
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given trivial name is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The trivial names are commonly used names which are not systematic ones. Many trivial names are accepted by IUPAC. Nitriles are derivatives of carboxylic acid. The trivial names of nitriles are deriving from the trivial names of the analogous carboxylic acids.
In naming organic compounds, the
Number the carbon chain in a way that the functional group and the substituents attached get the lowest number. The position of the functional group and substituents on the parent chain or ring is indicated by the respective locant number just before the suffix. Prefixes are used to denote the number of identical substituents. The substituents are written in alphabetical order when writing the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem F.30P
The structure and IUPAC name for the given trivial name is
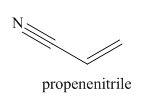
Explanation of Solution
The given trivial name is acrylonitrile.
The given name indicates that the high priority functional group is cynide. The trival name acrylonitrile correlates the derivative of acrylic acid. Structure for acrylic acid is
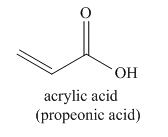
Nitriles are derived from acids where
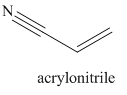
The main chain in this molecule is of three carbon atoms thus the root name is propan, and the suffix nitrile is added to the root name. The main chain is numbered starting from the carbon atom of the nitrile group. The main chain has a C=C bond; thus the IUPAC name for acrilonitrile is propenenitrile.
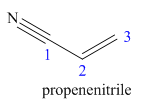
The structure for the given molecule is drawn based on the functional group, and the IUPAC named is written by adding locators to the substituents.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given trivial name is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The trivial names are commonly used names which are not systematic ones. Many trivial names are accepted by IUPAC. Nitriles are derivatives of carboxylic acid. The trivial names of nitriles are deriving from the trivial names of the analogous carboxylic acids.
In naming organic compounds, the functional groups other than the highest priority functional groups are treated as substituents. The root name is established by identifying the longest carbon chain or a ring containing functional group. Remove the e from the normal ane, ene, or yne ending, and add the suffix that corresponds to the highest-priority functional group. Nitriles are the derivatives of carboxylic acid where
Number the carbon chain in a way that the functional group and the substituents attached get the lowest number. The position of the functional group and substituents on the parent chain or ring is indicated by the respective locant number just before the suffix. Prefixes are used to denote the number of identical substituents. The substituents are written in alphabetical order when writing the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem F.30P
The structure and IUPAC name for the given trivial name is
Explanation of Solution
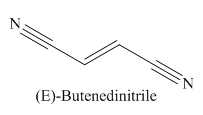
The given trivial name is fumaronitrile.
The given name indicates that the high priority functional group is cynide. The trival name fumaronitrile correlates to the derivative of fumaric acid (dicarboxylic acid). Structure for fumaric acid is
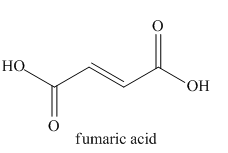
Nitriles are derived from acids where
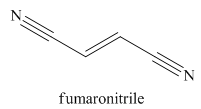
The main chain in this molecule is of four carbon atoms; thus the root name is butan. The structure has two cynide groups at both terminals; hence the suffix dinitrile is added to the root name. The main chain is numbered starting from the carbon atom of the nitrile group.
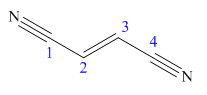
The main chain has a C=C bond; thus the IUPAC name for fumaronitrile is (E) butenedinitrile.
The structure for the given molecule is drawn based on the functional group, and the IUPAC named is written by adding locators to the substituents.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given trivial name is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The trivial names are commonly used names which are not systematic ones. Many trivial names are accepted by IUPAC. Nitriles are derivatives of carboxylic acid. The trivial names of nitriles are deriving from the trivial names of the analogous carboxylic acids.
In naming organic compounds, the functional groups other than the highest priority functional groups are treated as substituents. The root name is established by identifying the longest carbon chain or a ring containing functional group. Remove the e from the normal ane, ene, or yne ending, and add the suffix that corresponds to the highest-priority functional group. Nitriles are the derivatives of carboxylic acid where
Number the carbon chain in a way that the functional group and the substituents attached get the lowest number. The position of the functional group and substituents on the parent chain or ring is indicated by the respective locant number just before the suffix. Prefixes are used to denote the number of identical substituents. The substituents are written in alphabetical order when writing the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem F.30P
The structure and IUPAC name for the given trivial name is
Explanation of Solution
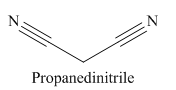
The given trivial name is malonitrile.
The given name indicates that the high priority functional group is cynide. The trival name malonitrile correlates to the derivative of malonic acid (dicarboxylic acid). Structure for malonic acid is
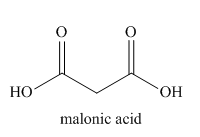
Nitriles are derived from acids where
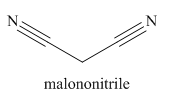
The main chain in this molecule is of three carbon atoms; thus the root name is propane. The structure has two cynide groups; hence the suffix dinitrile is added to the root name. The main chain is numbered starting from the carbon atom of nitrile group.
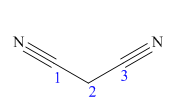
Hence the IUPAC name for malonitrile is propanedinitrile.
