1. Listed below are the n" ionization energies for a carbon atom. The units are megajoules per mole. IE: IE2 2.35 MJ/mol IE3 IE4 IES IEG 1.09 4.62 6.22 37.83 47.28 MJ/mol MJ/mol MJ/mol MJ/mol MJ/mol (a) Convert each ionization energy into ev for an individual atom rather than MJ for a mole of atoms. (b) Explain the large jump in ionization energy from IE, to IEs. Use electron configurations in your explanation. (c) How much energy (in eV) is needed to remove all the electrons from a carbon atom?
1. Listed below are the n" ionization energies for a carbon atom. The units are megajoules per mole. IE: IE2 2.35 MJ/mol IE3 IE4 IES IEG 1.09 4.62 6.22 37.83 47.28 MJ/mol MJ/mol MJ/mol MJ/mol MJ/mol (a) Convert each ionization energy into ev for an individual atom rather than MJ for a mole of atoms. (b) Explain the large jump in ionization energy from IE, to IEs. Use electron configurations in your explanation. (c) How much energy (in eV) is needed to remove all the electrons from a carbon atom?
Principles of Modern Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Chapter4: Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 39P: Chapter 3 introduced the concept of a double bond between carbon atoms, represented by C=C , with a...
Related questions
Question
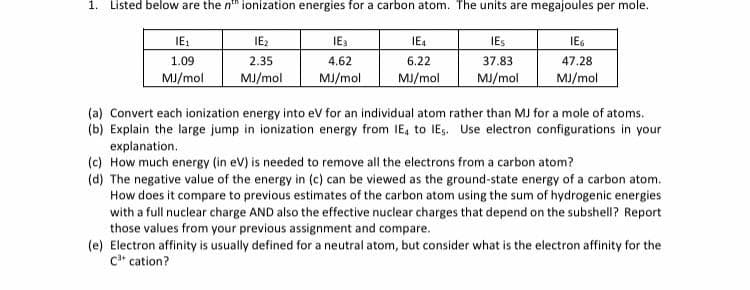
Transcribed Image Text:1. Listed below are the n" ionization energies for a carbon atom. The units are megajoules per mole.
IE:
IE2
IE3
IE4
IES
IEG
1.09
2.35
4.62
6.22
37.83
47.28
MJ/mol
MJ/mol
MJ/mol
MJ/mol
MJ/mol
MJ/mol
(a) Convert each ionization energy into eV for an individual atom rather than MJ for a mole of atoms.
(b) Explain the large jump in ionization energy from IE, to IEs. Use electron configurations in your
explanation.
(c) How much energy (in eV) is needed to remove all the electrons from a carbon atom?
(d) The negative value of the energy in (c) can be viewed as the ground-state energy of a carbon atom.
How does it compare to previous estimates of the carbon atom using the sum of hydrogenic energies
with a full nuclear charge AND also the effective nuclear charges that depend on the subshell? Report
those values from your previous assignment and compare.
(e) Electron affinity is usually defined for a neutral atom, but consider what is the electron affinity for the
c* cation?
Expert Solution
Step 1 given Information
Since you have posted a question with multiple sub-parts, we will solve first three sub-parts for you. To get remaining sub-part solved please repost the complete question and mention the sub-parts to be solved
Given data
| I. E. | I. E. (MJ/mol) |
| IE1 | 1.09 |
| IE2 | 2.35 |
| IE3 | 4.62 |
| IE4 | 6.22 |
| IE5 | 37.83 |
| IE6 | 47.28 |
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,