a) What is the most likely explanation for the failure of bm12 mice to make a CD4 T cell response to bovine insulin? In a second set of experiments, T cells from wild-type (WT) or bm12 mice were mixed in vitro with antigen-presenting cells (APCs), in the presence or absence of the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB), and T cell proliferation was measured. The data from these experiments are shown in Figure Q6.30B. b) What is the explanation for the results in Rows 1–4 of the table? c) Why does the T cell response to SEB (Rows 5–8) show a different pattern than the response to bovine insulin?
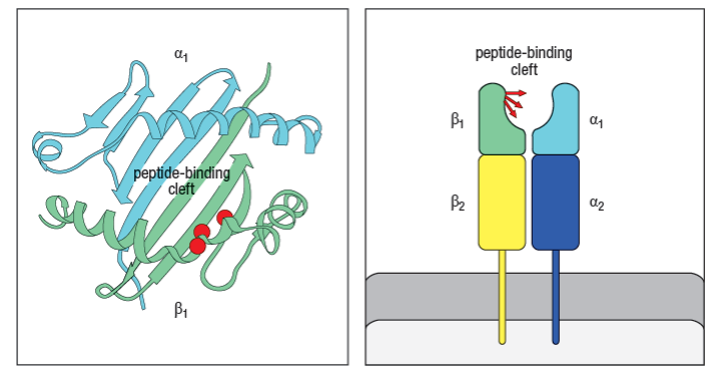
In the 1980s, a mutant strain of mice was identified, carrying amino acid changes in the MHC class II gene. This mutant strain was derived from C57Bl/6 mice, which carry the H-2b haplotype. Inbred H-2b mice express only one MHC class II protein, called Ab. The mutant strain, called ‘bm12’ was found to have 3 amino acid changes in the Ab protein, at positions 67, 70, and 71 of the Aβ chain. The positions of these amino acid changes on the MHC class II structure are shown below by the red circles in Figure Q6.30A. On the right, the side view diagram of MHC class II shows the direction of these three amino acid side chains.
Initial experiments with wild-type C57Bl/6 mice and bm12 mice showed that the wild-type mice made a robust CD4 T cell response after immunization with the insulin protein isolated from a cow; in contrast, the bm12 mice failed to make any detectable response to this foreign protein. Epitope mapping studies identified amino acid residues 1–14 of the bovine insulin A chain as the peptide recognized by CD4 T cells from wild-type mice.
a) What is the most likely explanation for the failure of bm12 mice to make a CD4 T cell response to bovine insulin?
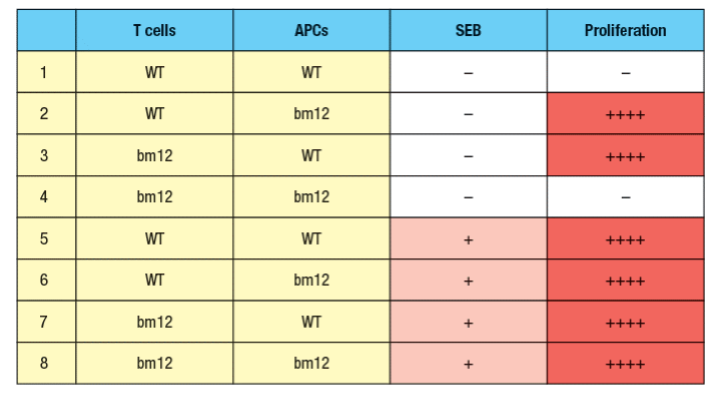
In a second set of experiments, T cells from wild-type (WT) or bm12 mice were mixed in vitro with antigen-presenting cells (APCs), in the presence or absence of the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB), and T cell proliferation was measured. The data from these experiments are shown in Figure Q6.30B.
b) What is the explanation for the results in Rows 1–4 of the table?
c) Why does the T cell response to SEB (Rows 5–8) show a different pattern than the response to bovine insulin?
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps






