
1.
Indicate the method used by Company P to account the investment in Company T under Case A and Case B.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Available-for-sale (AFS) securities: The category of passive investments which are held as idle funds to serve the future operating and strategic purposes, are referred to as available-for-sale securities. The percentage of passive investments in debt or equity will be less than 20%.
Fair value method: The method of accounting the investments in short-term debt, and short-term and long-term equity securities, with an ownership of less than 20% of the outstanding stock of the investee, is referred to as fair value method.
Equity-method: The investments in stock securities which claim significant influence with an ownership of 20% to 50% in the outstanding stock of the investee company, are referred to as investments in stock for significant influence. The method of accounting such investments is referred to as equity method.
Method used to account the investments in Case A and Case B:
| Details | Case A: 3,000 Shares Purchased | Case B: 8,750 Shares Purchased | |
| 1. | Accounting method | Fair value method | Equity method |
Table (1)
Description:
Method used to account for Case A: Since the investor company, Company P purchased 12%
Method used to account for Case B: Since the investor company, Company P purchased 35%
2.
a.
Journalize the purchase of investment in Company T stock for Case A and Case B.
2.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in
stockholders’ equity accounts. - Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Prepare journal entry to record purchase of investment on January 1, 2014.
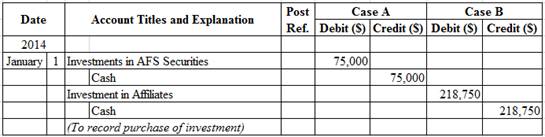
Table (2)
Description:
Case A:
- Investments in AFS Securities is an asset account. Since stock investments are purchased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute cost of investment in AFS securities.
Case B:
- Investments in Affiliates is an asset account. Since investments are purchased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute cost of investment in affiliates.
b.
Journalize the income reported by Company T, for Case A and Case B.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry for share of income received from Company T for Case A and Case B.
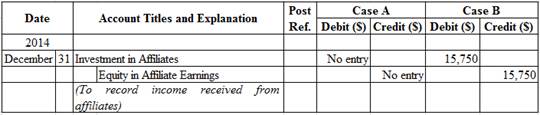
Table (3)
Description:
Case A: No entry is required for reporting net income of affiliate in fair value method.
Case B:
- Investments in Affiliates is an asset account. Since share of income received from investee increases the investment value, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Equity in Affiliate Earnings is a revenue account. Revenues increase stockholders’ equity value, and an increase in stockholders’ equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of income received from Company T.
c.
Journalize the dividends paid by Company T, for Case A and Case B.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry for dividends received from Company T.
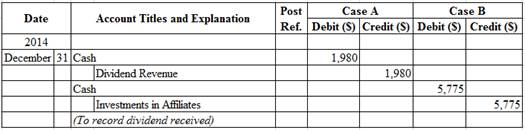
Table (4)
Description:
Case A:
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Dividend Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of dividend received.
Case B:
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Investments in Affiliates is an asset account. Since stock investments are reduced as an effect of receipt of dividends, asset value decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of dividend received.
d.
Journalize the
d.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry for adjusting the securities to the fair market value.
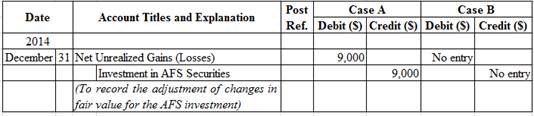
Table (5)
Description:
Case A:
- Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) is an adjustment account used to report gain or loss on adjusting cost of investment at fair market value. Since loss has occurred and losses decrease stockholders’ equity value, a decrease in stockholders’ equity value is debited. This loss is reported as component of Other Comprehensive Income (OCI) on the Statement of Comprehensive Income.
- Investments in AFS Securities is an asset account. The account is credited because the market price was decreased, and eventually the asset value decreased.
Working Notes:
Determine the unrealized gain or loss on investment in AFS securities.
Step 1: Compute the fair value of investment at the end of the year.
Step 2: Compute unrealized gain or loss on investment in AFS securities.
Note: Refer to Equations (6) and (1) for value and computation of fair value of investment and cost of investment.
Case B: Company P does not record any changes in the fair value of the investment at the year end because it is an equity-method investment.
3.
Complete the table for the investments of Company P for Case A and Case B.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Complete the table as shown below:
| Details | Dollar Amounts | |
| Case A | Case B | |
| Balance sheet | ||
| Investments | $66,000 | $228,725 |
| Stockholders’ equity | (9,000) | None |
| Income statement | ||
| Dividend revenue | 1,980 | - |
| Equity in earnings of affiliate | - | 15,750 |
Table (6)
Working Notes:
Find the carrying value of investment by preparing Investment in Affiliates account (Case B).
| Investment in Affiliates | ||||||
| Date | Details | Debit ($) | Date | Details | Credit ($) | |
| Cash | 218,750 | Cash dividends | 5,775 | |||
| Equity in affiliate earnings | 15,750 | |||||
| Total | 234,500 | Total | 5,775 | |||
| Ending Balance | $228,725 | |||||
Table (7)
Note: Refer to Equations (2), (3), and (5) for equity-method cost of investment, revenue, and cash dividends value.
Description:
Investments:
- Case A investments are AFS securities and should be reported at fair value. (Refer to Equation (6) for computation of value).
- Case B investments are securities with significant influence, and should be reported at carrying value of investment in proportion to the net income reported and dividends declared by Company T. (Refer to Table (7) for computation of value).
Stockholders’ equity:
- Case A investments are adjusted to fair value every year-end, so the unrealized loss is reported as a component of stockholders’ equity under accumulated other comprehensive income. (Refer to Equation (7) for computation of value).
- Case B investments are not adjusted to fair value every year-end because they are reported by equity method.
Dividend revenue:
- The dividend revenue from Case A investments are reported on the income statement. (Refer to Equation (4) for computation of value).
- The dividend revenue from Case B investments are reported as cash received, but not revenue. Hence, not reported on the income statement.
Equity in affiliate earnings:
- The net income reported by the investee company is not recorded by the investor for Case A investments.
- The net income reported by affiliate is recorded as investment revenue for Case B investments. Hence, are reported on the income statement. (Refer to Equation (3) for computation of value).
4.
Explain the reasons for the differences between the Case A and Case B investments.
4.
Explanation of Solution
The following are the reasons for the differences between the Case A and Case B investments:
- The treatment of fair value at the end of the year is different under two methods.
- The treatment of dividends received are different under two methods.
- The treatment of net income reported by affiliate are different under two methods.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter E Solutions
Financial Accounting - With Access

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





