phosphate. Contrast the properties of hexokinases I and IV with respect to oligomeric structure, mech- anism of regulation of their activity, Kè value, and dependence of catalytic activity on cellular location. Hexokinase I is found in, for instance, muscle tissue. Property subunit structutre mechanism of regulation KM value cellular location hexokinase I/II hexokinase IV
phosphate. Contrast the properties of hexokinases I and IV with respect to oligomeric structure, mech- anism of regulation of their activity, Kè value, and dependence of catalytic activity on cellular location. Hexokinase I is found in, for instance, muscle tissue. Property subunit structutre mechanism of regulation KM value cellular location hexokinase I/II hexokinase IV
Biochemistry
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Chapter27: Metabolic Integration And Organ Specialization
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 18P
Related questions
Question
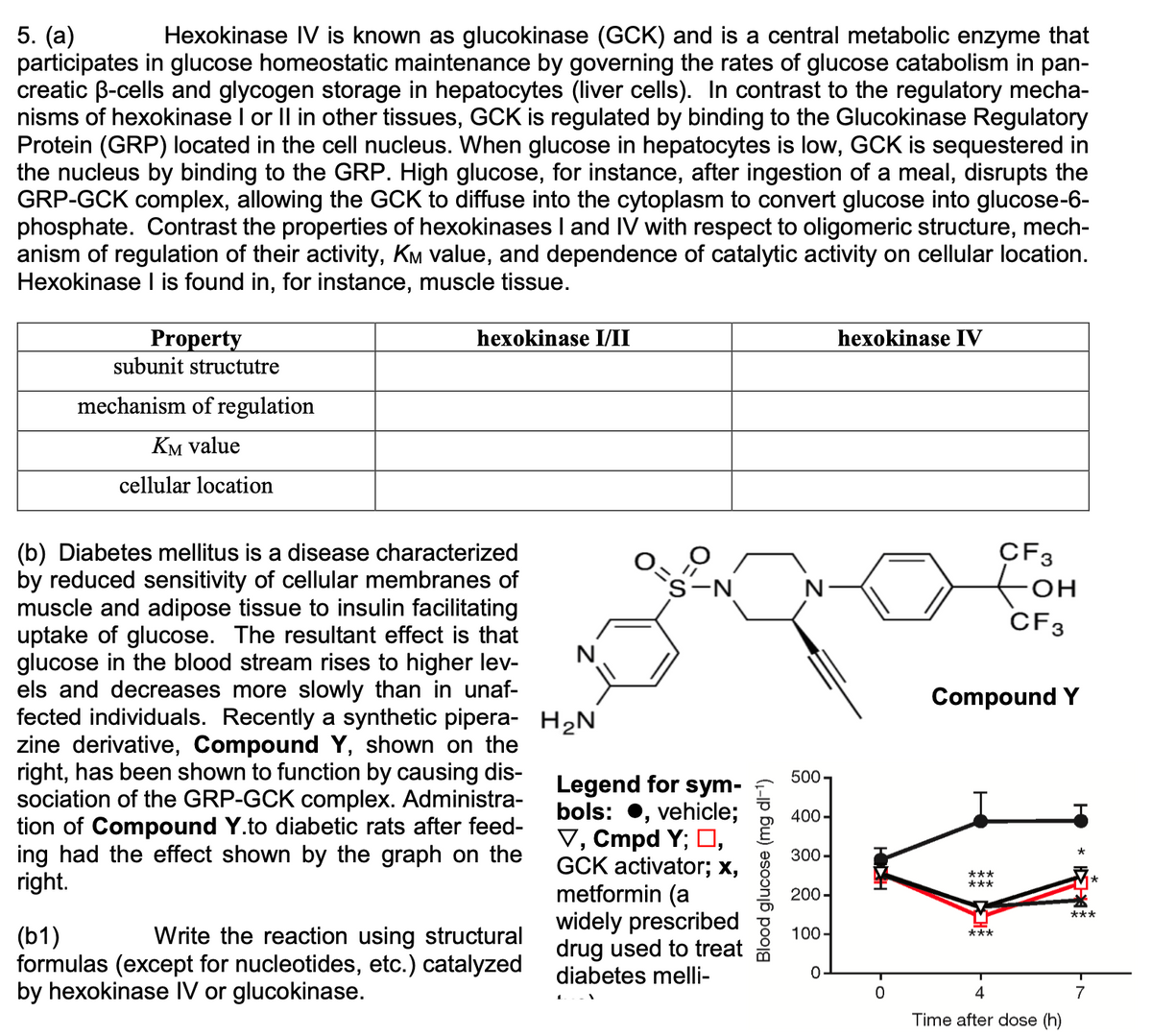
Transcribed Image Text:5. (а)
participates in glucose homeostatic maintenance by governing the rates of glucose catabolism in pan-
creatic B-cells and glycogen storage in hepatocytes (liver cells). In contrast to the regulatory mecha-
nisms of hexokinase I or Il in other tissues, GCK is regulated by binding to the Glucokinase Regulatory
Protein (GRP) located in the cell nucleus. When glucose in hepatocytes is low, GCK is sequestered in
the nucleus by binding to the GRP. High glucose, for instance, after ingestion of a meal, disrupts the
GRP-GCK complex, allowing the GCK to diffuse into the cytoplasm to convert glucose into glucose-6-
phosphate. Contrast the properties of hexokinases I and IV with respect to oligomeric structure, mech-
anism of regulation of their activity, KM value, and dependence of catalytic activity on cellular location.
Hexokinase I is found in, for instance, muscle tissue.
Hexokinase IV is known as glucokinase (GCK) and is a central metabolic enzyme that
Property
subunit structutre
hexokinase I/II
hexokinase IV
mechanism of regulation
KM value
cellular location
CF3
(b) Diabetes mellitus is a disease characterized
by reduced sensitivity of cellular membranes of
muscle and adipose tissue to insulin facilitating
uptake of glucose. The resultant effect is that
glucose in the blood stream rises to higher lev-
els and decreases more slowly than in unaf-
fected individuals. Recently a synthetic pipera- H2N
zine derivative, Compound Y, shown on the
right, has been shown to function by causing dis-
sociation of the GRP-GCK complex. Administra-
tion of Compound Y.to diabetic rats after feed-
ing had the effect shown by the graph on the
right.
to
`s-N
CF3
Compound Y
500-
Legend for sym-
bols: •, vehicle;
V, Cmpd Y; D,
GCK activator; x,
metformin (a
widely prescribed
drug used to treat
diabetes melli-
400-
300-
***
***
200-
***
(b1)
formulas (except for nucleotides, etc.) catalyzed
by hexokinase IV or glucokinase.
Write the reaction using structural
100-
***
4
Time after dose (h)
Blood glucose (mg dl-1)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax