Heating 9-alkylated 2-amino-6-chloropurine under acidic aqueous conditions gives 9-alkylated guanine. Provide a curly arrow mechanism for this transformation. CI 1) HCl in H2O (рH ~ 1) reflux HN' H2N 2) neutralisation H2N
Heating 9-alkylated 2-amino-6-chloropurine under acidic aqueous conditions gives 9-alkylated guanine. Provide a curly arrow mechanism for this transformation. CI 1) HCl in H2O (рH ~ 1) reflux HN' H2N 2) neutralisation H2N
Chapter21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions
Section21.SE: Something Extra
Problem 57AP
Related questions
Question
Please answer all parts
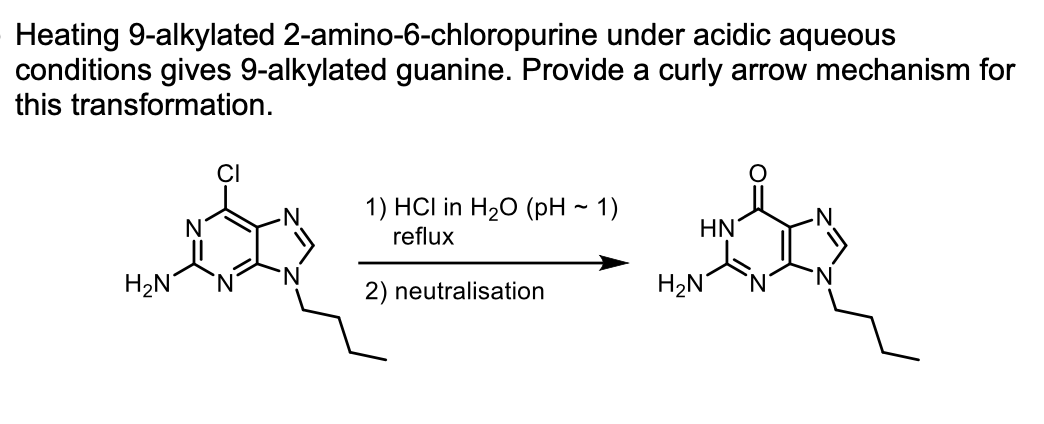
Transcribed Image Text:Heating 9-alkylated 2-amino-6-chloropurine under acidic aqueous
conditions gives 9-alkylated guanine. Provide a curly arrow mechanism for
this transformation.
1) HCl in H20 (pH ~ 1)
reflux
HN
H2N
2) neutralisation
H2N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning