
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
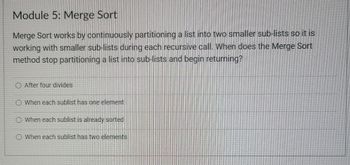
Transcribed Image Text:Module 5: Merge Sort
Merge Sort works by continuously partitioning a list into two smaller sub-lists so it is
working with smaller sub-lists during each recursive call. When does the Merge Sort
method stop partitioning a list into sub-lists and begin returning?
After four divides
When each sublist has one element
When each sublist is already sorted
When each sublist has two elements
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Apply the merge sort on the following list and sort the list in decreasing order: 91 98 29 93 98 53 68 33 33 47 You must show how the list is divided by the recursive calls to MERGE-SORT, then merged at each stage to obtain the final sorted list.arrow_forwardNeed help with standard ML languege I need to write a binarySearch function that recursively implements the binary search algorithm to search a sorted integer list for a specified integer and returns true if it is found, false otherwise. For example, binarySearch ([100,200,300,400,500], 200) returns true, whereas binarySearch([100,200,300,400,500], 299) returns false. Hint: Write a helper function mid that returns a tuple (index, value) representing the middle value in a list. For example, mid [10, 2, 40, 8, 22] returns (2,40) because the value 40 at index 2 is the middle value in the list. Similarly, mid [10, 20] would return (1, 20). Use mid in conjunction with slice to implement binarySearch.arrow_forwardThe list {118, 6, 43, 36, 25, 3, 26} after the first pass of Radix sort becomesarrow_forward
- (a) Write a method public static void insert(int[] a, int n, int x) that inserts x in order among the first n elements of a, assuming these elements are arranged in ascending order. Do NOT use arraylists. x is the last element in a. n does not include x. (b) Using the insert method from Part (a), write a recursive implementation of Insertion Sort.arrow_forwardint [] list = {18,57,8,89,7} and the length = 5 Sort the array using insertion sort algorithm. Fill out the trace table public class InsertionSort { /** The method for sorting the numbers */ public static void insertionSort(int[] list) { for (int i = 1; i < list.length; i++) { /** insert list[i] into a sorted sublist list[0..i-1] so that list[0..i] is sorted. */ int currentElement = list[i]; int k; for (k = i - 1; k >= 0 && list[k] > currentElement; k--) { list[k + 1] = list[k]; } // Insert the current element into list[k+1] list[k + 1] = currentElement; } } /** A test method */ public static void main(String[] args) { int[] list = {18,57,8,89,7}; insertionSort(list); for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) System.out.print(list[i] + " "); } }arrow_forwardImplement the following two sorting algorithms in a program called p3.py. Write two separate functions for these algorithms. Both functions must take a list of integers as the input parameter.1) Bogosort: first shuffle the list argument (i.e., randomize the positions of every element) and then check to see if the result is in sorted order. If it is, the algorithm terminates successfully and returns True, but if it is not then the process must be repeated.2) Bozosort: choose two elements in the list at random, swap them, and then check if the result is in sorted order. If it is, the algorithm terminates successfully and returns True, but if it is not then the process must be repeated.Write a main() function and call both sorting functions using the same list as their arguments. The list can be of any size (try a small list first). Does any of your algorithms terminate? If yes, count the number of iterations it uses to sort the list. Does it always use the same number of repetitions? If…arrow_forward
- **Cenaage Python** Question: A sequential search of a sorted list can halt when the target is less than a given element in the list. Modify the program to stop when the target becomes less than the current value being compared. In a sorted list, this would indicate that the target is not in the list and searching the remaining values is unnecessary. CODE: def sequentialSearch(target, lyst): """Returns the position of the target item if found, or -1 otherwise. The lyst is assumed to be sorted in ascending order.""" position = 0 while position < len(lyst): if target == lyst[position]: return position position += 1 return -1 def main(): """Tests with three lists.""" print(sequentialSearch(3, [0, 1, 2, 3, 4])) print(sequentialSearch(3, [0, 1, 2])) # Should stop at second position. print(sequentialSearch(3, [0, 4, 5, 6])) if __name__ == "__main__": main()arrow_forwardPerform the following operations utilizing c++ code.N.b array size to be used is ten.a)enqueue() i.e enqueue the list; Two,three,four,five,six,seven and eight and after display enqued list.b)dequeue() i.e delete or remove any two elements in the queue in a) above and after display the updated queue after deletion.c)ISfull() i.e Display if the queue is Full or not.d)Isempty() i.e Display if the queue is Empty or not.e)print() i.e print the final list of the elements of the Queue after performing tasks of a) - d).arrow_forwardThe optimised bubble sort offers none of the following benefits over conventional sorts for items that have already been sorted.arrow_forward
- Create three problem instances of size n is around 10, representing the best-case, worst-case and average-case for Radix Sort respectively. Show how the Radix Sort works on the best-case, and explain why each of them represents the best-case, worst-case and average-case respectively. psudocode for Radixsort attachedarrow_forwardLab 16 Implementing bubble sort In this lab, you will implement the bubble sort algorithm. The bubble sort is so called because it compares adjacent items, "bubbling" the smaller one up toward the beginning of the array. By comparing all pairs of adjacent items starting at the end of the array, the smallest item is guaranteed to reach the beginning of the array at the end of the first pass.The second pass begins again at the end of the array, ultimately placing the second smallest item in the second position. During the second pass, there is no need to compare the first and second items, because the smallest element is guaranteed to be in the first position.Bubble sort takes at most n - 1 passes for an array of n items. During the first pass, n - 1 pairs need to be compared. During the second pass, n - 2 pairs need to be compared. During the ith pass, n - i pairs need to be compared. During the last pass, n - (n - 1) or one pair needs to be compared. If, during any pass, no two…arrow_forwardA merge sort is used to sort an array of 1000 test scores in descending order. Which of the following statements is true?a) The sort is fastest if the original test scores are sorted from smallest to largestb) The sort is fastest if the original test scores are in completely sorted order.c) The sort is fastest if the original test scores are sorted from largest to smallest.d) The sort is the same, no matter what the order of the original elements.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education