
(a)
The budget constraint.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Since the income is $4,000 and price of good X is $50, the quantity of good X can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the consumer will consume 80X.
Since the income is $4,000 and price of good Y is $100, the quantity of good Y can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the consumer will consume 40Y.
Now, the budget constraint can be represented as follows:
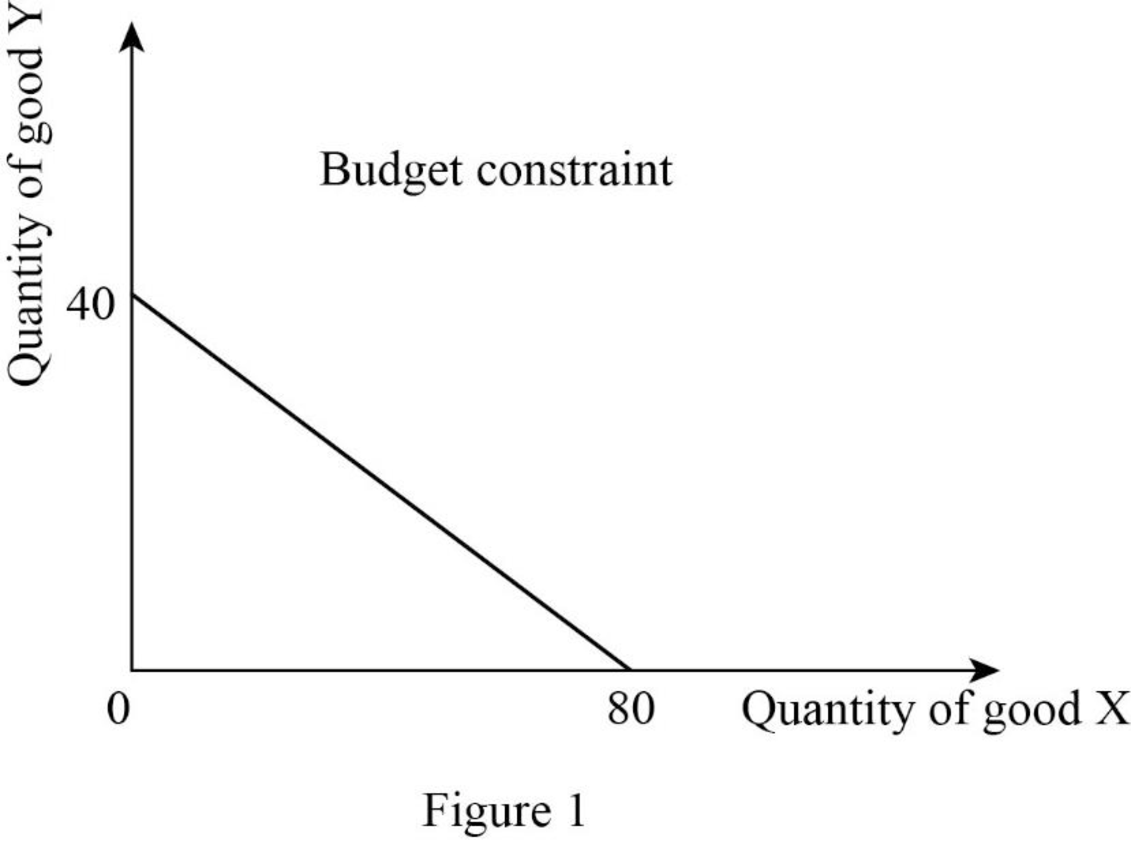
In Figure 1, the vertical axis measures the quantity of good Y and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of good X.
Budget constraints: Budget constraint refers to the possible combination of goods and services that a consumer can purchase at a given price level with the entire income.
(b)
The budget constraint.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Since the income is $3,000 and price of good X is $25, the quantity of good X can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the consumer will consume 120X.
Since the income is $3,000 and price of good Y is $200, the quantity of good Y can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the consumer will consume 15Y.
Now, the budget constraint can be represented as follows:
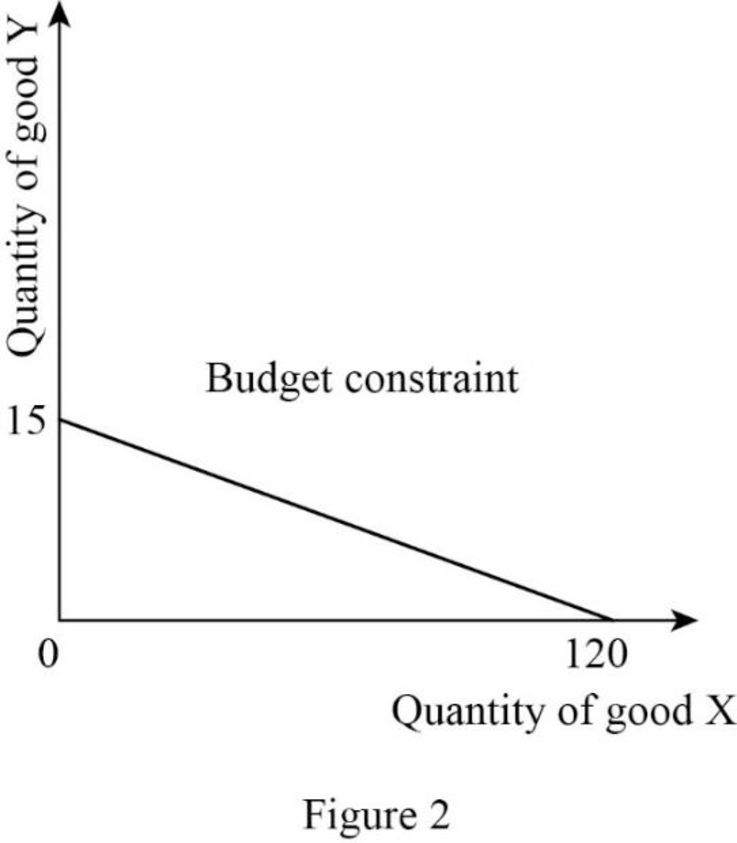
In Figure 2, the vertical axis measures the quantity of good Y and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of good X.
Budget constraints: Budget constraint refers to the possible combination of goods and services that a consumer can purchase at a given price level with the entire income.
(c)
The budget constraint.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Since the income is $2,000 and price of good X is $40, the quantity of good X can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the consumer will consume 50X.
Since the income is $2,000 and price of good Y is $150, the quantity of good Y can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the consumer will consume 13.33Y.
Now, the budget constraint can be represented as follows:
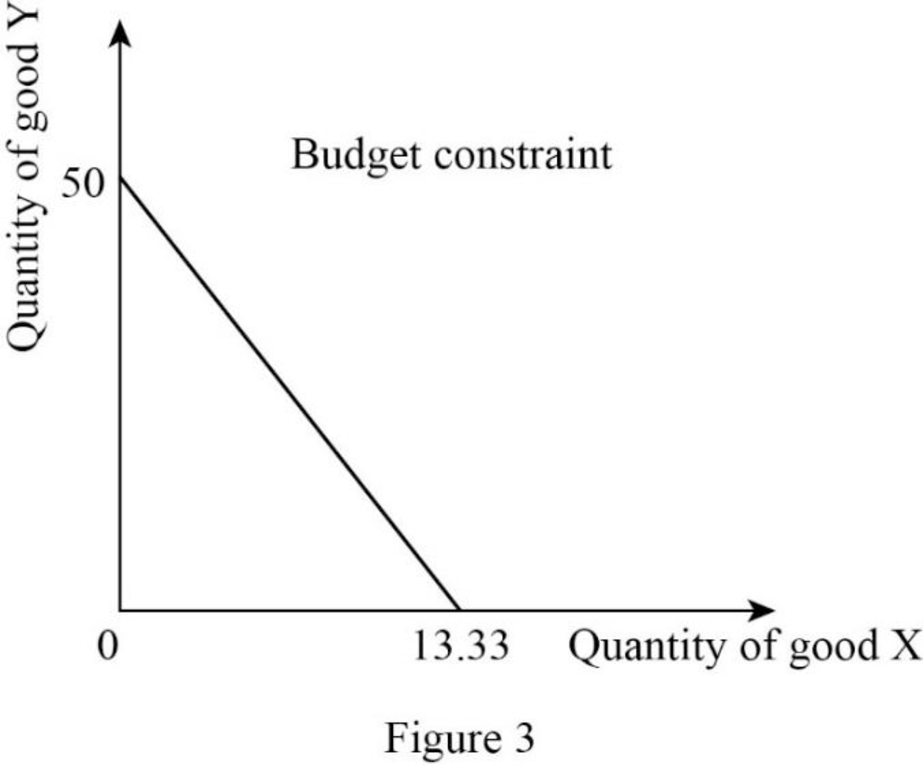
In Figure 3, the vertical axis measures the quantity of good Y and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of good X.
Budget constraints: Budget constraint refers to the possible combination of goods and services that a consumer can purchase at a given price level with the entire income.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter C Solutions
EBK MICROECONOMICS
- 34) Consider Dianna who has a $25 fast food budget per month. She can purchase salads (S), hamburgers (H), or chicken strips (C). The price of a salad is Ps=$3, the price of a hamburger is PB-$2 and the price of chicken strips is Pc $4. Fill in the table below. You will use your solutions to answer questions 34-36. # Hamburgers # Salads 1 2 2 MU Salads 36 30 c) 4; 3; 4 d) 5; 4; 5 MU/P Salads 1 2 3 4 5 MU hamburgers 5 In the optimal consumption bundle for Dianna, she will purchase chicken strips. a) 2; 1; 2 b) 3; 2; 3 28 22 16 36) Dianna total utility from her consumption bundle is a) 126 b) 504 c) 106 d) 398 MU/P # Hamburgers Chicken Strips T 2 3 7 salads, 4 5 35) Dianna's utility is maximized where the marginal utility per dollar spent on each item is equal to a) $10 b) $12 c) $14 d) $16 MU Chicken Strips 72 64 56 48 40 hamburgers, and MU/P Chicken Stripsarrow_forwardDan spends his money on baseball games and concert tickets. Baseball tickets cost $15, and concert tickets cost $25. His entertainment budget is $150. Dan's best friend Jay tells Dan that his favorite thing to do is go to concerts. In fact, going to concerts is popular with a lot of Dan's friends. Which statement below is likely to be correct? (A) Dan's budget constraint will shift up and the quantity of concerts he attends will likely increase. B Dan's budget constraint will stay the same and the quantity of concerts he attends will likely increase. D Dan's budget constraint will shift down and the quantity of concerts he attends will likely decrease. Dan's budget constraint will stay the same and the quantity of concerts he attends will likely decrease.arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer questions 1 through 8: A student has a monthly budget of $120 to spend on either burritos, which cost $6 each, or sodas, which cost $4 each. What is the largest number of burritos that the student could afford to purchase in one month? What is the largest number of sodas the student could afford to purchase in one month?arrow_forward
- consider your decision about how many hours to work. draw your budget constraint assuming that you pay no taxes on your income. on the same diagram, draw another budget constraint assuming that you pay 15 percent tax. show how the tax might lead to more hours of work,fewer hours or the same number of hours.explain.arrow_forwardTrue or false. A budget constraint, budget line or budget set is a graphical way to illustrate all possible combinations of two goods that a person can afford.arrow_forwardWith diminishing marginal utility, how do consumers decide how much to consume? Students are expected to give a detailed answer to this question. You must include an explanation about what diminishing marginal utility means in your answer. Concepts such as "budget constraint", "more is better", "utility". "marginal utility", and "marginal utility per dollar spent" must be used in your answer. No graph or calculation is required in this question.arrow_forward
- Kimiko is planning a party to celebrate her birthday. She has decided to serve sushi and yakitori meat skewers. Each serving of sushi is $8 and each yakitori skewer is $2. Kimiko has $240 to spend on the party. Please graph her budget line. Her friend, Barry, thinks there will not be enough food, so he gives Kimiko $80 more to spend on the party (she now has $320). How will this affect the budget line? a. There will be a parallel shift of the budget line away from the origin. b. There will be a parallel shift of the budget line towards the origin. c. There will be an outward shift of point A only. d. There will be an outward shift of point B only.arrow_forwardIf a consumer's income decreases, what will happen to the budget line? It will shift outward. It will become steeper. It will become flatter. It will shift inward.arrow_forward11)Which of the following describes what happens to a consumer's budget line if that consumer's budget increases? The budget line. A) becomes steeper. B) shifts farther away from the origin of the graph. C) does not change. D) becomes more horizontal. E) shifts closer to the origin of the grapharrow_forward
- QUESTION 23 Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram below. The absolute value of the slope of the budget line is: 10 8. 4 6. 8. 10 Quantity of C PC/PD. MUC/MUD. one-half. PD/PC. Quantity of Darrow_forwardDiagram the following budget constraint where Income - $10,000, Px – $100 and Py - $250.arrow_forwardWrite down the equation for the budget constraint and then graph it for .. Px = $100 Py = $25 Income = $5,000.00arrow_forward
 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning

