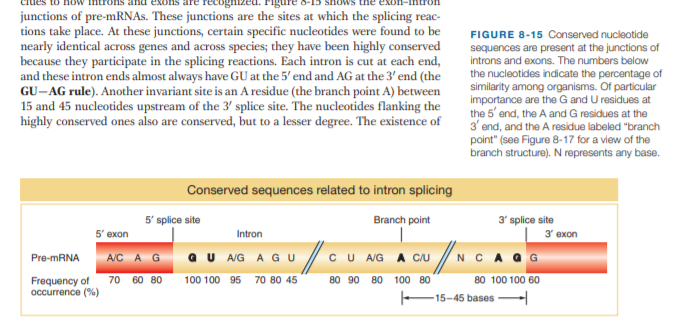
junctions of pre-mRNAs. These junctions are the sites at which the splicing reac- tions take place. At these junctions, certain specific nucleotides were found to be nearly identical across genes and across species; they have been highly conserved because they participate in the splicing reactions. Each intron is cut at each end, and these intron ends almost always have GU at the 5' end and AG at the 3' end (the GU-AG rule). Another invariant site is an A residue (the branch point A) between 15 and 45 nucleotides upstream of the 3' splice site. The nucleotides flanking the highly conserved ones also are conserved, but to a lesser degree. The existence of FIGURE 8-15 Conserved nucleotide sequences are present at the junctions of introns and exons. The numbers below the nucleotides indicate the percentage of similarity among organisms. Of particular importance are the G and U residues at the 5' and, the A and G residues at the 3' end, and the A residue labeled "branch point" (see Figure 8-17 for a view of the branch structure). N represents any base. Conserved sequences related to intron splicing 5' splice site Branch point 3' splice site 3' exon 5' еxon Intron A/C AG a U A/G A GU CU /G A CU NCA Q G Pre-MRNA Frequency of occurrence (%) 70 60 80 100 100 95 70 80 45 80 90 80 100 80 80 100 100 60 15-45 bases -
Gene Interactions
When the expression of a single trait is influenced by two or more different non-allelic genes, it is termed as genetic interaction. According to Mendel's law of inheritance, each gene functions in its own way and does not depend on the function of another gene, i.e., a single gene controls each of seven characteristics considered, but the complex contribution of many different genes determine many traits of an organism.
Gene Expression
Gene expression is a process by which the instructions present in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) are converted into useful molecules such as proteins, and functional messenger ribonucleic (mRNA) molecules in the case of non-protein-coding genes.
In Figure 8-15, what do you think would be the effect of
a G to A mutation in the first G residue of the intron?
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps




