Problem 8: The following load elongation data were recorded during the tensile testing of a copper bar measuring 0.505 in. (0.0128 m) in diameter, with a gauge length of 2 in. (0.0508 m). d. What is the percentage elongation at fracture? e. Calculate true stress-true strain values up to onset of necking.
Problem 8: The following load elongation data were recorded during the tensile testing of a copper bar measuring 0.505 in. (0.0128 m) in diameter, with a gauge length of 2 in. (0.0508 m). d. What is the percentage elongation at fracture? e. Calculate true stress-true strain values up to onset of necking.
Materials Science And Engineering Properties
1st Edition
ISBN:9781111988609
Author:Charles Gilmore
Publisher:Charles Gilmore
Chapter6: Introduction To Mechanical Properties
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6.2P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Problem 8: The following load elongation data were recorded during the tensile
testing of a copper bar measuring 0.505 in. (0.0128 m) in diameter, with a gauge
length of 2 in. (0.0508 m).
d. What is the percentage elongation at fracture?
e. Calculate true stress-true strain values up to onset of necking.
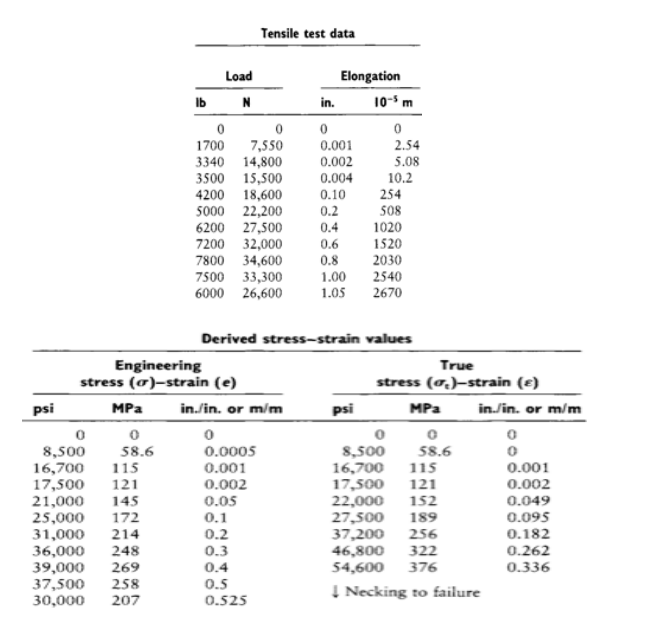
Transcribed Image Text:Tensile test data
Load
Elongation
Ib N
in.
10- m
7,550
3340 14,800
3500 15,500
4200 18,600
2.54
5.08
10.2
1700
0.001
0.002
0.004
0.10
254
5000 22,200
6200 27,500
7200 32,000
7800 34,600
7500 33,300
6000 26,600
0.2
508
1020
1520
0.4
0.6
0.8
2030
1.00
2540
1.05
2670
Derived stress-strain values
True
Engineering
stress (o)-strain (e)
stress (7,)-strain (e)
psi
MPa
in./in. or m/m
psi
MPa
in./in. or m/m
8,500
16,700
17,500
21,000
25,000
31,000
36,000
39,000
37,500
30,000
58.6
0.0005
0.001
8,500
16,700
17,500
22,000
27,500
37,200
46,800
54,600
58.6
115
115
0.001
121
0.002
121
0.002
152
145
172
0.05
0.049
0.1
0.2
189
256
322
0.095
214
248
0.182
0.262
0.3
269
258
0.4
376
0.336
0.5
0.525
I Necking to failure
207
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Materials Science And Engineering Properties
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781111988609
Author:
Charles Gilmore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337094740
Author:
Segui, William T.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Materials Science And Engineering Properties
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781111988609
Author:
Charles Gilmore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337094740
Author:
Segui, William T.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning