3.The TTT diagram of a plain carbon steel is given in Fig. 1. Identify whether this steel is a hypoeutectoid, eutectoid or hypereutectoid steel. Explain why the transformation happens slowly at 850°C as well as at 300°C. Determine the microstructures expected in this type of steel after the following heat treatment processes. a) Austenize at 900°C, quench to 400°C and hold for 1000 s and quench to 25°C. b) Austenize at 900°C, quench to 25°C. c) Austenize at 900°C, quench to 675°C and hold for 1 s, quench to 400°C and hold for 900 s and slowly cool to 25°C.
3.The TTT diagram of a plain carbon steel is given in Fig. 1. Identify whether this steel is a hypoeutectoid, eutectoid or hypereutectoid steel. Explain why the transformation happens slowly at 850°C as well as at 300°C. Determine the microstructures expected in this type of steel after the following heat treatment processes. a) Austenize at 900°C, quench to 400°C and hold for 1000 s and quench to 25°C. b) Austenize at 900°C, quench to 25°C. c) Austenize at 900°C, quench to 675°C and hold for 1 s, quench to 400°C and hold for 900 s and slowly cool to 25°C.
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
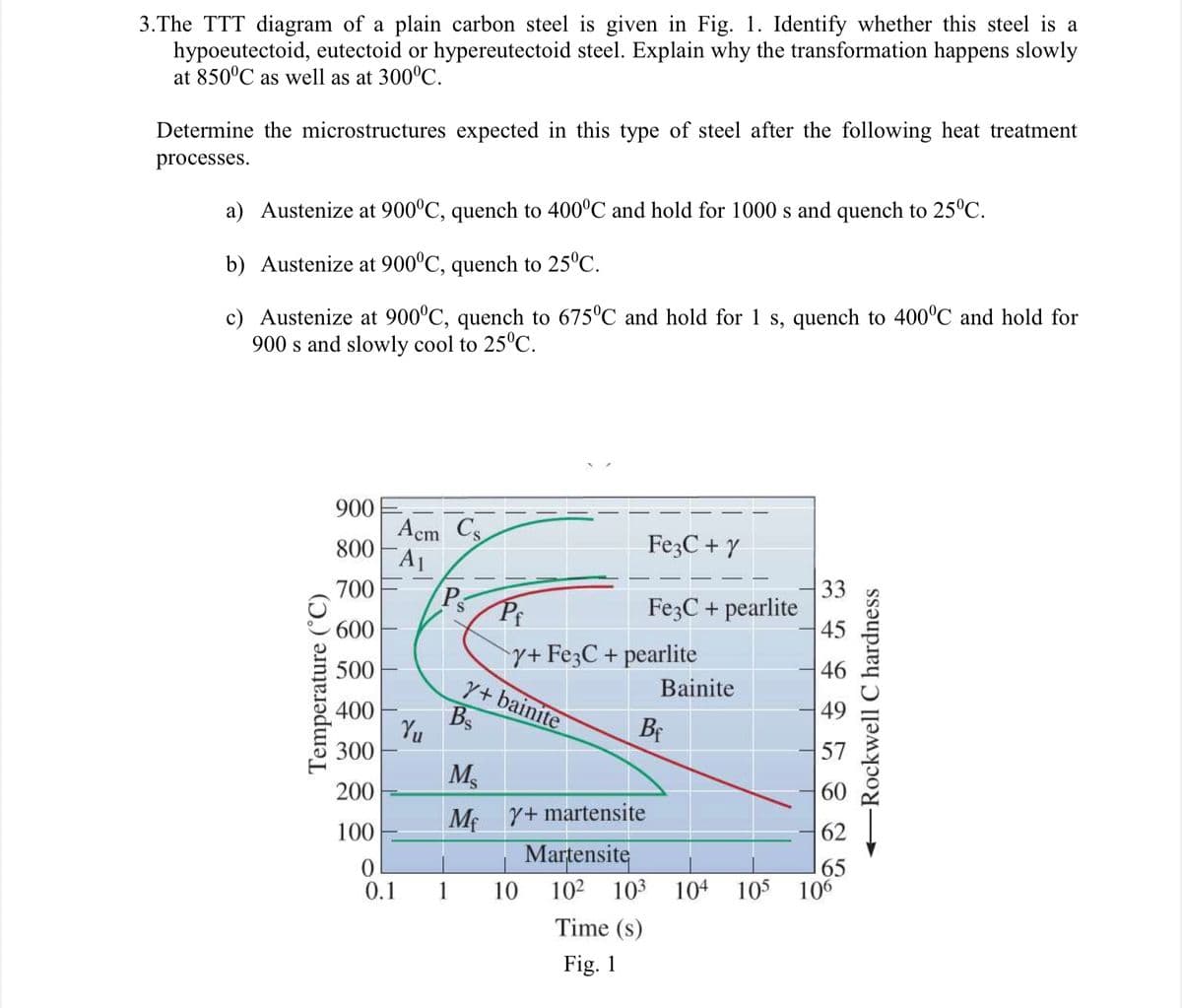
Transcribed Image Text:3.The TTT diagram of a plain carbon steel is given in Fig. 1. Identify whether this steel is a
hypoeutectoid, eutectoid or hypereutectoid steel. Explain why the transformation happens slowly
at 850°C as well as at 300°C.
Determine the microstructures expected in this type of steel after the following heat treatment
processes.
a) Austenize at 900°C, quench to 400°C and hold for 1000 s and quench to 25°C.
b) Austenize at 900°C, quench to 25°C.
c) Austenize at 900°C, quench to 675°C and hold for 1 s, quench to 400°C and hold for
900 s and slowly cool to 25°C.
900
Acm Cs
800
A1
FezC + Y
33
Fe3C + pearlite
45
700
Ps
600
++ Fe3C + pearlite
Y+ bainite
Bs
500
46
Bainite
400
Yu
Bf
300
57
Ms
200
60
Mf Y+ martensite
100
62
Martensite
102
65
103 104 105 106
0.1
1
10
Time (s)
Fig. 1
Temperature (°C)
Rockwell C hardness
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY