
(a)
Draw the budget constraint when income = $4,000; PX = $50; PY = $100.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Since the income is $4,000 and price of good X is $50, the quantity of good X can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the consumer will consume 80X.
Since the income is $4,000 and price of good Y is $100, the quantity of good Y can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the consumer will consume 40Y.
Now, the budget constraint can be represented as follows:
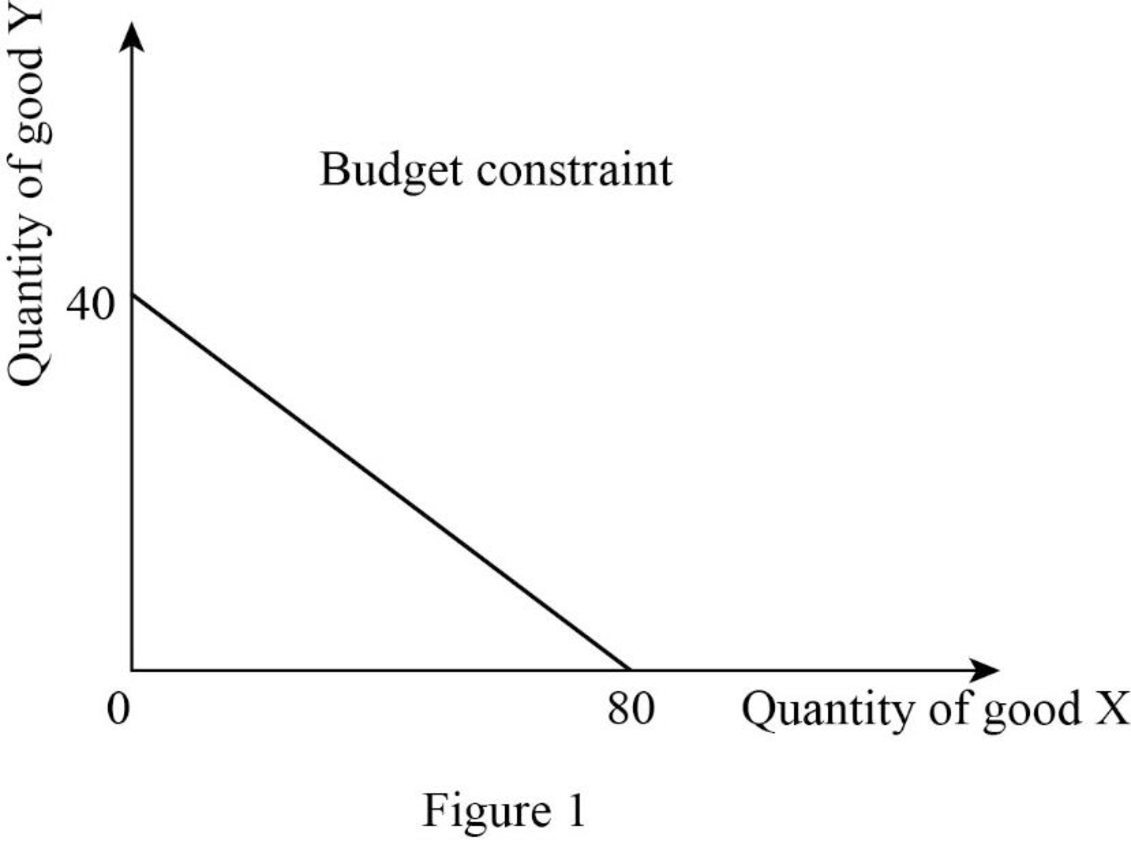
In Figure 1, the vertical axis measures the quantity of good Y and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of good X.
(b)
Draw the budget constraint when income = $3,000; PX = $25; PY = $200.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Since the income is $3,000 and price of good X is $25, the quantity of good X can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the consumer will consume 120X.
Since the income is $3,000 and price of good Y is $200, the quantity of good Y can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the consumer will consume 15Y.
Now, the budget constraint can be represented as follows:
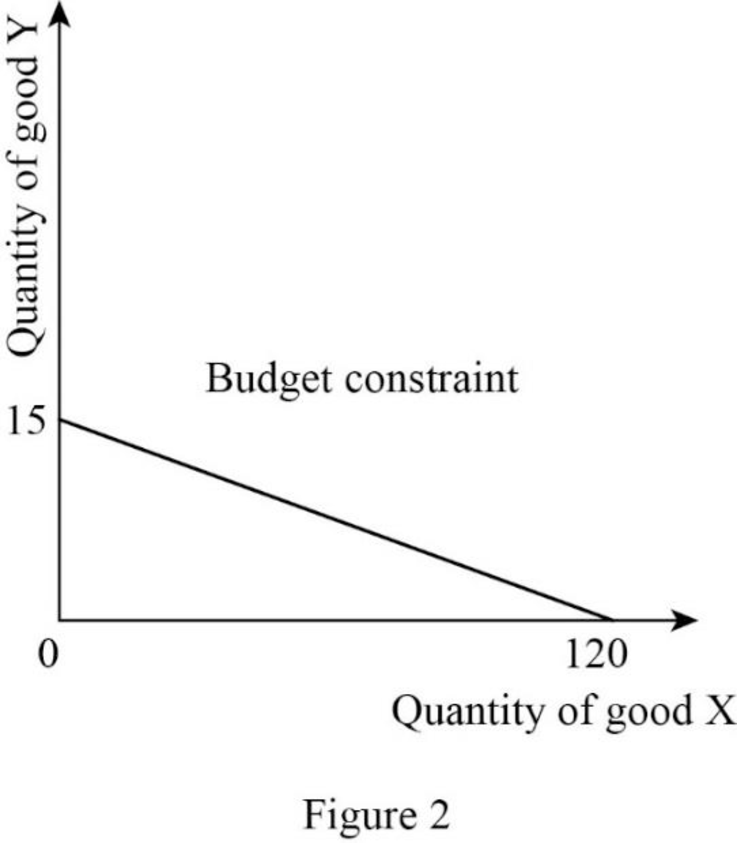
In Figure 2, the vertical axis measures the quantity of good Y and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of good X.
(c)
Draw the budget constraint when income = $2,000; PX = $40; PY = $150.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Since the income is $2,000 and price of good X is $40, the quantity of good X can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the consumer will consume 50X.
Since the income is $2,000 and price of good Y is $150, the quantity of good Y can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the consumer will consume 13.33Y.
Now, the budget constraint can be represented as follows:
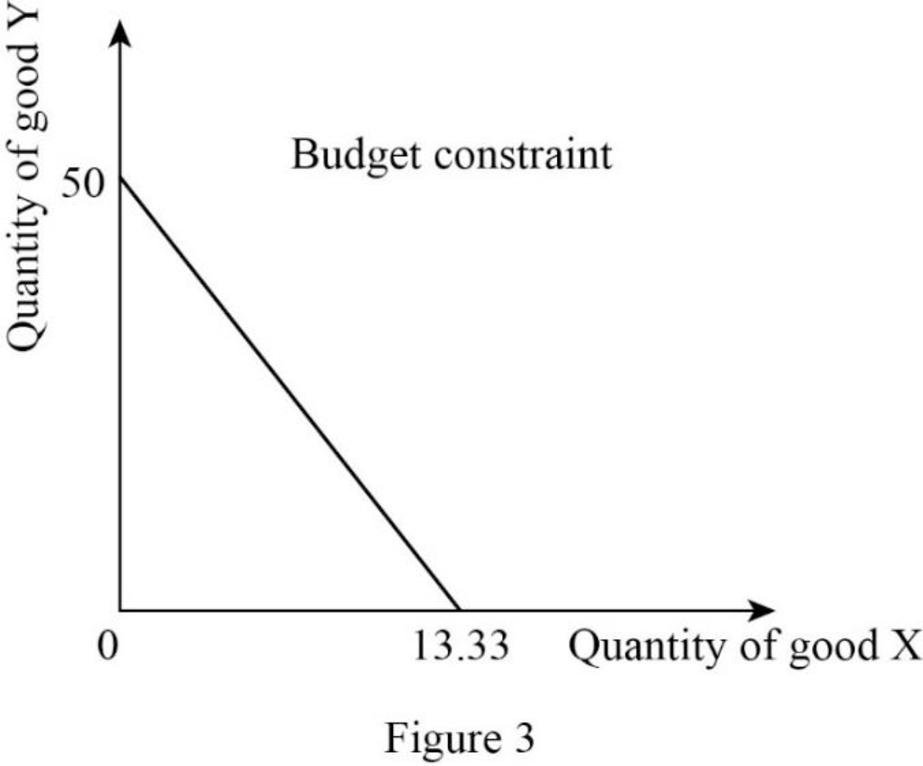
In Figure 3, the vertical axis measures the quantity of good Y and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of good X.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter E Solutions
Economics (MindTap Course List)
- Question 4 Given the following budget line ???+???=? And that the slope of the budget line depends only on relative prices, show what happens to the budget line when: (a) ?? rises (b) ? reduces (c) Both ?? and ?? rise by the same proportion (d) a consumer is given an in-kind transfer of 40 units of good ? (e) the government imposes a quantity tax (t) on good ?arrow_forwardAnthony’s Budget Line Anthony has already committed most of his income to his monthly living expenses and saving a few dollars each month. Having made these decisions, Anthony has a remaining budget of $15 a week, which he spends on two goods: coffee and magazines. The price of a cup of coffee is $2.50 and the price of a magazine is $5. 1. Construct a table showing the alternative combinations of the two goods that Anthony might purchase in a given week. 2. Use the data in your table to graph Anthony’s budget line. 3. What is the opportunity cost of each cup of coffee? What is the opportunity cost of each magazine? 4. Based on this information, do we know how many cups of coffee or magazines Anthony should buy each week? Why or why not? 5. Anthony decides he wants to upgrades to the $5 cup of coffee- the larger cup with extra flavoring! Using a graph, show how this will change Anthony’s budget line. (Note: This is most easily demonstrated by putting both budget lines on the…arrow_forwardKimiko is planning a party to celebrate her birthday. She has decided to serve sushi and yakitori meat skewers. Each serving of sushi is $8 and each yakitori skewer is $2. Kimiko has $240 to spend on the party. Please graph her budget line. Her friend, Barry, thinks there will not be enough food, so he gives Kimiko $80 more to spend on the party (she now has $320). How will this affect the budget line? a. There will be a parallel shift of the budget line away from the origin. b. There will be a parallel shift of the budget line towards the origin. c. There will be an outward shift of point A only. d. There will be an outward shift of point B only.arrow_forward
- (Figure and Table: The Budget Line) Use Figure and Table: The Budget Line. A(n) _____ in the price of potatoes would rotate the budget line, changing the intercept on the _____ axis and moving it _____ the origin. Select one: a. decrease; vertical; away from b. increase; horizontal; away from c. increase; vertical; away from d. decrease; horizontal; towardarrow_forwardWhat can you use to establish whether a budget has been allocated to maximise total utility? Market equilibrium Budget line Consumer equilibrium Marginal utility Total utilityarrow_forwardKimiko is planning a party to celebrate her birthday. She has decided to serve sushi and yakitori meat skewers. Each serving of sushi is $8 and each yakitori skewer is $2. Kimiko has $240 to spend on the party, and her budget line is shown below. Her friend Barry thinks there will not be enough food, so he gives Kimiko $80 more to spend on the party (she now has $320). Show Kimiko\'s new budget line in the graph below and answer the question.arrow_forward
- Diagram the following budget constraint where Income - $10,000, Px – $100 and Py - $250.arrow_forwardExplain how the budget constraint might change if income and prices of all goods increased in same proportion?arrow_forwardIf BC2 is the relevant budget constraint, then the consumer will purchase bundle A. B. B. C. C. D. D. E. E. F.arrow_forward
- Maria spends all of her income of $2,000 on food (F) and clothing (C). The prices per unit are: PF = $5 and PC = $20. Graph Maria’s budget line, with F on the vertical axis and C on the horizontal axis.arrow_forwardDiscuss Budget linearrow_forwardIf a consumer's income decreases, what will happen to the budget line? It will shift outward. It will become steeper. It will become flatter. It will shift inward.arrow_forward

