A researcher wanted to determine if carpeted or uncarpeted rooms contain more bacteria. The table shows the results for the number of bacteria per cubic foot for both types of rooms. A normal probability plot and boxplot indicate that the data are approximately normally distributed with no outliers. Do carpeted rooms have more bacteria than uncarpeted rooms at the a 0.01 level of significance? Question Help Full data set Uncarpeted 5.3 Carpeted 13.4 9.7 11.4 14.1 15.9 4.7 9.1 Click the icon to view the Student t-distribution table. 7.7 12.8 8.2 4.6 12.9 9.2 12.4 9.6 What are the null and alternative hypotheses? Ho versus H Calculate the test statistic, to (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Now find the critical value. Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box within your choice. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) OA. t ? Click to select your answer(s). 11:45 PM 20 11/24/2019 O Type here to search ASUS delete pt sc osnod SETO insert 12 0 break 19 f7 EX f5 f4 backspace f3 12 0 & 7 esc $ 4 # 3 2 P U Y T R E W KLLL Q tab G J CO I 96 A researcher wanted to determine if carpeted or uncarpeted rooms contain more bacteria. The table shows the results for the number of bacteria per cubic foot for both types of rooms. A normal probability plot and boxplot indicate that the data are approximately normally distributed with no outliers. Do carpeted rooms have more bacteria than uncarpeted rooms at the a 0.01 level of significance? Carpeted 13.4 9.7 11.4 14.1 FBClick the icon to view the Student t-distribution table. 12.9 9.2 A. t B. t/2 Do carpeted rooms have more bacteria than uncarpeted rooms at the a = 0.01 level of significance? A. No, because the test statistic is not in the critical region. B. Yes, because the test statistic is not in the critical region. O C. No, because the test statistic is in the critical region. D. Yes, because the test statistic is in the critical region answer(s). Click to select your O Et Type here to search SUS pause break f12 m 19 f7 f6 D/ f5 f4 f3 f2 f7 & esc 7 6 # 5 CO SA 96
A researcher wanted to determine if carpeted or uncarpeted rooms contain more bacteria. The table shows the results for the number of bacteria per cubic foot for both types of rooms. A normal probability plot and boxplot indicate that the data are approximately normally distributed with no outliers. Do carpeted rooms have more bacteria than uncarpeted rooms at the a 0.01 level of significance? Question Help Full data set Uncarpeted 5.3 Carpeted 13.4 9.7 11.4 14.1 15.9 4.7 9.1 Click the icon to view the Student t-distribution table. 7.7 12.8 8.2 4.6 12.9 9.2 12.4 9.6 What are the null and alternative hypotheses? Ho versus H Calculate the test statistic, to (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Now find the critical value. Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box within your choice. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) OA. t ? Click to select your answer(s). 11:45 PM 20 11/24/2019 O Type here to search ASUS delete pt sc osnod SETO insert 12 0 break 19 f7 EX f5 f4 backspace f3 12 0 & 7 esc $ 4 # 3 2 P U Y T R E W KLLL Q tab G J CO I 96 A researcher wanted to determine if carpeted or uncarpeted rooms contain more bacteria. The table shows the results for the number of bacteria per cubic foot for both types of rooms. A normal probability plot and boxplot indicate that the data are approximately normally distributed with no outliers. Do carpeted rooms have more bacteria than uncarpeted rooms at the a 0.01 level of significance? Carpeted 13.4 9.7 11.4 14.1 FBClick the icon to view the Student t-distribution table. 12.9 9.2 A. t B. t/2 Do carpeted rooms have more bacteria than uncarpeted rooms at the a = 0.01 level of significance? A. No, because the test statistic is not in the critical region. B. Yes, because the test statistic is not in the critical region. O C. No, because the test statistic is in the critical region. D. Yes, because the test statistic is in the critical region answer(s). Click to select your O Et Type here to search SUS pause break f12 m 19 f7 f6 D/ f5 f4 f3 f2 f7 & esc 7 6 # 5 CO SA 96
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.4: Distributions Of Data
Problem 19PFA
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
Please help
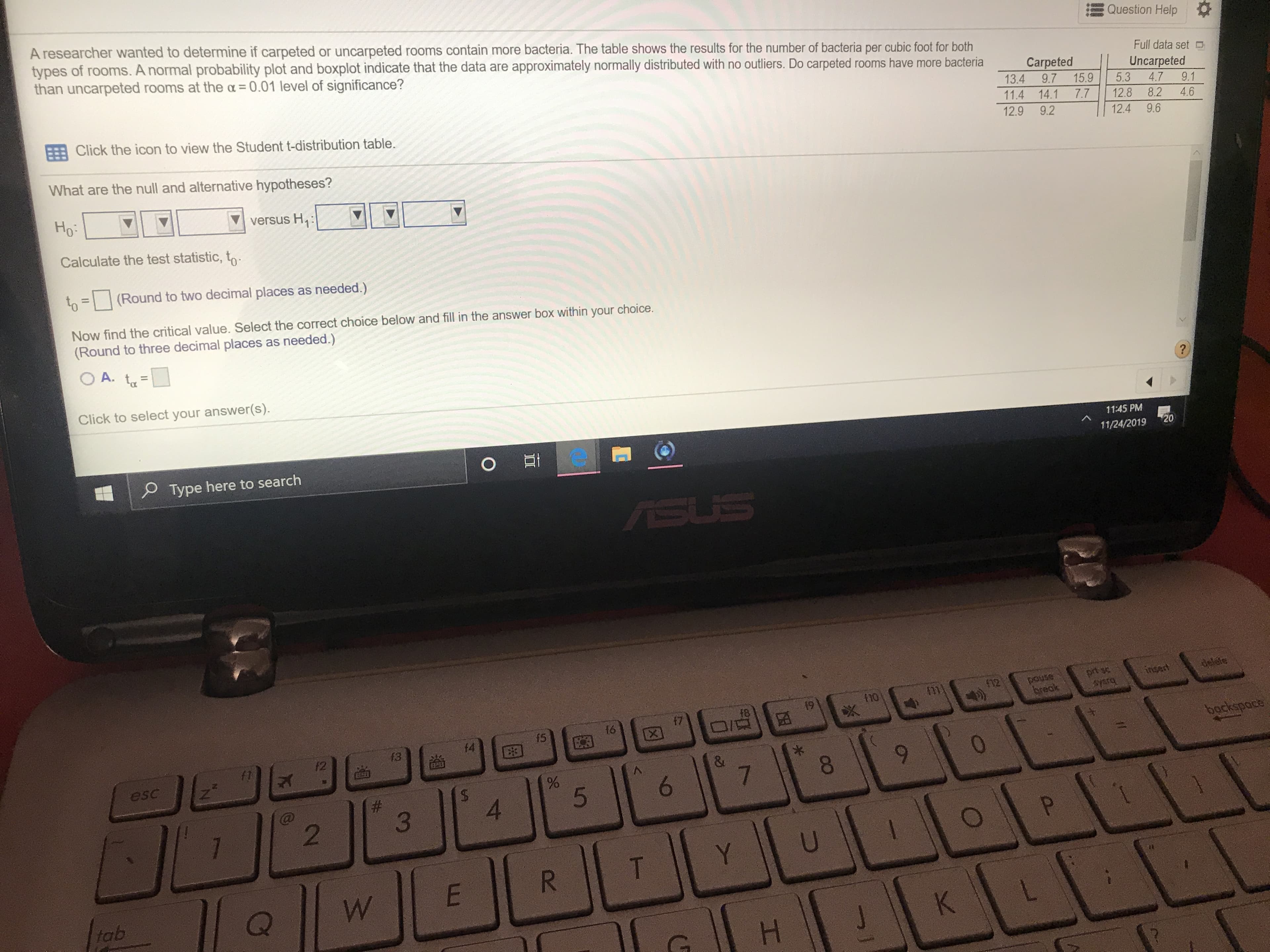
Transcribed Image Text:A researcher wanted to determine if carpeted or uncarpeted rooms contain more bacteria. The table shows the results for the number of bacteria per cubic foot for both
types of rooms. A normal probability plot and boxplot indicate that the data are approximately normally distributed with no outliers. Do carpeted rooms have more bacteria
than uncarpeted rooms at the a 0.01 level of significance?
Question Help
Full data set
Uncarpeted
5.3
Carpeted
13.4
9.7
11.4 14.1
15.9
4.7
9.1
Click the icon to view the Student t-distribution table.
7.7
12.8
8.2
4.6
12.9
9.2
12.4
9.6
What are the null and alternative hypotheses?
Ho
versus H
Calculate the test statistic, to
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Now find the critical value. Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box within your choice.
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
OA. t
?
Click to select your answer(s).
11:45 PM
20
11/24/2019
O
Type here to search
ASUS
delete
pt sc
osnod
SETO
insert
12
0
break
19
f7
EX
f5
f4
backspace
f3
12
0
&
7
esc
$
4
#
3
2
P
U
Y
T
R
E
W
KLLL
Q
tab
G
J
CO
I
96
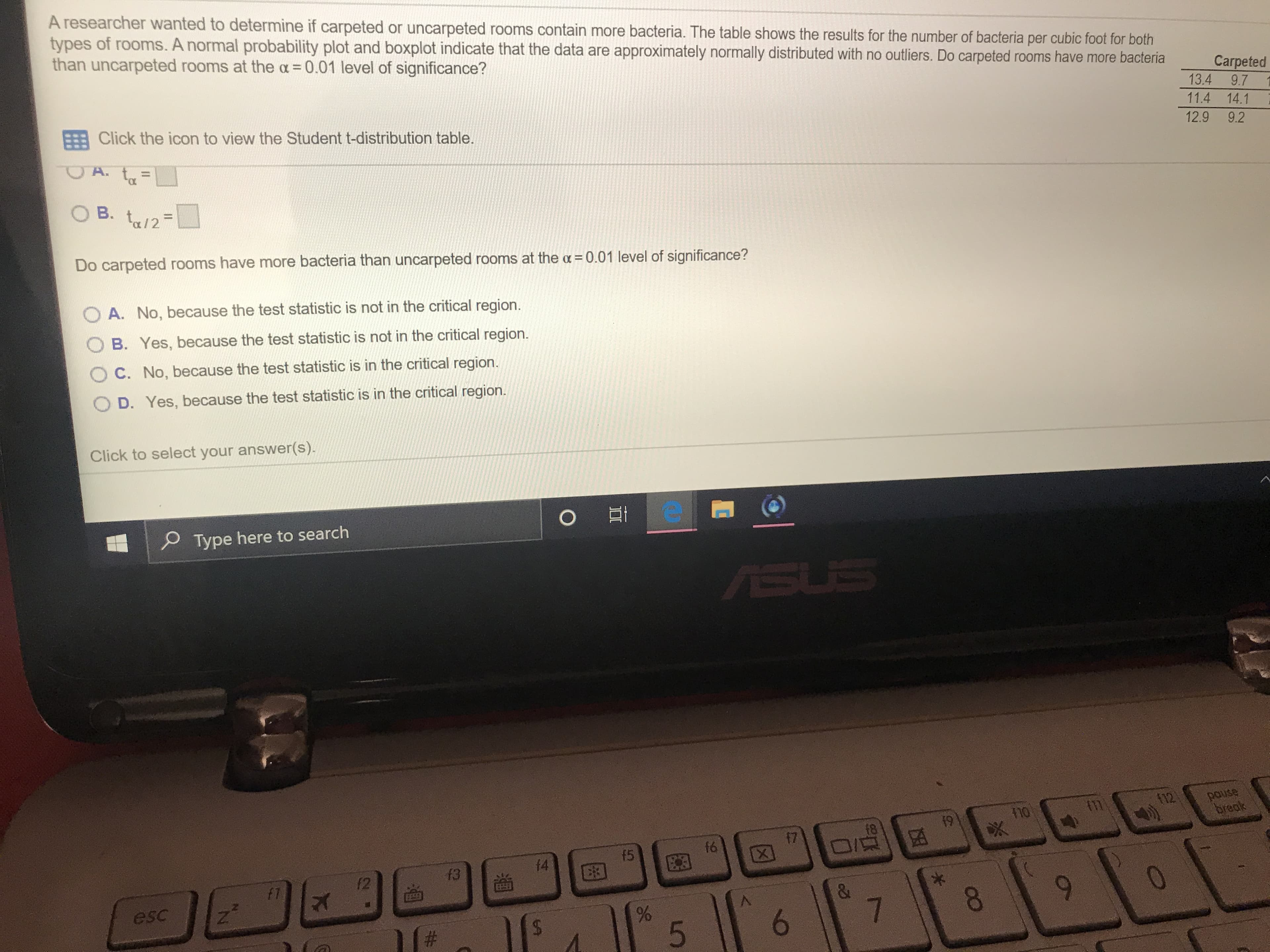
Transcribed Image Text:A researcher wanted to determine if carpeted or uncarpeted rooms contain more bacteria. The table shows the results for the number of bacteria per cubic foot for both
types of rooms. A normal probability plot and boxplot indicate that the data are approximately normally distributed with no outliers. Do carpeted rooms have more bacteria
than uncarpeted rooms at the a 0.01 level of significance?
Carpeted
13.4
9.7
11.4 14.1
FBClick the icon to view the Student t-distribution table.
12.9 9.2
A. t
B. t/2
Do carpeted rooms have more bacteria than uncarpeted rooms at the a = 0.01 level of significance?
A. No, because the test statistic is not in the critical region.
B. Yes, because the test statistic is not in the critical region.
O C. No, because the test statistic is in the critical region.
D. Yes, because the test statistic is in the critical region
answer(s).
Click to select your
O Et
Type here to search
SUS
pause
break
f12
m
19
f7
f6
D/
f5
f4
f3
f2
f7
&
esc
7
6
#
5
CO
SA
96
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill