
The ac bridge circuit of Fig. 9.85 is called a Wien bridge. It is used for measuring the frequency of a source. Show that when the bridge is balanced,
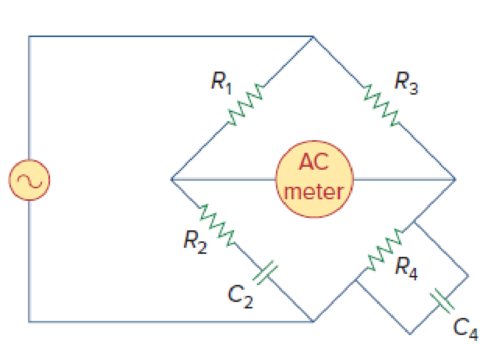
Figure 9.85
Show that when the bridge in Figure 9.85 is balanced the value of frequency is
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 9.85 in the textbook.
Formula used:
Write a general expression to calculate the impedance of a resistor.
Here,
Write a general expression to calculate the impedance of a capacitor.
Here,
Write a general expression to calculate the angular frequency.
Here,
Calculation:
The given circuit is redrawn as shown in Figure 1.
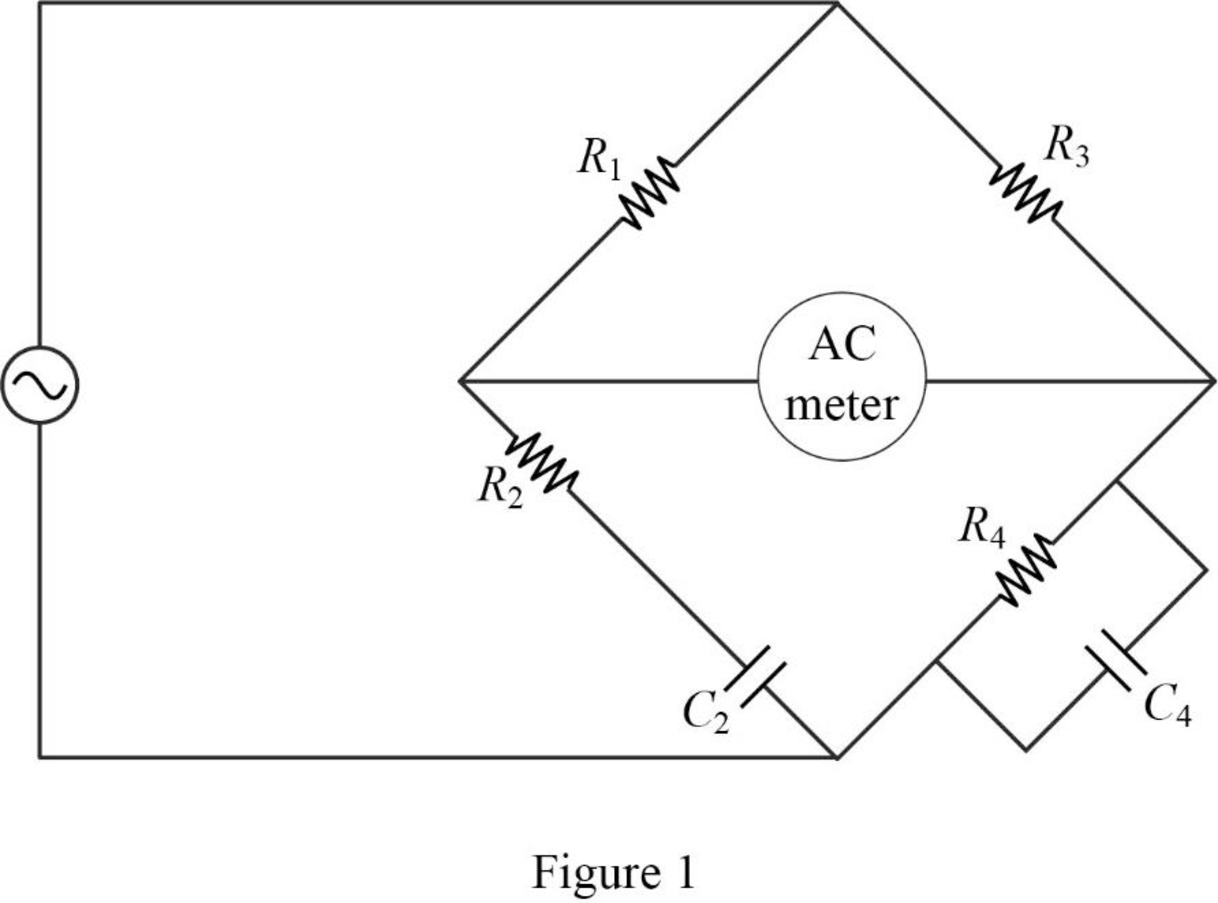
Use equation (1) to find
Use equation (2) to find
Now, the impedance diagram of Figure 1 is drawn as shown in Figure 2.
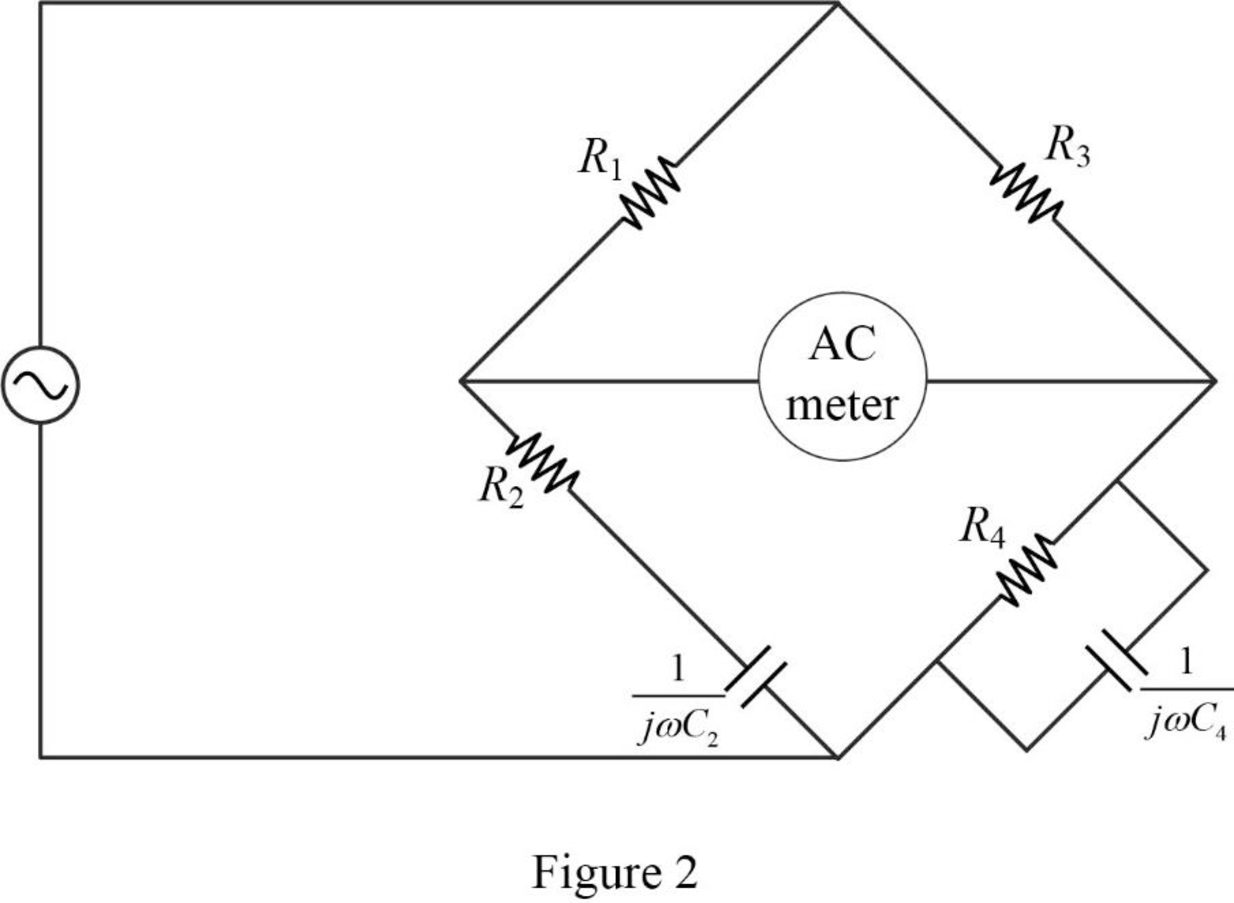
Refer to Figure 2, the impedance of resistor
Therefore, the equivalent impedance
Refer to Figure 2, the impedance of resistor
The equivalent impedance
Simplify the above equation as follows:
Let,
The balance of equation of an ac bridge is,
The above equation as rearranged as follows:
Substitute
Take the conjugate of denominator to rationalize the fraction in left hand side.
Equate the real and imaginary part in above equation.
Divide equation (4) by (5).
Simplify the above equation to find
Rearrange equation (3) to find
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, when the bridge is balanced, the value of frequency
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
FUND.OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS(LL)-W/CONNECT