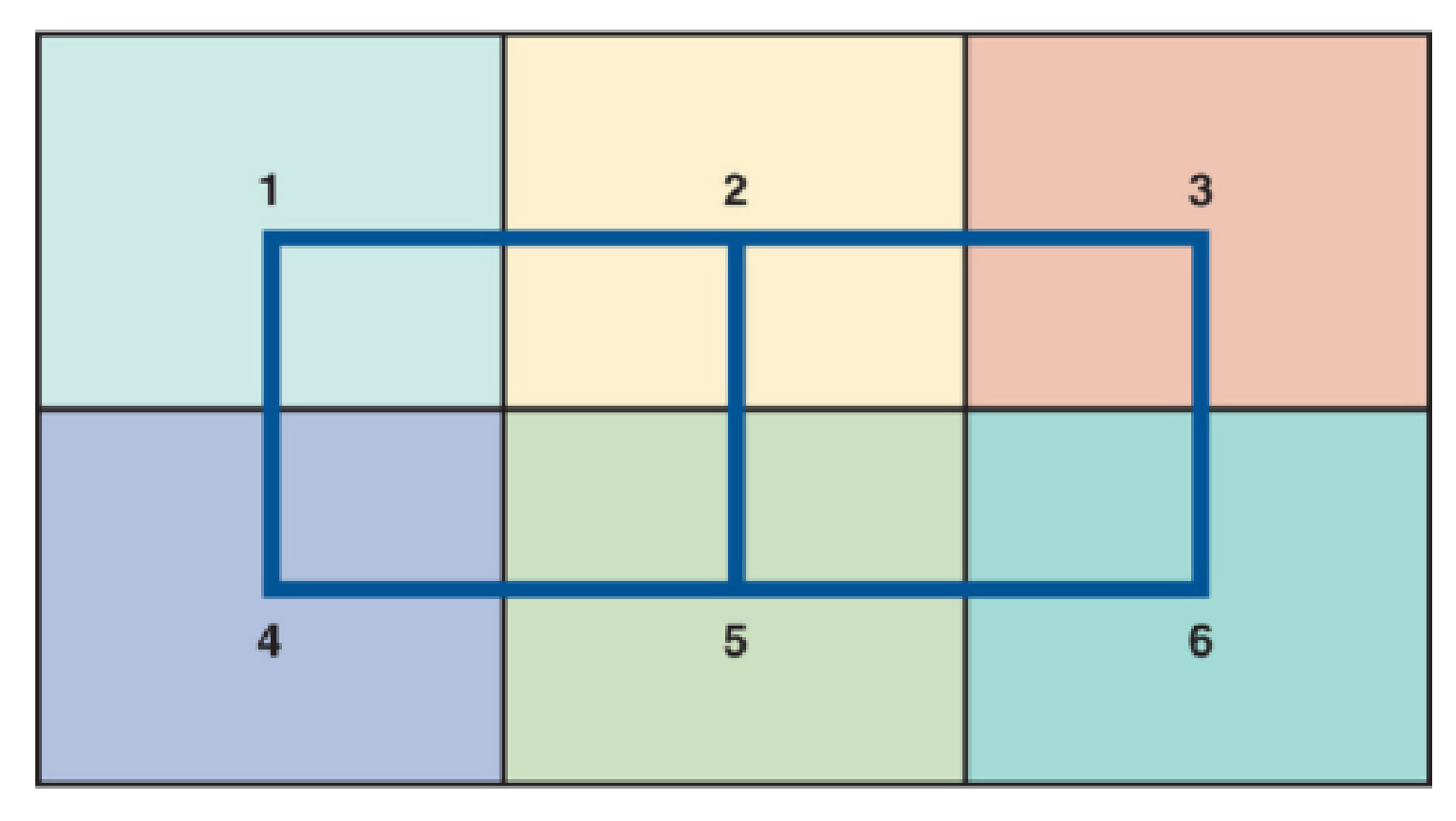
Roy Creasey Enterprises, a machine shop, is planning to move to a new, larger location. The new building will be 60 feet long by 40 feet wide. Creasey envisions the building as having six distinct production areas, roughly equal in size. He feels strongly about safety and intends to have marked pathways throughout the building to facilitate the movement of people and materials. See the following building schematic.
Building Schematic (with work areas 1–6)
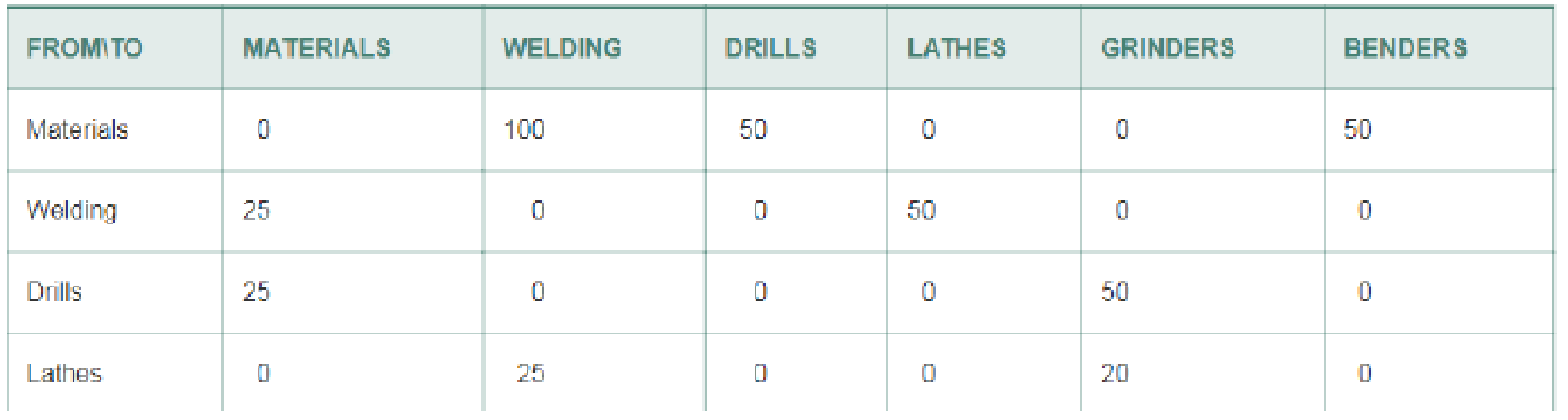
His foreman has completed a month-long study of the number of loads of material that have moved from one process to another in the current building. This information is contained in the following flow matrix.
Flow Matrix Between Production Processes

Finally, Creasey has developed the following matrix to indicate distances between the work areas shown in the building schematic.
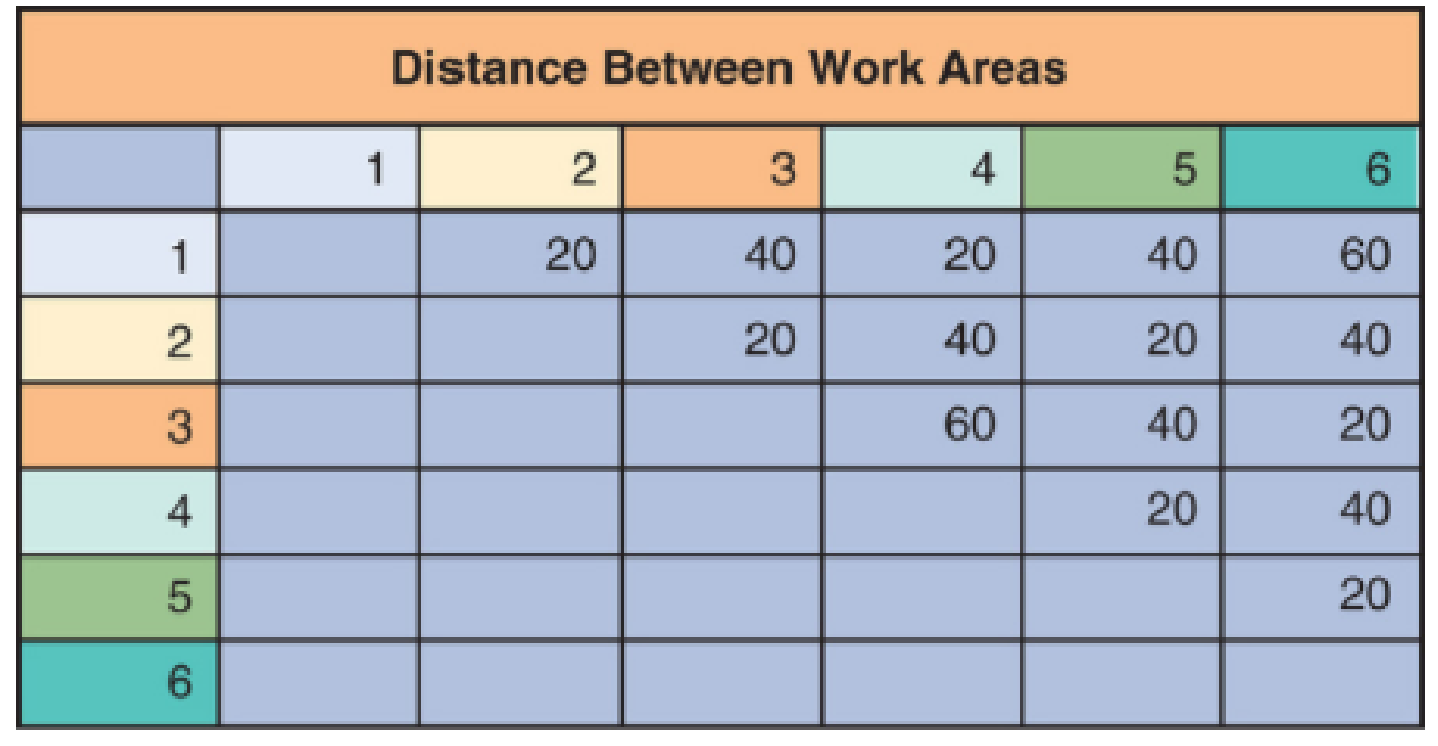
What is the appropriate layout of the new building?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
OPEARATIONS MANAG.REV CUSTOM 2017
- MGT-314 (Operations Management) MCQ: 1. Tesla is launching a new model of their cars. It is known as the Tesla-model X. Their production facility in Chicago cannot fit the assembly line needed for making the new model. They bought robots, tools, and materials to expand the manufacturing facility. This assembly line is only going to make model-X's and no other models. Their layout is: a) Services Layout b) Product Layout c) Fixed Position Layout d) Process Layout 2. A country is only as strong as its citizens. Due to Bangladesh being a third world country, the crisis is everywhere. With a massive number of people believing in hard work for a minimum wage, these blue-collar employees are having the harshest time surviving this countrywide condition. They simply don't have the means to withstand this situation and that is where the government comes in to aid these people with essentials such as food and equipment (Tran) which will help them to stay afloat from this pandemic. While…arrow_forwardPlease create an objective true using these two solutions. Solution1 - More accommodation/residence should be built in the airport itself as it would allow Pascal to save a lot of time consumed while reaching the airport from his house. He would stay in the built-in residence only during his workdays and in his house on the weekend. It will also allow many passengers to stay if their flights get postponed/canceled due to any reason. Solution 2 - If a prayer room/area is built in the airport itself, it will allow Rajput and other diverse travelers and people who work in the airport to complete their prayer in its proper time. Rajput could complete that specific prayer between the time after he checks in his luggage and the boarding time. PLEASE FOLLOW THESE REQUIRMENTS ASWELL OTHERWISE QUESTION WILL BE MARKED INCOMPLETE: Three levels of objectives are included. At the 1st-level, three or more objectives are included. Each 1st-level objective is broken into two or more 2nd-level…arrow_forwardOM Builders Inc. is starting a brand-new development of 10 residential houses in an up and coming neighborhood. The previous housing development completed by OM Builders Inc. was its first development and experienced significant issues with town permits, scheduling, delayed shipments, incorrect furniture and equipment and meeting the closing date of homes. The owner of the firm has met with his management team to discuss how the company can ensure a more efficient, less error-prone project for this new development. The management team decided to use project management tools suggested by a recent graduate the firm hired from a Global Business Management college program. The objectives for the new development are to reduce the number of errors, ensure that schedules are prepared properly and followed and the completion of the project by the promised closing date. The company is currently negotiating with the current owners of the land to be developed and a deal is imminent. During the…arrow_forward
- Entriken Machinery specializes in developing weed-harvesting equipment that is used to clear small lakes of weeds. Dick Entriken, president of Entriken Machinery, is convinced that harvesting weeds is far better than using chemicals to kill weeds. Chemicals cause pollution, and the weeds seem to grow faster after chemicals have been used. Dick is contemplating the construction of a machine that could harvest weeds on narrow rivers and waterways. The activities that are necessary to build one of these experimental weed-harvesting machines are listed in the accompanying table. ---------------------------------------------- Activity Immediate Time (weeks) predecessor --------------------------------------------- A - 6 B - 5 C A 3 D A 2 E…arrow_forwardEntriken Machinery specializes in developing weed-harvesting equipment that is used to clear small lakes of weeds. Dick Entriken, president of Entriken Machinery, is convinced that harvesting weeds is far better than using chemicals to kill weeds. Chemicals cause pollution, and the weeds seem to grow faster after chemicals have been used. Dick is contemplating the construction of a machine that could harvest weeds on narrow rivers and waterways. The activities that are necessary to build one of these experimental weed-harvesting machines are listed in the accompanying table. ---------------------------------------------- Activity Immediate Time (weeks) predecessor --------------------------------------------- A - 6 B - 5 C A 3 D A 2 E…arrow_forwardEntriken Machinery specializes in developing weed-harvesting equipment that is used to clear small lakes of weeds. Dick Entriken, president of Entriken Machinery, is convinced that harvesting weeds is far better than using chemicals to kill weeds. Chemicals cause pollution, and the weeds seem to grow faster after chemicals have been used. Dick is contemplating the construction of a machine that could harvest weeds on narrow rivers and waterways. The activities that are necessary to build one of these experimental weed-harvesting machines are listed in the accompanying table. ---------------------------------------------- Activity Immediate Time (weeks) predecessor --------------------------------------------- A - 6 B - 5 C A 3 D A 2 E…arrow_forward
- Entriken Machinery specializes in developing weed-harvesting equipment that is used to clear small lakes of weeds. Dick Entriken, president of Entriken Machinery, is convinced that harvesting weeds is far better than using chemicals to kill weeds. Chemicals cause pollution, and the weeds seem to grow faster after chemicals have been used. Dick is contemplating the construction of a machine that could harvest weeds on narrow rivers and waterways. The activities that are necessary to build one of these experimental weed-harvesting machines are listed in the accompanying table. ---------------------------------------------- Activity Immediate Time (weeks) predecessor --------------------------------------------- A - 6 B - 5 C A 3 D A 2 E…arrow_forward7. Using the assembly-line balancing procedures for any assembly-line balancing problem, which of the following is most correct? Multiple Choice The theoretical minimum number of workstations is always less than number of workstations actually used. The theoretical minimum number of workstations is sometimes more than number of workstations actually used. The theoretical minimum number of workstations is sometimes less than Y and sometimes more than number of workstations actually used. The theoretical minimum number of workstations is always less than or equal to number of workstations actually used. The theoretical minimum number of workstations is never less than number of workstations actually used.arrow_forwardThe Gardner Theater, a community playhouse, needs to determine the lowest-cost production budget for an upcoming show. Specifically, they have to determine which set pieces to construct and which, if any, set pieces to rent from another local theater at a predetermined fee. However, the organization has only two weeks to fully construct the set before the play goes into technical rehearsals. The theater has two part-time carpenters who work up to 12 hours a week, each at $10 an hour. Additionally, the theater has a part-time scenic artist who can work 15 hours per week to paint the set and props as needed at a rate of $15 per hour. The set design requires 20 flats (walls), two hanging drops with painted scenery, and three large wooden tables (props). The number of hours required for each piece for carpentry and painting is shown below: Gardner Theater Hours Required/Piece Carpentry Painting Flats 0.5 2.0 Hanging Drops 2.0 12.0 Props 3.0 4.0 Hours Available 48.0…arrow_forward
- Case- R. C. Coleman’s Warehouse Project C. Coleman distributes a variety of food products that are sold through grocery store and supermarket outlets. The company receives orders directly from the individual outlets, with a typical order requesting the delivery of several cases of anywhere from 20 to 50 different products. Under the company’s current warehouse operation, warehouse clerks dispatch order-picking personnel to fill each order and have the goods moved to the warehouse shipping area Because of the high labor costs and relatively low productivity of hand order picking, management has decided to automate the warehouse operation by installing a computer-controlled order-picking system along with a conveyor system for moving goods from storage to the warehouse shipping area. R. C. Coleman’s director of material management has been named the project manager in charge of the automated warehouse system. After consulting with members of the engineering staff and warehouse…arrow_forward1.The chief engineer of firm XYZ is responsible for supervising the construction work of a road. He has identified the activities and their durations for each stage of operation. Activity Duration (days) Preceding activities A 5 - B 10 - C 1 - D 8 B E 10 B F 9 B G 3 A,D H 7 A,D I 4 F J 3 F K 5 C,J L 8 H,E,I,K M 4 CJ Draw a network diagram (AOA) for this road construction project. Which are the critical activities? How long the project will take?arrow_forwardConstruct a multi-activity chart. Assume the operator is handling 3 machines. His travel timefrom the machine is 0.5 minutes, loading of materials is 1 minute, unloading is 1 minute, machiningis 8 minutes, and inspection & packing is 0.5 minutes. The analyst will observe the operator up tothree cycles. Compute the following1. Idle Time of operator __________ minutes2. Idle time of machine 1 __________ minutes3. Idle Time of machine 2 __________ minutes4. Idle time of machine 3 ___________ minutes5. The third cycle of machining will be finished on _________ minutesarrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.





