Pharmaceutical Benefits Managers (PBMs) are intermediaries between upstream drug manufacturers and downstream insurance companies. They design formularies (lists of drugs that insurance will cover) and negotiate prices with drug companies. PBMs want a wider variety of drugs available te their insured populations, but at low prices. Suppose that a PBM is negotiating with the makers of two nondrowsy allergy drugs, Claritin and Allegra, for inclusion on the formulary. The "value" or "surplus" created by including one nondrowsy allergy drug on the formulary is $228 million, but the value of adding a second drug is only $68 million. Assume the PBM bargains by telling each drug company that it's going to reach an agreement with the other drug company. Under the non-strategic view of bargaining, the PBM would earn a surplus of of s million, while each drug company would m million. Now sunnos
Pharmaceutical Benefits Managers (PBMs) are intermediaries between upstream drug manufacturers and downstream insurance companies. They design formularies (lists of drugs that insurance will cover) and negotiate prices with drug companies. PBMs want a wider variety of drugs available te their insured populations, but at low prices. Suppose that a PBM is negotiating with the makers of two nondrowsy allergy drugs, Claritin and Allegra, for inclusion on the formulary. The "value" or "surplus" created by including one nondrowsy allergy drug on the formulary is $228 million, but the value of adding a second drug is only $68 million. Assume the PBM bargains by telling each drug company that it's going to reach an agreement with the other drug company. Under the non-strategic view of bargaining, the PBM would earn a surplus of of s million, while each drug company would m million. Now sunnos
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
5th Edition
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Chapter16: Bargaining
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 16.6IP
Related questions
Question
100%
Please Solve In 15mins
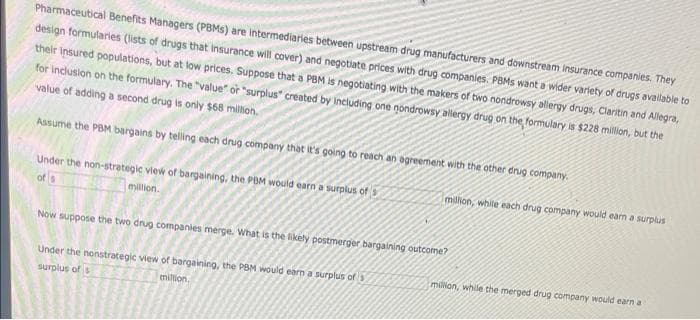
Transcribed Image Text:Pharmaceutical Benefits Managers (PBMS) are intermediaries between upstream drug manufacturers and downstream insurance companies. They
design formularies (lists of drugs that insurance will cover) and negotiate prices with drug companies. PBMs want a wider variety of drugs available to
their insured populations, but at low prices. Suppose that a PBM is negotiating with the makers of two nondrowsy allergy drugs, Claritin and Allegra,
for inclusion on the formulary. The "value" or "surplus" created by including one nondrowsy allergy drug on the formulary is $228 million, but the
value of adding a second drug is only $68 million.
Assume the PBM bargains by telling each drug company that it's going to reach an agreement with the other drug company.
million, white each drug company would earn a surplus
Under the non-strategic view of bargaining, the PBM would earn a surplus of
of s
million.
Now suppose the two drug companies merge. What is the likely postmerger bargaining outcome?
Under the nonstrategic view of bargaining, the PBM would earn a surplus of 3
million, while the merged drug company would earn a
surplus of s
million,
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
