Protein Concept Map Add these terms to your concept map should include these concepts and details: Structure (functional groups, shape); Monomer; Linkage; Properties; Functions; Key terms from the Partial List of Key Terms from the Minds Partial List of Key Terms essential amino acid amino acid side group/R-group peptide bond polypeptide receptor neurotransmitter hormone secondary structure tertiary structure quaternary structure fair test hydrophobic hydrophilic intermolecular force of attraction
Protein Concept Map Add these terms to your concept map should include these concepts and details: Structure (functional groups, shape); Monomer; Linkage; Properties; Functions; Key terms from the Partial List of Key Terms from the Minds Partial List of Key Terms essential amino acid amino acid side group/R-group peptide bond polypeptide receptor neurotransmitter hormone secondary structure tertiary structure quaternary structure fair test hydrophobic hydrophilic intermolecular force of attraction
Chapter14: Nutrients That Promote Growth And Regulate Body Functions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem A2CR
Related questions
Question
Protein Concept Map
Add these terms to your concept map should include these concepts and details:
Structure (functional groups, shape);
Monomer;
Linkage;
Properties;
Functions;
Key terms from the Partial List of Key Terms from the Minds
Partial List of Key Terms
essential amino acid
amino acid
side group/R-group
peptide bond
polypeptide
receptor
neurotransmitter
hormone
secondary structure
tertiary structure
quaternary structure
fair test
hydrophobic
hydrophilic
intermolecular force of attraction
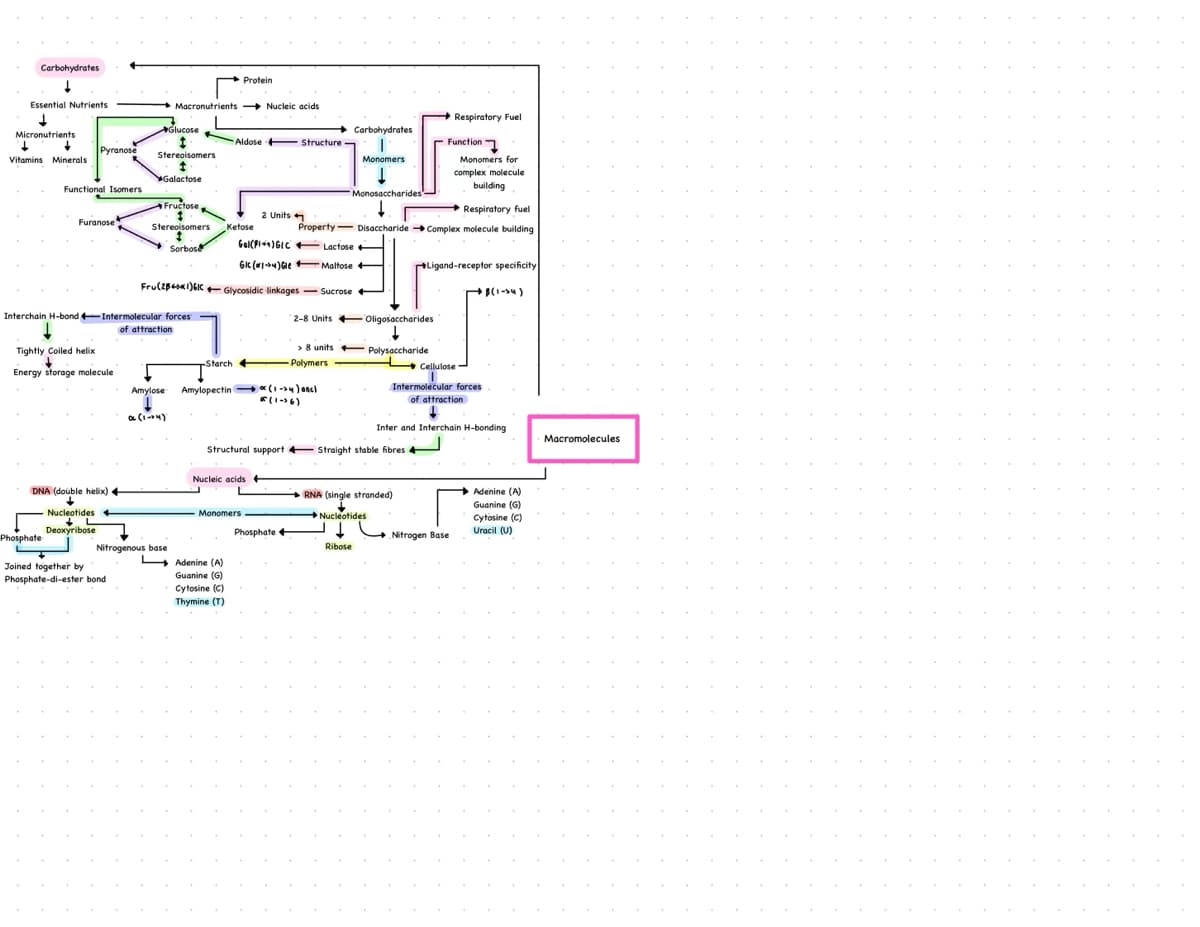
Transcribed Image Text:Carbohydrates
↓
Essential Nutrients
↓
Micronutrients
narrians
↓
↓
Vitamins Minerals
Pyranose
Functional Isomers
Furanose
Phosphate
Tightly Coiled helix
Energy storage molecule
DNA (double helix) +
Nucleotides +
L
Deoxyribose
Interchain H-bond+Intermolecular forces
Joined together by
Phosphate-di-ester bond
Glucose Aldose Structure-
t
Stereoisomers
Galactose
Fructose,
1
Stereoisomers
Macronutrients Nucleic acids
of attraction
↓
Amylose
I
Nitrogenous base
Sorbose
Protein
Ketose
Gal(PI)GIC
GIC (1) GleMaltose
Fru(2861)61+Glycosidic linkages - Sucrose
2-8 Units
Starch +
+
Monomers
Adenine (A)
Guanine (G)
Cytosine (C)
Thymine (T)
2 Units
Amylopectin*(1-34) oncl
Property Disaccharide
> 8 units
-Polymers
Carbohydrates
*(1-36)
Monomers
↓
Monosaccharides
Phosphate +
Lactose
Structural support Straight stable fibres 4
Nucleic acids +
Oligosaccharides
↓
Polysaccharide
→ Respiratory Fuel
RNA (single stranded)
Nucleotides
1
Ribose
Function
Monomers for
complex molecule
building
Respiratory fuel
Complex molecule building
Ligand-receptor specificity
·B(1-34)
Cellulose
Intermolecular forces
of attraction
↓
Inter and Interchain H-bonding
Nitrogen Base
Adenine (A)
Guanine (G)
Cytosine (C)
Uracil (U)
Macromolecules
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Health Safety And Nutrition F/Young Child
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:
9781305144767
Author:
MAROTZ
Publisher:
Cengage

Health Safety And Nutrition F/Young Child
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:
9781305144767
Author:
MAROTZ
Publisher:
Cengage