
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
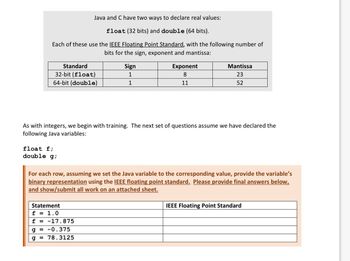
Transcribed Image Text:Java and C have two ways to declare real values:
float (32 bits) and double (64 bits).
Each of these use the IEEE Floating Point Standard, with the following number of
bits for the sign, exponent and mantissa:
Standard
32-bit (float)
64-bit (double)
float f;
double g;
Sign
1
1
Exponent
8
11
As with integers, we begin with training. The next set of questions assume we have declared the
following Java variables:
Statement
f = 1.0
f = -17.875
g= -0.375
g= 78.3125
Mantissa
23
52
For each row, assuming we set the Java variable to the corresponding value, provide the variable's
binary representation using the IEEE floating point standard. Please provide final answers below,
and show/submit all work on an attached sheet.
IEEE Floating Point Standard
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Introduction
The IEEE floating-point standard is a widely adopted set of rules and formats for representing real numbers in binary form within digital computer systems. It defines the structure of floating-point numbers, specifying the allocation of bits for the sign, exponent, and mantissa, ensuring consistency and interoperability in numerical computations across different hardware and programming languages.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Given three floating-point numbers x, y, and z, output x to the power of z, x to the power of (y to the power of z), the absolute value of (x minus y), and the square root of (x to the power of z). Output each floating-point value with two digits after the decimal point, which can be achieved as follows: {your_value2:.2f} {your_value3:.2f} {your_value4:.2f}') print (f'{your_value1:.2f} Ex: If the input is: 5.0 1.5 3.2 Then the output is: 172.47 361.66 3.50 13.13 461710 3116374.qx3zqy7 LAB ACTIVITY 2.14.1: LAB: Using math functions 1 import math 2 111 Type your code here. main.py 0/10 Load default template...arrow_forward..5-- I have a python programing question In 1937, a German mathematician named Lothar Collatz formulated an intriguing hypothesis (it still remains unproven) which can be described in the following way: 1. take any non-negative and non-zero integer number and name it c0; 2. if it's even, evaluate a new c0 as c0 ÷ 2; 3. otherwise, if it's odd, evaluate a new c0 as 3 × c0 + 1; 4. if c0 ≠ 1, skip to point 2. The hypothesis says that regardless of the initial value of c0, it will always go to 1. Of course, it's an extremely complex task to use a computer in order to prove the hypothesis for any natural number (it may even need artificial intelligence), but you can use Python to check some individual numbers. Maybe you'll even find the one which would disprove the hypothesis. Write a program which reads one natural number and executes the above steps as long as c0remains different from 1(c0 != 1). Moreover, we'll add another task - we want you to count the steps needed to achieve the goal.…arrow_forwardHELP NEEDED ASAP! Language: JAVA The following code sequence is supposed to compare a float and a double with the same value and output that they are equal. What is wrong with the following code sequence? Why is it not showing the correct answer? Write your code to fix the problem. float piF = 3.141592653589793f; double piD = 3.141592653589793; if(piF == piD) System.out.println("piF and piD are equal"); else System.out.println("piF and piD are not equal");arrow_forward
- Solve this using JavaScriptarrow_forwardn this lab, you complete a prewritten Python program for a carpenter who creates personalized house signs. The program is supposed to compute the price of any sign a customer orders, based on the following facts: The charge for all signs is a minimum of $35.00. The first five letters or numbers are included in the minimum charge; there is a $4 charge for each additional character. If the sign is make of oak, add $20.00. No charge is added for pine. Black or white characters are included in the minimum charge; there is an additional $15 charge for gold-leaf lettering.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education