On the following graph, use the green point (triangle symbol) to plot the annual total revenue when the market price is $50, $75, $100, $125, $150, $175, and $200 per bike. 3180 2940 Tal Revn 2700 2460 2220 1980 1740 1500 A 1260+ O 5 so 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250 275 300 PRICE (Dallars per bika) According to the midpoint method, the price elasticity of demand between points A and B is approximately Suppose the price of bikes is currently $125 per bike, shown as point A on the Inital graph. Because the demand between points A and B is a $25-per-bike decrease in price will lead to v in total revenue per day. In general, In order for a price increase to cause an increase in total revenue, demand must be TOTAL REVENUE (Dalars)
On the following graph, use the green point (triangle symbol) to plot the annual total revenue when the market price is $50, $75, $100, $125, $150, $175, and $200 per bike. 3180 2940 Tal Revn 2700 2460 2220 1980 1740 1500 A 1260+ O 5 so 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250 275 300 PRICE (Dallars per bika) According to the midpoint method, the price elasticity of demand between points A and B is approximately Suppose the price of bikes is currently $125 per bike, shown as point A on the Inital graph. Because the demand between points A and B is a $25-per-bike decrease in price will lead to v in total revenue per day. In general, In order for a price increase to cause an increase in total revenue, demand must be TOTAL REVENUE (Dalars)
Chapter6: Elasticities
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13P: A movie production company faces a linear demand curve for its film, and it seeks to maximize total...
Related questions
Question
Graph and solve attachments:
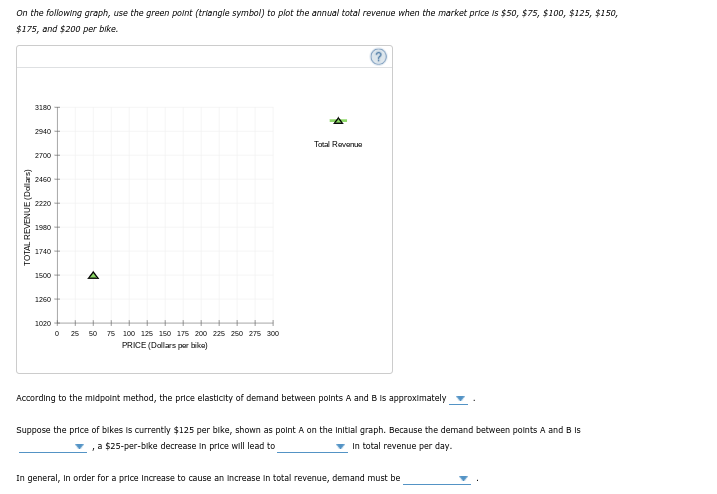
Transcribed Image Text:On the following graph, use the green polnt (triangle symbol) to plot the annual total revenue when the market price is $50, $75, $100, $125, $150,
$175, and $200 per bike.
3180
2940
Tatal Revane
2700
2460
2220
1980
1740
1500
A
1260
1020
++
25 50
75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250 275 300
PRICE (Dallars par bika)
According to the midpolnt method, the price elasticity of demand between polnts A and B Is approximately
Suppose the price of bikes is currently $125 per bike, shown as polnt A on the Initial graph. Because the demand between polnts A and B Is
a $25-per-bike decrease In price will lead to
In total revenue per day.
In general, In order for a price Increase to cause an Increase In total revenue, demand must be
TOTAL REVENUE (Dallars)
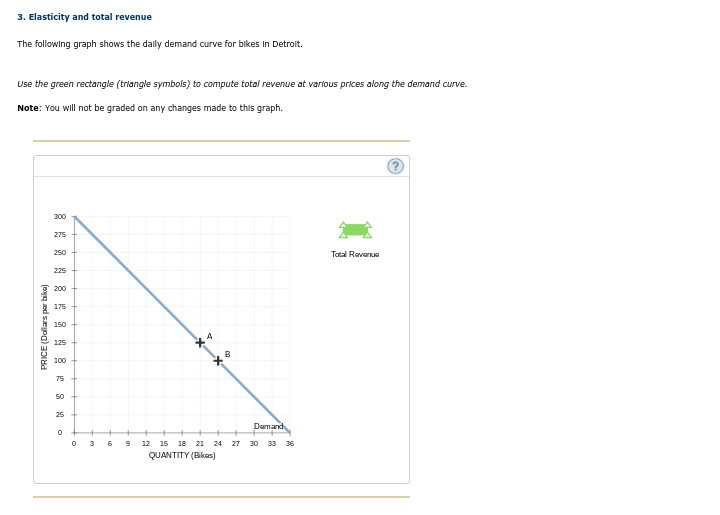
Transcribed Image Text:3. Elasticity and total revenue
The following graph shows the dally demand curve for bikes In Detrolt.
Use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to compute total revenue at various prices along the demand curve.
Note: You will not be graded on any changes made to this graph.
300
275
250
Tatal Revenu
225
200
175
150
125
*4
100
75
50 +
25
Damand
3
6
12
15 18
21
24
27
30 33
36
QUANTITY (Bikas)
PRICE (Dallars par bike)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506893
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506893
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
