12 3. To explore the consequences of coupling ATP hydrolysis under physiological conditions to a thermodynamically unfavorable biochemical reaction, consider the hypothetical transformation X - Y, for which AG° = 20 kJ/mol. (a) What is the ratio [Y]/[X] at equilibrium? (b) Suppose X and Y participate in a sequence of reactions during which ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP and Pi. The overall reaction is →Y+ ADP + P X + ATP + H2O Calculate [Y]/[X] for this reaction at equilibrium. Assume that the temperature is 25 C and the equilibrium concentrations of ATP, ADP, and Piare all 1 M. (c) We know that [ATP], [ADP], and [Pi] are not 1 M under physiological conditions. Calculate [Y]/[X] for the ATP-coupled reaction when the values of [ATP], [ADP], and [Pi] are those found in rat myocytes (look at the Table 13-5). TABLE 13-5 Total Concentrations of Adenine Nucleotides, Inorganic Phosphate, and Phosphocreatine in Some Cells Concentration (MM) ATP ADP AMP PCr Rat hepatocyte 3.38 1.32 0.29 4.8 0. Rat myocyte 8.05 0.04 8.05 28 0.93 2.72 0.06 4.7 Rat neuron 2.59 0.7 0.25 0. 2.25 0.02 1.65 Human erythrocyte E. coli cell 0.82 7.9 1.04 7.90 For erythrocytes the concentrations are those of the cytosol (human erythrocytes lack a nucleus and mitochondria). In the other types of cells the data are for the entire cell contents, although the cytosol and the mitochondria have very different concentrations of ADP. PCr is phosphocreatine, discussed on p. 516. BThis value reflects total concentration; the true value for free ADP may be much lower (p. 509). Cellular ATP concentration is usually far above the equilibrium concentration, making ATPA very potent source of chemical energy.
12 3. To explore the consequences of coupling ATP hydrolysis under physiological conditions to a thermodynamically unfavorable biochemical reaction, consider the hypothetical transformation X - Y, for which AG° = 20 kJ/mol. (a) What is the ratio [Y]/[X] at equilibrium? (b) Suppose X and Y participate in a sequence of reactions during which ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP and Pi. The overall reaction is →Y+ ADP + P X + ATP + H2O Calculate [Y]/[X] for this reaction at equilibrium. Assume that the temperature is 25 C and the equilibrium concentrations of ATP, ADP, and Piare all 1 M. (c) We know that [ATP], [ADP], and [Pi] are not 1 M under physiological conditions. Calculate [Y]/[X] for the ATP-coupled reaction when the values of [ATP], [ADP], and [Pi] are those found in rat myocytes (look at the Table 13-5). TABLE 13-5 Total Concentrations of Adenine Nucleotides, Inorganic Phosphate, and Phosphocreatine in Some Cells Concentration (MM) ATP ADP AMP PCr Rat hepatocyte 3.38 1.32 0.29 4.8 0. Rat myocyte 8.05 0.04 8.05 28 0.93 2.72 0.06 4.7 Rat neuron 2.59 0.7 0.25 0. 2.25 0.02 1.65 Human erythrocyte E. coli cell 0.82 7.9 1.04 7.90 For erythrocytes the concentrations are those of the cytosol (human erythrocytes lack a nucleus and mitochondria). In the other types of cells the data are for the entire cell contents, although the cytosol and the mitochondria have very different concentrations of ADP. PCr is phosphocreatine, discussed on p. 516. BThis value reflects total concentration; the true value for free ADP may be much lower (p. 509). Cellular ATP concentration is usually far above the equilibrium concentration, making ATPA very potent source of chemical energy.
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter24: Biochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 34GQ: The first step of the metabolic process known as glycolysis is the conversion of glucose to glucose-...
Related questions
Question
Part c
![12
3. To explore the consequences of coupling ATP hydrolysis under physiological conditions to a
thermodynamically unfavorable biochemical reaction, consider the hypothetical transformation X
- Y, for which AG° = 20 kJ/mol.
(a) What is the ratio [Y]/[X] at equilibrium?
(b) Suppose X and Y participate in a sequence of reactions during which ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP
and Pi. The overall reaction is
→Y+ ADP + P
X + ATP + H2O
Calculate [Y]/[X] for this reaction at equilibrium. Assume that the temperature is 25 C and the
equilibrium concentrations of ATP, ADP, and Piare all 1 M.
(c) We know that [ATP], [ADP], and [Pi] are not 1 M under physiological conditions. Calculate [Y]/[X]
for the ATP-coupled reaction when the values of [ATP], [ADP], and [Pi] are those found in rat
myocytes (look at the Table 13-5).](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F079cba43-566f-4c95-9de9-a2e279b041b7%2F671f8e0d-9ab0-47c4-a6ec-cdf264eee5a9%2Fmtvy918.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:12
3. To explore the consequences of coupling ATP hydrolysis under physiological conditions to a
thermodynamically unfavorable biochemical reaction, consider the hypothetical transformation X
- Y, for which AG° = 20 kJ/mol.
(a) What is the ratio [Y]/[X] at equilibrium?
(b) Suppose X and Y participate in a sequence of reactions during which ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP
and Pi. The overall reaction is
→Y+ ADP + P
X + ATP + H2O
Calculate [Y]/[X] for this reaction at equilibrium. Assume that the temperature is 25 C and the
equilibrium concentrations of ATP, ADP, and Piare all 1 M.
(c) We know that [ATP], [ADP], and [Pi] are not 1 M under physiological conditions. Calculate [Y]/[X]
for the ATP-coupled reaction when the values of [ATP], [ADP], and [Pi] are those found in rat
myocytes (look at the Table 13-5).
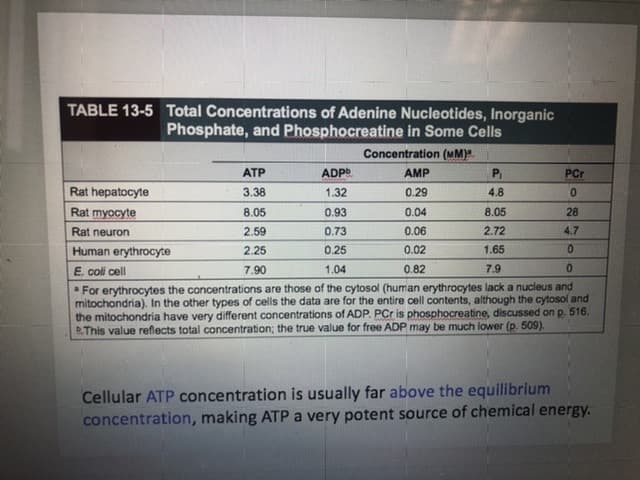
Transcribed Image Text:TABLE 13-5 Total Concentrations of Adenine Nucleotides, Inorganic
Phosphate, and Phosphocreatine in Some Cells
Concentration (MM)
ATP
ADP
AMP
PCr
Rat hepatocyte
3.38
1.32
0.29
4.8
0.
Rat myocyte
8.05
0.04
8.05
28
0.93
2.72
0.06
4.7
Rat neuron
2.59
0.7
0.25
0.
2.25
0.02
1.65
Human erythrocyte
E. coli cell
0.82
7.9
1.04
7.90
For erythrocytes the concentrations are those of the cytosol (human erythrocytes lack a nucleus and
mitochondria). In the other types of cells the data are for the entire cell contents, although the cytosol and
the mitochondria have very different concentrations of ADP. PCr is phosphocreatine, discussed on p. 516.
BThis value reflects total concentration; the true value for free ADP may be much lower (p. 509).
Cellular ATP concentration is usually far above the equilibrium
concentration, making ATPA very potent source of chemical energy.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285869759
Author:
Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285869759
Author:
Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning