
Concept explainers
(a)
Accounting Cycle: The accounting cycle refers to the entire process of recording the accounting transactions of an organization and then processing them. The accounting cycle starts when a transaction takes places and it ends at the time when these transactions are recorded in the financial statements of the company.
To Prepare: the
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entries for the transactions 1-9.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2017 | |||||
| February | 1 | Cash | 12,000 | ||
| Unearned Service Revenue | 12,000 | ||||
| (To record the service revenue received in advance.) | |||||
| February | 1 | Equipment (1) | 9,600 | ||
| Cash | 3,000 | ||||
| Accounts Payable | 6,600 | ||||
| (To record the purchase of computer equipment.) | |||||
| March | 1 | Patents | 9,600 | ||
| Cash | 9,600 | ||||
| (To record the acquisition of patents.) | |||||
| March | 28 |
| 140,000 | ||
| Service Revenue | 140,000 | ||||
| (To record sales on account.) | |||||
| March | 29 | Cash | 133,000 | ||
| Accounts Receivable | 133,000 | ||||
| (To record the cash collected from customers.) | |||||
| March | 29 | Accounts Payable | 16,370 | ||
| Cash | 16,370 | ||||
| (To record amount paid on accounts payable.) | |||||
| March | 29 | Operating Expenses | 97,525 | ||
| Cash | 97,525 | ||||
| (To record the payment of operating expenses.) | |||||
| March | 31 | Allowance for Doubtful Accounts | 200 | ||
| Accounts Receivable | 200 | ||||
| (To record the writing off receivable) | |||||
| March | 31 |
| 500 | ||
|
| 500 | ||||
| (To record the depreciation expense of the equipment sold.) | |||||
| March | 31 | Cash | 1,620 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation-Equipment (3) | 8,500 | ||||
| Loss on Disposal of Plant Assets (4) | 880 | ||||
| Equipment | 11,000 | ||||
| (To record the sale of equipment.) | |||||
Table (1)
Working Notes:
Calculate the total amount of equipment.
Calculate the depreciation expense for building.
Calculate the amount of accumulated depreciation for equipment sold on March 31, 2017.
Calculate the amount of gain / (loss) on disposal of equipment.
(e)
To prepare: a
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a bank reconciliation statement as on March 31, 2017.
| A Corporation | ||
| Bank Reconciliation | ||
| March 31, 2017 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash balance as per bank statement, March 31, 2017 | 64,594 | |
| Add: Deposits in transit | 1,620 | |
| Less: Outstanding Checks | ||
| #440 | 3,444 | |
| #454 | 5,845 | |
| #455 | 3,000 | |
| #456 | 9,600 | (21,889) |
| Adjusted cash balance per bank | 44,325 | |
| Cash balance as per books, March 31, 2017 | $44,425 | |
| Less: Bank Service Charge | 100 | |
| Adjusted cash balance per books | 44,325 | |
Table (2)
(f)
To journalize: the entries related to bank reconciliation and all
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Journalize the entries related to bank reconciliation and all adjusting entries.
| Date | Account Titles and Narration | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2017 | |||||
| March | 31 | Operating Expenses | 100 | ||
| Cash | 100 | ||||
| (To record the payment of operating expenses.) | |||||
| March | 31 | Unearned Service Revenue | 2,000 | ||
| Service Revenue (5) | 2,000 | ||||
| (To record the service revenue earned.) | |||||
| March | 31 |
| 800 | ||
| Allowance for Doubtful Accounts | 800 | ||||
| (To record the bad debt expense) | |||||
| March | 31 | Depreciation Expense (7) | 505 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation-Equipment | 505 | ||||
| (To record the depreciation expense of the equipment.) | |||||
| March | 31 | Depreciation Expense (8) | 750 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation-Building | 750 | ||||
| (To record the depreciation expense of the building.) | |||||
| March | 31 | Patent Amortization Expense (9) | 80 | ||
| Patents | 80 | ||||
| (To record the amortization expense ) | |||||
| March | 31 | Income Tax Expense (10) | 12,258 | ||
| Income Taxes Payable | 12,258 | ||||
| (To record the income tax expense.) | |||||
Table (3)
Working notes:
Calculate the service revenue earned as on March 31, 2017.
Calculate the bad debt expense.
Calculate the depreciation expense on equipment.
Calculate the depreciation expense on building.
Calculate the amortization expense for patent purchased on March 1, 2017.
Calculate the amount of income tax expense.
Description
March 31: Record the adjusting entry for operating expense paid in cash
- Operating Expense is an expense and is increased by $100 that decreases the stockholders' equity due to payment of bank service charges. Therefore, Operating Expense account is debited with $100.
- Cash is an asset and is decreased by $100 due to the amount paid of bank service charges in cash. Therefore, Cash account is credited with $100.
March 31: Record the adjusting entry for service revenue earned.
- Unearned Service Revenue is a liability and it decreases by $2,000 due to the service revenue is earned. Therefore, Unearned Service Revenue is debited with $2,000.
- Service Revenue is a component of
Stockholders’ Equity . It is increased by $2,000. Therefore, Service Revenue account is credited with $2,000.
March 31: Record the adjusting entry for bad Debt Expense.
- Bad Debt Expense is an expense that decreases the stockholders’ equity account. It is increased by $800 due to writing off of accounts receivable. Therefore, Bad Debt Expense account is debited with $800.
- Allowance for Doubtful Accounts is a contra asset with a normal credit balance. Its increased value decreases the value of the asset by $800. Therefore, Allowance for Doubtful Accounts account is credited with $800.
March 31: Record the adjusting entry for Depreciation expense for equipment.
- Depreciation expense is an expense, and it decreases the stockholder’s equity by $505. Therefore, Depreciation expense – Equipment is debited with $505.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset with a normal credit balance. It is increased by $505 that decreases the value of assets by $505. Therefore, the Accumulated depreciation-Equipment account is credited with $505.
March 31: Record the adjusting entry for Depreciation expense for building.
- Depreciation expense is an expense, and it decreases the stockholder’s equity by $750. Therefore, Depreciation expense – Building is debited with $750.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset with a normal credit balance. It is increased by $750 that decreases the value of assets by $750. Therefore, the Accumulated depreciation-Building account is credited with $750.
March 31: Record the adjusting entry for amortization expense for patents
- Amortization expense is an expense, and it decreases the stockholder’s equity by $80. Therefore, Amortization Expense is debited with $80.
- Patent is an intangible asset and is decreased by $80 due to amortization. Therefore, Patents account is credited with $80.
March 31: Record the adjusting entry for income tax expense
- Income Tax expense is an expense, and it decreases the stockholder’s equity by $12,258. Therefore, Income Tax Expense is debited with $12,258.
- Income Tax Payable is a liability and is increased by $12,258 due to income tax expense accrued. Therefore, Interest Payable account is credited with $12,258.
(b), (c), & (f)
To post: all the journal entries for transaction 1-9, entries related to bank reconciliation, and the adjusting entries into the T-accounts.
(b), (c), & (f)
Explanation of Solution
Post the all the journal entries for transaction 1-9, entries related to bank reconciliation, and the adjusting entries into the T-accounts to determine the balances of the respective accounts.
Cash is an asset with a normal debit balance.
| Cash Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| December 31, 2016 | Balance | 24,300 | February 1 | Equipment | 3,000 | |
| February 1 | Unearned Service Revenue | 12,000 | March 1 | Patents | 9,600 | |
| March 29 | Accounts Receivable | 133,000 | March 29 | Accounts Payable | 16,370 | |
| March 31 | Equipment | 1,620 | March 29 | Operating Expenses | 97,525 | |
| March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 44,425 | ||||
| March 31,2017 | Total | 170,920 | March 31 | Total | 170,920 | |
| March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 44,425 | March 31 | Adjustment | 100 | |
| March 31 | Ending Balance | 44,325 | ||||
| March 31 | Total | 44,425 | March 31 | Total | 44,425 | |
Table (1)
Accounts Receivable is an asset with a normal debit balance.
| Accounts Receivable Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| December 31, 2016 | Balance | 22,400 | March 29 | Cash | 133,000 | |
| March 28 | Service Revenue | 140,000 | March 31 | Allowance for Doubtful Accounts | 200 | |
| March 31 | Ending Balance | 29,200 | ||||
| March 31,2017 | Total | 162,400 | March 31,2017 | Total | 162,400 | |
Table (2)
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts is an asset with a normal credit balance.
| Allowance for Doubtful Accounts | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| March 31 | Accounts Receivable | 200 | December 31, 2016 | Balance | 1,200 | |
| March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 1,000 | ||||
| March 31,2017 | Total | 1,200 | March 31,2017 | Total | 1,200 | |
| March 31 | Ending Balance | 1,800 | March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 1,000 | |
| March 31 | Adjustment | 800 | ||||
| March 31,2017 | Total | 1,800 | March 31,2017 | Total | 1,800 | |
Table (3)
Equipment is an asset with a normal debit balance.
| Equipment Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| December 31, 2016 | Balance | 20,000 | March 31 | Cash | 1,620 | |
| March 31 | Accumulated Depreciation-Equipment | 8,500 | ||||
| March 31 | Loss on Disposal of Plant Assets | 880 | ||||
| February 1 | Cash | 3,000 | March 31 | Ending Balance | 18,600 | |
| February 1 | Accounts Payable | 6,600 | ||||
| March 31 | Total | 29,600 | March 31 | Total | 29,600 | |
Table (4)
Accumulated Depreciation-Equipment is a contra asset account with a normal credit balance.
| Accumulated Depreciation-Equipment Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| March 31 | Equipment | 8,500 | December 31, 2016 | Balance | 15,000 | |
| March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 7,000 | March 31 | Depreciation expense | 500 | |
| March 31 | Total | 15,500 | March 31 | Total | 15,500 | |
| Mach 31 | Ending Balance | 7,505 | March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 7,000 | |
| March 31 | Adjustment | 505 | ||||
| March 31 | Total | 7,505 | March 31 | Total | 7,505 | |
Table (5)
Land is an asset with a normal debit balance.
| Land Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| December 31, 2016 | Balance | 20,000 | March 31 | Ending Balance | 20,000 | |
| March 31 | Total | 20,000 | March 31 | Total | 20,000 | |
Table (6)
Building is an asset with a normal debit balance.
| Building Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| December 31, 2016 | Balance | 100,000 | March 31 | Ending Balance | 100,000 | |
| March 31 | Total | 100,000 | March 31 | Total | 100,000 | |
Table (7)
Accumulated Depreciation-Building is a contra asset account with a normal credit balance.
| Accumulated Depreciation-Equipment Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 15,000 | December 31, 2016 | Balance | 15,000 | |
| March 31 | Total | 15,000 | March 31 | Total | 15,000 | |
| Mach 31 | Ending Balance | 15,750 | March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 15,000 | |
| March 31 | Adjustment | 750 | ||||
| March 31 | Total | 15,750 | March 31 | Total | 15,750 | |
Table (8)
Patents is an intangible asset account with a normal debit balance.
| Patents Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| March 31 | Balance | 9,600 | March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 9,600 | |
| March 31 | Total | 9,600 | March 31 | Total | 9,600 | |
| March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 9,600 | March 31 | Adjustment | 80 | |
| March 31 | Ending Balance | 9,520 | ||||
| March 31 | Total | 9,600 | March 31 | Total | 9,600 | |
Table (9)
Accounts Payable is a liability with a normal credit balance.
| Accounts Payable Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| March 29 | Cash | 16,370 | December 31, 2016 | Balance | 12,370 | |
| March 31 | Ending Balance | 2,600 | February 1 | Equipment | 6,600 | |
| March 31,2017 | Total | 18,970 | March 31,2017 | Total | 18,970 | |
Table (10)
Unearned Service Revenue is a liability with a normal credit balance.
| Unearned Service Revenue Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 12,000 | February 1 | Service Revenue | 12,000 | |
| March 31,2017 | Total | 12,000 | March 31,2017 | Total | 12,000 | |
| March 31 | Adjustment | 2,000 | March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 12,000 | |
| March 31 | Ending Balance | 10,000 | ||||
| March 31 | Total | 12,000 | March 31 | Total | 12,000 | |
Table (11)
Income Taxes Payable is a liability with a normal credit balance.
| Income Taxes Payable Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| March 31 | Ending Balance | 12,258 | March 31 | Adjustment | 12,258 | |
| March 31,2017 | Total | 12,258 | March 31,2017 | Total | 12,258 | |
Table (12)
Common Stock is a component of stockholders’ equity with a normal credit balance.
| Common Stock Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| March 31 | Ending Balance | 90,000 | December 31,2016 | Balance | 90,000 | |
| March 31,2017 | Total | 90,000 | March 31,2017 | Total | 90,000 | |
Table (13)
Retained Earnings is a component of stockholders’ equity with a normal credit balance.
| Retained Earnings Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| March 31 | Ending Balance | 53,130 | December 31,2016 | Balance | 53,130 | |
| March 31,2017 | Total | 53,130 | March 31,2017 | Total | 53,130 | |
Table (14)
Service Revenue is a component of stockholders’ equity with a normal credit balance.
| Service Revenue Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 140,000 | March 28 | Accounts Receivable | 140,000 | |
| March 31,2017 | Total | 140,000 | March 31,2017 | Total | 140,000 | |
| March 31 | Ending Balance | 142,000 | March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 140,000 | |
| March 31 | Adjustment | 2,000 | ||||
| March 31,2017 | Total | 142,000 | March 31,2017 | Total | 142,000 | |
Table (15)
Operating Expense is a component of stockholders’ equity with a normal debit balance.
| Operating Expense Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| March 29 | Cash | 97,525 | March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 97,525 | |
| March 31,2017 | Total | 97,525 | March 31,2017 | Total | 97,525 | |
| March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 97,525 | March 31 | Ending Balance | 97,625 | |
| March 31 | Adjustment | 100 | ||||
| March 31,2017 | Total | 97,625 | March 31,2017 | Total | 97,625 | |
Table (16)
Depreciation Expense is a component of stockholders’ equity account with a normal debit balance.
| Depreciation Expense Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| March 31 | Accumulated Depreciation-Equipment | 500 | March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 500 | |
| March 31,2017 | Total | 14,975 | March 31,2017 | Total | 14,975 | |
| March 31 | Balance before adjustment | 500 | March 31 | Ending Balance | 1,755 | |
| March 31 | Adjustment | 505 | ||||
| March 31 | Adjustment | 750 | ||||
| March 31,2017 | Total | 1,755 | March 31,2017 | Total | 1,755 | |
Table (17)
Loss on Disposal of Plant Assets is a component of stockholders’ equity account with a normal debit balance.
| Loss on Disposal Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| March 31 | Equipment | 880 | March 31 | Ending Balance | 880 | |
| January 31,2017 | Total | 880 | January 31,2017 | Total | 880 | |
Table (18)
Amortization Expense is a component of stockholders’ equity account with a normal debit balance.
| Amortization Expense Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| March 31 | Adjustment | 80 | March 31 | Ending Balance | 80 | |
| March 31,2017 | Total | 80 | March 31,2017 | Total | 80 | |
Table (19)
Bad Debt Expense is a component of stockholders’ equity account with a normal debit balance.
| Bad Debt Expense Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| March 31 | Adjustment | 800 | March 31 | Ending Balance | 800 | |
| March 31 | Total | 800 | March 31 | Total | 800 | |
Table (20)
Income Tax Expense is a component of stockholders’ equity account with a normal debit balance.
| Income Tax Expense Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) | |
| March 31 | Adjustment | 12,258 | March 31 | Ending Balance | 12,258 | |
| March 31 | Total | 12,258 | March 31 | Total | 12,258 | |
Table (21)
(d) & (g)
To prepare: an unadjusted and an adjusted trial balance at March 31, 2017.
(d) & (g)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare an unadjusted and an adjusted trial balance at March 31, 2017.
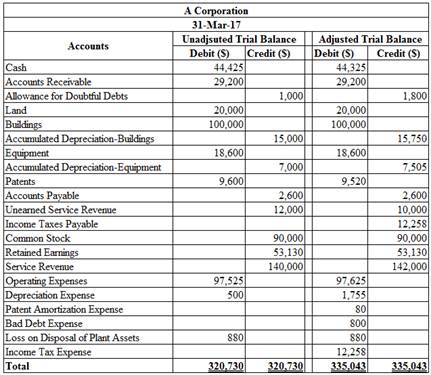
Figure (1)
(h)
To prepare: the income statement of A Corporation for the year ended March 31, 2017.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the income statement of A Corporation for the year ended March 31, 2017.
| A Corporation | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the year ended March 31, 2017 | ||
| Details | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenue | ||
| Service Revenue | – | 142,000 |
| Less: Operating Expenses | ||
| Operating Expense | 97,625 | |
| Depreciation Expense | 1,755 | |
| Bad Debt Expense | 800 | |
| Amortization Expense | 80 | |
| Total Operating Expenses | (100,260) | |
| Income from operations | 41,740 | |
| Less: Other expenses and losses | ||
| Loss on Disposal of Plant Assets | (880) | |
| Income before income taxes | 40,860 | |
| Less: Income Tax Expense | (12,258) | |
| Net Income | 28,602 | |
Table (22)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Financial Acct Print Ll W/ Wp
- Adjusting Entries Kretz Corporation prepares monthly financial statements and therefore adjusts its accounts at the end of every month. The following information is available for March 2016: Kretz Corporation takes out a 90-day, 8%, $15,000 note on March 1, 2016, with interest and principal to be paid at maturity. The asset account Office Supplies on Hand has a balance of $1,280 on March 1, 2016. During March, Kretz adds $750 to the account for purchases during the period. A count of the supplies on hand at the end of March indicates a balance of $1,370. The company purchased office equipment last year for $62,600. The equipment has an estimated useful life of six years and an estimated salvage value of $5,000. The companys plant operates seven days per week with a daily payroll of $950. Wage earners are paid every Sunday. The last day of the month is Thursday, March 31. The company rented an idle warehouse to a neighboring business on February 1, 2016, at a rate of $2,500 per month. On this date, Kretz Corporation credited Rent Collected in Advance for six months rent received in advance. On March 1, 2016, Kretz Corporation credited a liability account, Customer Deposits, for $4,800. This sum represents an amount that a customer paid in advance and that Kretz will earn evenly over a four-month period. Based on its income for the month, Kretz Corporation estimates that federal income taxes for March amount to $3,900. Required For each of the preceding situations, prepare in general journal form the appropriate adjusting entry to be recorded on March 31, 2016.arrow_forwardOn October 31, the Vermillion Igloos Hockey Club received 800,000 in cash in advance for season tickets for eight home games. The transaction was recorded as a debit to Cash and a credit to Unearned Admissions. By December 31, the end of the fiscal year, the team had played three home games and received an additional 450,000 cash admissions income at the gate. a. Journalize the adjusting entry as of December 31. b. List the title of the account and the related balance that will appear on the income statement. c. List the title of the account and the related balance that will appear on the balance sheet.arrow_forwardIncome Statement and Balance Sheet Fort Worth Corporation began business in January 2016 as a commercial carpet-cleaning and drying service. Shares of stock were issued to the owners in exchange for cash. Equipment was purchased by making a down payment in cash and signing a note payable for the balance. Services are performed for local restaurants and office buildings on open account, and customers are given 15 days to pay their accounts. Rent for office and storage facilities is paid at the beginning of each month. Salaries and wages are paid at the end of the month. The following amounts are from the records of Fort Worth Corporation at the end of its first month of operations: Required Prepare an income statement for the month ended January 31, 2016. Prepare a balance sheet at January 31, 2016. What information would you need about Notes Payable to fully assess Fort Worths longterm viability? Explain your answer.arrow_forward
- Prepare journal entries to record the following transactions for the month of July: A. on first day of the month, paid rent for current month, $2,000 B. on tenth day of month, paid prior month balance due on accounts, $3,100 C. on twelfth day of month, collected cash for services provided, $5,500 D. on twenty-first day of month, paid salaries to employees, $3,600 E. on thirty-first day of month, paid for dividends to shareholders, $800arrow_forwardThe transactions completed by PS Music during June 2019 were described at the end of Chapter 1. The following transactions were completed during July, the second month of the businesss operations: July 1.Peyton Smith made an additional investment in PS Music by depositing 5,000 in PS Musics checking account. 1.Instead of continuing to share office space with a local real estate agency, Peyton decided to rent office space near a local music store. Paid rent for July, 1,750. 1.Paid a premium of 2,700 for a comprehensive insurance policy covering liability, theft, and fire. The policy covers a one-year period. 2.Received 1,000 cash from customers on account. 3.On behalf of PS Music, Peyton signed a contract with a local radio station, KXMD, to provide guest spots for the next three months. The contract requires PS Music to provide a guest disc jockey for 80 hours per month for a monthly fee of 3,600. Any additional hours beyond 80 will be billed to KXMD at 40 per hour. In accordance with the contract, Peyton received 7,200 from KXMD as an advance payment for the first two months. 3.Paid 250 to creditors on account. 4.Paid an attorney 900 for reviewing the July 3 contract with KXMD. (Record as Miscellaneous Expense.) 5.Purchased office equipment on account from Office Mart, 7,500. 8.Paid for a newspaper advertisement, 200. 11.Received 1,000 for serving as a disc jockey for a party. 13.Paid 700 to a local audio electronics store for rental of digital recording equipment. 14.Paid wages of 1,200 to receptionist and part-time assistant. Enter the following transactions on Page 2 of the two-column journal: 16.Received 2,000 for serving as a disc jockey for a wedding reception. 18.Purchased supplies on account, 850. July 21. Paid 620 to Upload Music for use of its current music demos in making various music sets. 22.Paid 800 to a local radio station to advertise the services of PS Music twice daily for the remainder of July. 23.Served as disc jockey for a party for 2,500. Received 750, with the remainder due August 4, 2019. 27.Paid electric bill, 915. 28.Paid wages of 1,200 to receptionist and part-time assistant. 29.Paid miscellaneous expenses, 540. 30.Served as a disc jockey for a charity ball for 1,500. Received 500, with the remainder due on August 9, 2019. 31.Received 3,000 for serving as a disc jockey for a party. 31.Paid 1,400 royalties (music expense) to National Music Clearing for use of various artists music during July. 31.Withdrew 1,250 cash from PS Music for personal use. PS Musics chart of accounts and the balance of accounts as of July 1, 2019 (all normal balances), are as follows: Instructions 1. Enter the July 1, 2019, account balances in the appropriate balance column of a four-column account. Write Balance in the Item column and place a check mark () in the Posting Reference column. (Hint: Verify the equality of the debit and credit balances in the ledger before proceeding with the next instruction.) 2. Analyze and journalize each transaction in a two-column journal beginning on Page 1, omitting journal entry explanations. 3. Post the journal to the ledger, extending the account balance to the appropriate balance column after each posting. 4. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance as of July 31, 2019.arrow_forwardThe transactions completed by PS Music during June 2019 were described at the end of Chapter 1. The following transactions were completed during July, the second month of the business's operations: July 1. Peyton Smith made an additional investment in PS Music by depositing 5,000 in PS Music's checking account. 1. Instead of continuing to share office space with a local real estate agency, Peyton decided to rent office space near a local music: store. Paid rent for July, 1,750. 1. Paid a premium of 2,700 for a comprehensive insurance policy covering liability, theft, and fire. The policy covers a one-year period. 2. Received 1,000 cash from customers on account. 3. On behalf of PS Music, Peyton signed a contract with a local radio station, KXMD, to provide guest spots for the next three months. The contract requires PS Music to provide a guest disc jockey for SO hours per month for a monthly fee of 3,600. Any additional hours beyond SO will be billed to KXMD at 40 per hour. In accordance with the contract, Peyton received 7,200 from KXMD as an advance payment for the first two months. 3. Paid 250 to creditors on account. 4. Paid an attorney 900 for reviewing the July 3 contract with KXMD. (Record as Miscellaneous Expense.) 5. Purchased office equipment on account from Office Mart, 7,500. 8. Paid for a newspaper advertisement, 200. 11. Received 1,000 for serving as a disc jockey for a party. 13. Paid 700 to a local audio electronics store for rental of digital recording equipment. 11. Paid wages of 1,200 to receptionist and part-time assistant. Enter the following transactions on Page 2 of the two-column journal: 16. Received 2,000 for serving as a disc jockey for a wedding reception. 18. Purchased supplies on account, 850. July 21. Paid 620 to Upload Music for use of its current music demos in making various music sets. 22. Paid 800 to a local radio station to advertise the services of PS Music twice daily for the remainder of July. 23. Served as disc jockey for a party for 2,500. Received 750, with the remainder due August 4, 2019. 27. Paid electric bill, 915. 28. Paid wages of 1,200 to receptionist and part-time assistant. 29. Paid miscellaneous expenses, 540. 30. Served as a disc jockey for a charity ball for 1,500. Received 500, with the remainder due on August 9, 2019. 31. Received 3,000 for serving as a disc jockey for a party. 31. Paid 1,400 royalties (music expense) to National Music Clearing for use of various artists' music during July. 31. Withdrew l,250 cash from PS Music for personal use. PS Music's chart of accounts and the balance of accounts as of July 1, 2019 (all normal balances), are as follows: 11 Cash 3,920 12 Accounts receivable 1,000 14 Supplies 170 15 Prepaid insurance 17 Office Equipment 21 Accounts payable 250 23 Unearned Revenue 31 Peyton smith, Drawing 4,000 32 Fees Earned 500 41 Wages Expense 6,200 50 Office Rent Expense 400 51 Equipment Rent Expense 800 52 Utilities Expense 675 53 Supplies Expense 300 54 music Expense 1,590 55 Advertising Expense 500 56 Supplies Expense 180 59 Miscellaneous Expense 415 Instructions 1.Enter the July 1, 2019, account balances in the appropriate balance column of a four-column account. Write Balance in the Item column and place a check mark () in the Posting Reference column. (Hint: Verify the equality of the debit and credit balances in the ledger before proceeding with the next instruction.) 2.Analyze and journalize each transaction in a two-column journal beginning on Page 1, omitting journal entry explanations. 3.Post the journal to the ledger, extending the account balance to the appropriate balance column after each posting. 4.Prepare an unadjusted trial balance as of July 31, 2019.arrow_forward
- Kelly Pitney began her consulting business, Kelly Consulting, on April 1, 2019. The accounting cycle for Kelly Consulting for April, including financial statements, was illustrated in this chapter. During May, Kelly Consulting entered into the following transactions: Instructions 1. The chart of accounts for Kelly Consulting is shown in Exhibit 9, and the post-closingtrial balance as of April 30, 2019, is shown in Exhibit 17. For each account in the post-closing trial balance, enter the balance in the appropriate Balance column of a four-column account. Date the balances May 1, 2019, and place a check mark () in the Posting Reference column. Journalize each of the May transactions in a twocolumn journal starting on Page 5 of the journal and using Kelly Consultings chart of accounts. (Do not insert the account numbers in the journal at this time.) 2. Post the journal to a ledger of four-column accounts. 3. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance. 4. At the end of May, the following adjustment data were assembled. Analyze and use these data to complete parts (5) and (6). a. Insurance expired during May is 275. b. Supplies on hand on May 31 are 715. c. Depreciation of office equipment for May is 330. d. Accrued receptionist salary on May 31 is 325. e. Rent expired during May is 1,600. f. Unearned fees on May 31 are 3,210. 5. (Optional) Enter the unadjusted trial balance on an end-of-period spreadsheet and complete the spreadsheet. 6. Journalize and post the adjusting entries. Record the adjusting entries on Page 7 of the journal. 7. Prepare an adjusted trial balance. 8. Prepare an income statement, a statement of owners equity, and a balance sheet. 9. Prepare and post the closing entries. Record the closing entries on Page 8 of the journal. Indicate closed accounts by inserting a line in both Balance columns opposite the closing entry. 10. Prepare a post-closing trial balance.arrow_forwardKelly Pitney began her consulting business, Kelly Consulting, on April 1, 2016. The accounting cycle for Kelly Consulting for April, including financial statements, was illustrated in this chapter. During May, Kelly Consulting entered into the following transactions: Instructions 1. The chart of accounts for Kelly Consulting is shown in Exhibit 9, and the post-closing trial balance as of April 30, 2016, is shown in Exhibit 17. For each account in the post-closing trial balance, enter the balance in the appropriate Balance column of a four-column account. Date the balances May 1, 2016, and place a check mark () in the Posting Reference column. Journalize each of the May transactions in a two column journal starting on Page 5 of the journal and using Kelly Consultings chart of accounts. (Do not insert the account numbers in the journal at this time.) 2. Post the journal to a ledger of four-column accounts. 3. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance. 4. At the end of May, the following adjustment data were assembled. Analyze and use these data to complete parts (5) and (6) a. Insurance expired during May is 275. b. Supplies on hand on May 31 are 715. c. Depreciation of office equipment for May is 330. d. Accrued receptionist salary on May 31 is 325. e. Rent expired during May is 1,600. f. Unearned fees on May 31 are 3,210. 5.(Optional) Enter the unadjusted trial balance on an end-of-period spreadsheet and complete the spreadsheet. 6.Journalize and post the adjusting entries. Record the adjusting entries on Page 7 of the journal. 7.Prepare an adjusted trial balance. 8.Prepare an income statement, a statement of owners equity, and a balance sheet. 9.Prepare and post the closing entries. Record the closing entries on Page 8 of the journal. (Income Summary is account #33 in the chart of accounts.) Indicate closed accounts by inserting a line in both the Balance columns opposite the closing entry. 10.Prepare a post-closing trial balance.arrow_forward
 Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College PubCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College PubCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





