Mutations can be classified as small-scale or large-scale, depending on the number of nucleotides involved in the mutation. Small-scale mutations involve a change in a small number of nucleotides (usually one to three nucleotides) within a single gene. Large-scale mutations, sometimes called chromosomal mutations, involve changes in large sections of chromosomes. Determine whether each of the following small-scale mutations is a point mutation, insertion mutation, or deletion mutation. a) The sequence of nucleotides in part of a gene is changed from CCGATG to CCGGATG. insertion mutation b) The sequence of nucleotides in part of a gene is changed from CCGATG to CCGAGG. point mutation c) The sequence of nucleotides in part of a gene is changed from CCGGAG to CTGGAG. point mutation d) The sequence of nucleotides in part of a gene is changed from CCGATG to CCGACTG. insertion mutation e) The sequence of nucleotides in part of a gene is changed from CCAGATG to CCGATG. deletion mutation
Mutations can be classified as small-scale or large-scale, depending on the number of nucleotides involved in the mutation. Small-scale mutations involve a change in a small number of nucleotides (usually one to three nucleotides) within a single gene. Large-scale mutations, sometimes called chromosomal mutations, involve changes in large sections of chromosomes. Determine whether each of the following small-scale mutations is a point mutation, insertion mutation, or deletion mutation. a) The sequence of nucleotides in part of a gene is changed from CCGATG to CCGGATG. insertion mutation b) The sequence of nucleotides in part of a gene is changed from CCGATG to CCGAGG. point mutation c) The sequence of nucleotides in part of a gene is changed from CCGGAG to CTGGAG. point mutation d) The sequence of nucleotides in part of a gene is changed from CCGATG to CCGACTG. insertion mutation e) The sequence of nucleotides in part of a gene is changed from CCAGATG to CCGATG. deletion mutation
Biology 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Chapter14: Dna Structure And Function
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 34CTQ: Quinolone antibiotics treat bacterial infections by blocking the activity of topoisomerase. Why does...
Related questions
Question
100%
I need help because i don't understand my homework
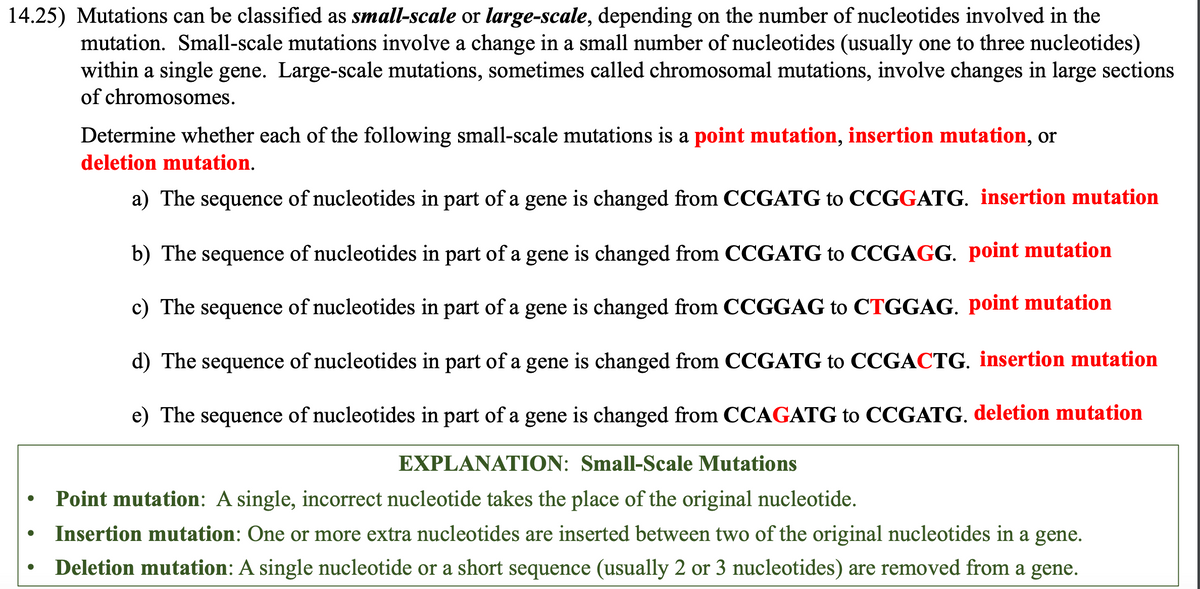
Transcribed Image Text:14.25) Mutations can be classified as small-scale or large-scale, depending on the number of nucleotides involved in the
mutation. Small-scale mutations involve a change in a small number of nucleotides (usually one to three nucleotides)
within a single gene. Large-scale mutations, sometimes called chromosomal mutations, involve changes in large sections
of chromosomes.
Determine whether each of the following small-scale mutations is a point mutation, insertion mutation, or
deletion mutation.
a) The sequence of nucleotides in part of a gene is changed from CCGATG to CCGGATG. insertion mutation
b) The sequence of nucleotides in part of a gene is changed from CCGATG to CCGAGG. point mutation
c) The sequence of nucleotides in part of a gene is changed from CCGGAG to CTGGAG. point mutation
d) The sequence of nucleotides in part of a gene is changed from CCGATG to CCGACTG. insertion mutation
e) The sequence of nucleotides in part of a gene is changed from CCAGATG to CCGATG. deletion mutation
EXPLANATION: Small-Scale Mutations
Point mutation: A single, incorrect nucleotide takes the place of the original nucleotide.
Insertion mutation: One or more extra nucleotides are inserted between two of the original nucleotides in a gene.
Deletion mutation: A single nucleotide or a short sequence (usually 2 or 3 nucleotides) are removed from a gene.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax