
Concept explainers
Comprehensive budgeting problem (Learning Objectives 2 & 3)
Martin Manufacturing is preparing its
| Current Assets as of December 31 (prior year): | |
| Cash | $ 4.500 |
| Accounts receivable, net | $ 47,000 |
| Inventory | $ 15,700 |
| Property, plant, and equipment, net | $120,000 |
| Accounts payable | $ 42,400 |
| Capital stock | $124,000 |
| $23,100 |
- a. Actual sales in December were $70,000. Selling price per unit is projected to remain stable at $10 per unit throughout the budget period. Sales for the first five months of the upcoming year are budgeted to be as follows:
| January | $ 80,000 |
| February | $ 92,000 |
| March | $ 99,000 |
| April | $ 97,000 |
| May | $ 85,000 |
- b. Sales are 30% cash and 70% credit. All credit sales are collected in the month following the sale.
- c. Martin Manufacturing has a policy stating that each month’s ending inventory of finished goods should be 25% of the following month’s sales (in units).
- d. Of each month’s direct materials purchases, 20% are paid for in the month of purchase, while the remainder is paid for in the month following purchase. Two pounds of direct material is needed per unit at $2 per pound. Ending inventory of direct materials should be 10% of next month’s production needs.
- e. Most of the labor at the manufacturing facility is indirect, but there is some direct labor incurred. The direct labor hours per unit is 0.01. The direct labor rate per hour is $12 per hour. All direct labor is paid for in the month in which the work is performed. The direct labor total cost for each of the upcoming three months is as follows:
| January | $996 |
| February | $1,125 |
| March | $1,182 |
- f. Monthly manufacturing
overhead costs are $5,000 for factory rent, $3,000 for other fixed manufacturing expenses, and $1.20 per unit for variable manufacturing overhead. Nodepreciation is included in these figures. All expenses are paid in the month in which they are incurred. - g. Computer equipment for the administrative offices will be purchased in the upcoming quarter. In January, Martin Manufacturing will purchase equipment for $5,000 (cash), while February’s cash expenditures will be $12,000 and March’s cash expenditures will be $16,000.
- h. Operating expenses are budgeted to be $1.00 per unit sold plus fixed operating expenses of $1,000 per month. All operating expenses are paid in the month in which they are incurred. No depreciation is included in these figures.
- i. Depreciation on the building and equipment for the general and administrative offices is budgeted to be $4,600 for the entire quarter, which includes depreciation on new acquisitions.
- j. Martin Manufacturing has a policy that the ending cash balance in each month must be at least $4,000. It has a line of credit with a local bank. The company can borrow in increments of $1,000 at the beginning of each month, up to a total outstanding loan balance of $150,000. The interest rate on these loans is 1% per month simple interest (not compounded). The company would pay down on the line of credit balance in increments of $1,000 if it has excess funds at the end of the quarter. The company would also pay the accumulated interest at the end of the quarter on the funds borrowed during the quarter.
- k. The company’s income tax rate is projected to be 30% of operating income less interest expense. The company pays $10,000 cash at the end of February in estimated taxes.
Requirements
- 1. Prepare a schedule of cash collections for January, February, and March, and for the quarter in total. Use the following format:
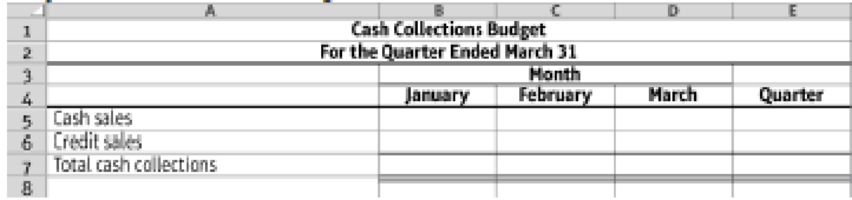
9.4-49 Full Alternative Text
- 2. Prepare a production budget, using the following format:
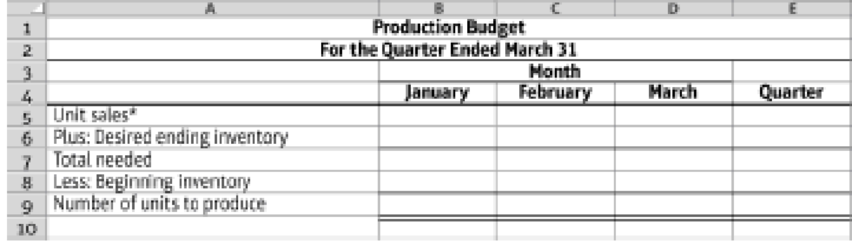
9.4-50 Full Alternative Text
*Hint: Unit sales = Sales in dollars/Selling price per unit
- 3. Prepare a direct materials budget, using the following format:
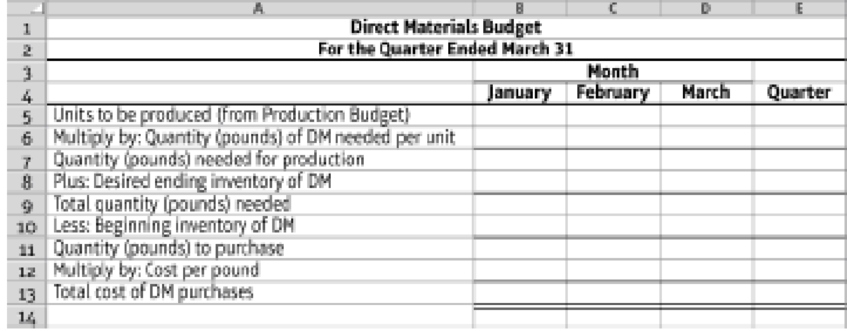
9.4-51 Full Alternative Text
- 4. Prepare a cash payments budget for the direct material purchases from Requirement 3, using the following format. (Use the accounts payable balance at December 31 of prior year for the prior month payment in January.)
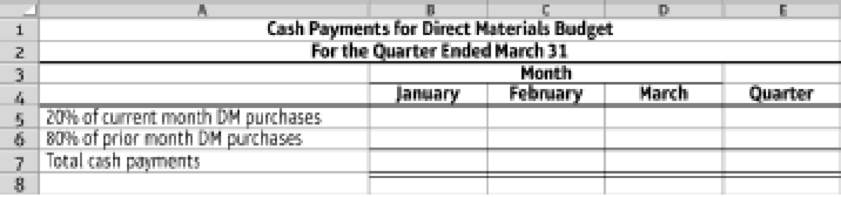
9.4-52 Full Alternative Text
- 5. Prepare a cash payments budget for direct labor, using the following format:
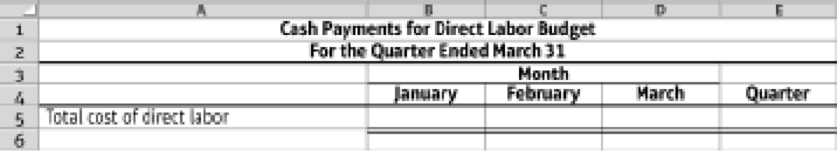
9.4-53 Full Alternative Text
- 6. Prepare a cash payments budget for manufacturing overhead costs, using the following format:
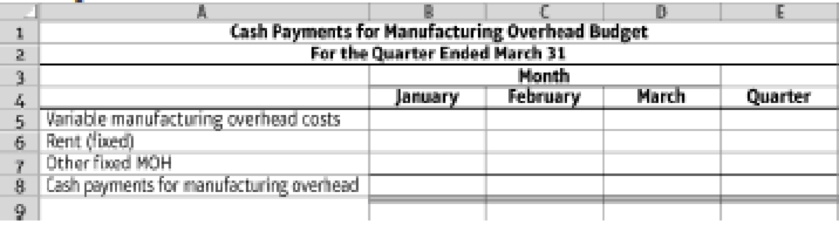
9.4-54 Full Alternative Text
- 7. Prepare a cash payments budget for operating expenses, using the following format:
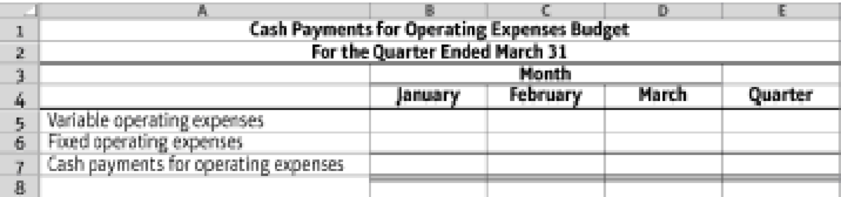
9.4-55 Full Alternative Text
- 8. Prepare a combined
cash budget , using the following format:
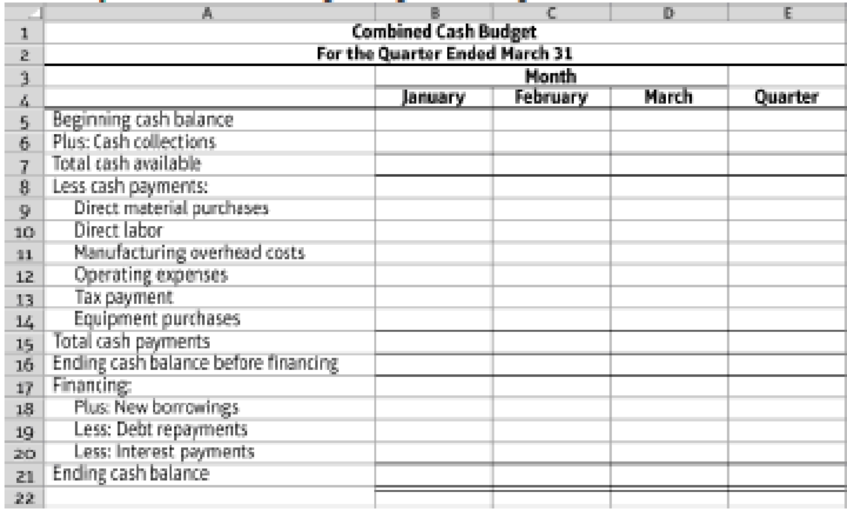
9.4-56 Full Alternative Text
- 9. Calculate the budgeted
manufacturing cost per unit, using the following format (assume that fixed manufacturing overhead is budgeted to be $0.80 per unit for the year):
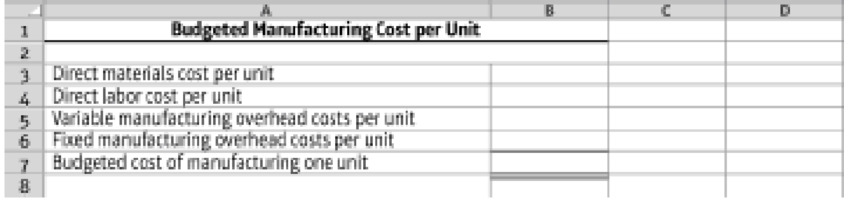
9.4-57 Full Alternative Text
- 10. Prepare a
budgeted income statement for the quarter ending March 31, using the following format:
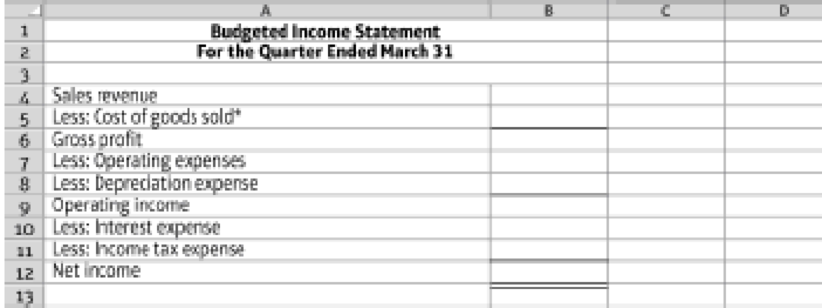
9.4-58 Full Alternative Text
*Hint: Cost of goods sold = Budgeted cost of manufacturing one unit × Number of units sold
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Managerial Accounting, Student Value Edition Plus MyLab Accounting with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (5th Edition)
- Relevant data from the operating budget of The Framers are: Other data: Capital assets were sold in quarter 1 and $8,000 was collected in quarter 1 and $500 collected in quarter 2. Dividends of $500 will be paid in May The beginning cash balance was $50,000 and a required minimum cash balance is $10,000. Prepare a cash budget for the first two quarters of the year.arrow_forwardApplying Excel: Master Budgeting Beech Corporation is a master budget for the 3rd quarter of the calendar year. The company’s balance sheet is shown below: June Corporation Balance Sheet June 30 Assets Cash $ 90,000 Accounts receivable 136,000 Inventory 62,000 Building + equipment, net of depreciation 210,000 Total assets $498,000 Liability and Stockholder’s Equity Accounts payable $ 71,100 Common stock 327,000 Retained earnings 99,900 Total liability and stockholder’s equity $498,000 Beech’s managers have made the following assumptions and estimates: Estimated sales for July, August, September, and October will be $210,000, $230,000, $220,000, and $240,000 respectively. All sales are credit and all credit sales are collected. (Note: there are no cash sales). Thirty-five percent (35%) the month’s credit sales are collected in the month the sales are made, and the remaining 65% is collected the…arrow_forwardPlease prepare a consolidated budget pivot table in Excel by budget class and year. Please upload your excel document. Budget Class – Staff Costs • Salary of the Project Manager @ USD 5,000 per month. • Salary of the Admin Finance Officer @ USD 3,500 per month. • Salary of Admin. & Finance Assistant @USD 1,000 per month • Salary of Driver @USD 500 per month Budget Class – Equipment & Furniture Cost of the office equipment and furniture required for the project is USD 30,000 for three years to be procured during the 1st year of the project. Budget Class – Operating Costs (training) Two trainers are required for each training. Each training lasts for 5 days. The total number of participants for each training is 30. • DSA/ ticket cost of each participant @ USD1, 000 per training. • Total number of 5-day trainings planned for each year is 4. • Fee for Trainer @ USD 2,000 per training. • Cost of logistic arrangements for each training @ USD 10,000. In addition to the main direct…arrow_forward
- Direct Labor Budget for Service The School of Accounting (SOA) at State University is planning its annual fundraising campaign for accounting alumni. This year, the SOA is planning a call-a-thon and will ask Beta Alpha Psi members to volunteer to make phone calls to a list of 7,000 alumni. The Dean's office has agreed to let Beta Alpha Psi use their offices from 6 p.m. to 9 p.m. each weekday so that they will have access to phones. Each volunteer will be provided with a phone and a script with an introduction and suggested responses to various questions that had been asked in the past. Carol Johnson, Beta Alpha Psi faculty advisor, estimates the following: Of the 7,000 phone numbers, roughly 10 percent will be wrong numbers (because alumni change addresses and phone numbers without updating State University). In that case, the student is instructed to apologize to the answering party, hang up, and move on to the next phone number. Each of these calls takes about three minutes. Another…arrow_forwardICE TASK 4 – Budgeting Techniques The University of Africa requires all second-year engineering students to have their own laptop computers to do practical work and tasks. During the last quarter of 2022, a private company, Laptops for Students Proprietary Limited (“LFS”) was established to supply laptops according to the specifications set by the university, at affordable prices. At that time, a loan of R800 000 was granted to LFS and the funds were deposited into the bank account. Prior to the receipt of the loan amount no cash transactions occurred. The following additional information is available for LFS: According to estimates, 200 of the 400 second year engineering students will buy their laptops from LFS. There are two types of laptops which will be supplied, namely Exceptional at a selling price of R10 000 and Superior at a selling price of R8 000. Since the Exceptional laptop has a more powerful hard drive, it is expected that 60% of the 200 students will prefer to…arrow_forwardManagement Accounting Course Project – Part 1, B Group The Terranova Company is preparing information to complete its master budget for the quarter ending December 31, 2020. The company intends to make unit sales in the related months as follows: September 5,000 October 9,750 November 11,700 December 14,625 Units are to be sold for $10 each. Sales are 60% for cash and 40% on credit. Credit sales are collected in the month following the sale. *Required: 1) Prepare a sales budget for Terranova for the quarter ending December 31, 2020. Show activity by month and in total. (Hint: a quarter = 3 months.) 2) Complete a schedule of expected cash collections for the quarter ending December 31, 2020. Show activity by month and in total.arrow_forward
- A company has completed the operating budget and the cash budget. It is now preparing the budgeted balance sheet. Please use the below image as your guide for the next 5 questions. Identify the document that contains equipment purchases A B C D Earrow_forwardRoberds Tech is a for-profit vocational school. The school bases its budgets on two measures of activity (i.e., cost drivers), namely student and course. The school uses the following data in its budgeting: Fixed element per month Variable element per student Variable element per course Revenue $ 0 $ 298 $ 0 Faculty wages $ 0 $ 0 $ 3,100 Course supplies $ 0 $ 52 $ 40 Administrative expenses $ 26,500 $ 27 $ 52 In March, the school budgeted for 1,910 students and 88 courses. The school's income statement showing the actual results for the month appears below: Roberds Tech Income Statement For the Month Ended March 31 Actual students 1,810 Actual courses 91 Revenue $ 411,340 Expenses: Faculty wages 214,950 Course supplies 62,590 Administrative expenses 84,562 Total expense 362,102 Net operating income $ 49,238 Required: Prepare a flexible budget performance report showing both the school's activity variances and revenue and spending…arrow_forwardPersonal Budget At the beginning of the school year, Katherine Malloy decided to prepare a cash budget for the months of September, October, November, and December. The budget must plan for enough cash on December 31 to pay the spring semester tuition, which is the same as the fall tuition. The following information relates to the budget: Cash balance, September 1 (from a summer job) $8,860 Purchase season football tickets in September 120 Additional entertainment for each month 310 Pay fall semester tuition in September 4,800 Pay rent at the beginning of each month 430 Pay for food each month 240 Pay apartment deposit on September 2 (to be returned December 15) 600 Part-time job earnings each month (net of taxes) 1,100 a. Prepare a cash budget for September, October, November, and December. Enter all amounts as positive values except an overall cash decrease which should be indicated with a minus sign. KATHERINE MALLOY Cash Budget For the Four…arrow_forward
- Pelican Merchandising & More is a family-owned store. The business is now approaching the end of the year and is in the process of identifying its cash needs for the first quarter of the new year. You are the management accountant of the entity and have been tasked to prepare the cash budget for the business for the quarter ending March 31, 2022.(i) Extracts from the sales and purchases budgets are as follows: Month2021 - 2022 CashSales SalesOnAccount CashPurchases PurchasesOnAccount November 2021 $138,100 $480,000 $345,000 December 2021 $156,500 $600,000 $25,800 $380,000 January 2022 $170,975 $650,000 $44,625 $400,000 February 2022 $135,740 $700,000 $30,400 $480,000 March 2022 $226,420 $800,000 $55,100 $540,000 (ii) An analysis of the records shows that trade receivables (accounts receivable) are settledaccording to the following credit pattern, in accordance with the credit terms 4/30, n90:55% in the month of sale35% in the first month following the…arrow_forwardPelican Merchandising & More is a family-owned store. The business is now approaching the end of the year and is in the process of identifying its cash needs for the first quarter of the new year. You are the management accountant of the entity and have been tasked to prepare the cash budget for the business for the quarter ending March 31, 2022.(i) Extracts from the sales and purchases budgets are as follows: Month2021 - 2022 CashSales SalesOnAccount CashPurchases PurchasesOnAccount November 2021 $138,100 $480,000 $345,000 December 2021 $156,500 $600,000 $25,800 $380,000 January 2022 $170,975 $650,000 $44,625 $400,000 February 2022 $135,740 $700,000 $30,400 $480,000 March 2022 $226,420 $800,000 $55,100 $540,000 (ii) An analysis of the records shows that trade receivables (accounts receivable) are settledaccording to the following credit pattern, in accordance with the credit terms 4/30, n90:55% in the month of sale35% in the first month following the…arrow_forward1. At the beginning of the school year, Katherine Malloy decided to prepare a cash budget for the months of September, October, November, and December. The budget must plan for enough cash on December 31 to pay the spring semester tuition, which is the same as the fall tuition. The following information relates to the budget: Cash balance, September 1 (from a summer job) $7,060arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