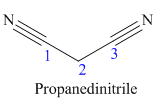
The structure for the given molecule is drawn based on the functional group, and the IUPAC named is written by adding locators to the substituents.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given trivial name is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The trivial names are commonly used names which are not systematic ones. Many trivial names are accepted by IUPAC. Nitriles are derivatives of carboxylic acid. The trivial names of nitriles are deriving from the trivial names of the analogous carboxylic acids.
In naming organic compounds, the functional groups other than the highest priority functional groups are treated as substituents. The root name is established by identifying the longest carbon chain or a ring containing functional group. Remove the e from the normal ane, ene, or yne ending, and add the suffix that corresponds to the highest-priority functional group. Nitriles are the derivatives of carboxylic acid where
Number the carbon chain in a way that the functional group and the substituents attached get the lowest number. The position of the functional group and substituents on the parent chain or ring is indicated by the respective locant number just before the suffix. Prefixes are used to denote the number of identical substituents. The substituents are written in alphabetical order when writing the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem F.30P
The structure and IUPAC name for the given trivial name is
Explanation of Solution
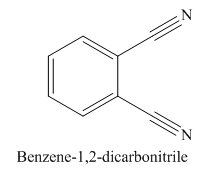
The given trivial name is phthalonitrile.
The given name indicates that the high priority functional group is cynide. The trival name phthalonitrile correlates to the derivative of phthalic acid (dicarboxylic acid). Structure for phthalic acid is
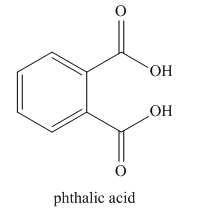
Nitriles are derived from acids where
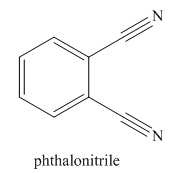
The parent ring in this molecule is benzene ring; thus the root name is benzene. The structure has two cynide groups attached directly to the ring; hence the suffix dicarbonitrile is added to the root name. The ring is numbered such that carbon atoms attached to nitrile groups get least number.
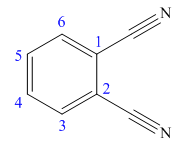
The IUPAC name for phthalonitrile is bemezene-1, 2-dicarbonitrile because two cynide groups are at C1 and C2.
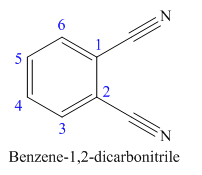
The structure for the given molecule is drawn based on the functional group, and the IUPAC named is written by adding locators to the substituents.
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given trivial name is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The trivial names are commonly used names which are not systematic ones. Many trivial names are accepted by IUPAC. Nitriles are derivatives of carboxylic acid. The trivial names of nitriles are deriving from the trivial names of the analogous carboxylic acids.
In naming organic compounds, the functional groups other than the highest priority functional groups are treated as substituents. The root name is established by identifying the longest carbon chain or a ring containing functional group. Remove the e from the normal ane, ene, or yne ending, and add the suffix that corresponds to the highest-priority functional group. Nitriles are the derivatives of carboxylic acid where
Number the carbon chain in a way that the functional group and the substituents attached get the lowest number. The position of the functional group and substituents on the parent chain or ring is indicated by the respective locant number just before the suffix. Prefixes are used to denote the number of identical substituents. The substituents are written in alphabetical order when writing the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem F.30P
The structure and IUPAC name for the given trivial name is
Explanation of Solution
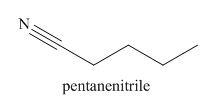
The given trivial name is valeronitrile.
The given name indicates that the high priority functional group is cynide. The trival name valeronitrile correlates to the derivative of valeric acid. Structure for valeric acid is
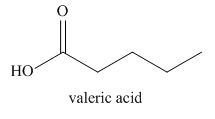
Nitriles are derived from acids where
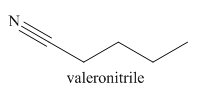
The main chain in this molecule is of five carbon atoms; thus the root name is pentane. The structure has a cynide group; hence the suffix nitrile is added to the root name. The main chain is numbered starting from the carbon atom of nitrile group.
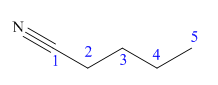
Hence the IUPAC name for valronitrile is pentanenitrile.
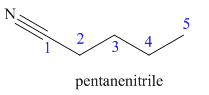
The structure for the given molecule is drawn based on the functional group, and the IUPAC named is written by adding locators to the substituents.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter F Solutions
ORG.CHEM W/TEXT+SOLU.MANUAL
- Pls help ASAP. WRITE THE IUPAC NAMEarrow_forwardwhat is the IUPAC NAME give explanation tooarrow_forwardThe second question was incorrect. "The IUPAC nomenclature of benzene compounds primarily will use benzene as the root name. However, common names for substituted benzene compounds exist that use the base names from its derived compounds. The principal functional group will serve as the common root name." Would you mind trying again please? Thank youarrow_forward
- Answer the following question by referring to the ball-and-stick modelof fentanyl, a potent narcotic analgesic used in surgical procedures. Question : Identify the functional groups ?arrow_forwardGive typed full explanation not a single word hand written otherwise leave it Spell out the full name of each compound. A, B, C, & Darrow_forwardillustrate strctures & gve the iupac name of the compound that meet the ff descriptionsarrow_forward
