
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780133594140
Author: James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
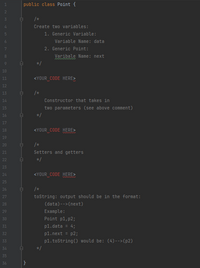
Transcribed Image Text:```java
public class Point {
/*
Create two variables:
1. Generic Variable:
Variable Name: data
2. Generic Point:
Variable Name: next
*/
<YOUR_CODE_HERE>
/*
Constructor that takes in
two parameters (see above comment)
*/
<YOUR_CODE_HERE>
/*
Setters and getters
*/
<YOUR_CODE_HERE>
/*
toString: output should be in the format:
(data) -->(next)
Example:
Point p1, p2;
p1.data = 4;
p1.next = p2;
p1.toString() would be: (4)-->(p2)
*/
}
```
### Explanation:
This code snippet outlines a skeletal structure for a Java class named `Point`. Here's a breakdown of the sections specified in the class:
1. **Generic Variables:**
- **data:** A variable that stores a value.
- **next:** A reference that points to another `Point` object, establishing a generic connection between objects.
2. **Constructor:**
- This section should define a constructor that initializes the `data` and `next` variables using parameters.
3. **Setters and Getters:**
- Methods for accessing and modifying the private variables `data` and `next`.
4. **toString Method:**
- This method should return a string representation of the `Point` object in the format `(data) --> (next)`. In the provided example, if `Point p1` has `data` set to 4 and `next` pointing to `p2`, then `p1.toString()` would return `(4)-->(p2)`.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- #include <iostream>using namespace std;class Player{private:int id;static int next_id;public:int getID() { return id; }Player() { id = next_id++; }};int Player::next_id = 1;int main(){Player p1;Player p2;Player p3;cout << p1.getID() << " ";cout << p2.getID() << " ";cout << p3.getID();return 0;} Run the program and give its output.arrow_forwardin c++ Define a class named “Variable” that manages a variable name (string)and a description (string). It should not provide the default constructor.The class must at least provide the following methods:- toString() method that can return a string in the following format: VAR(<var-name>) DESC(<var-desc>) such as VAR(isSuccessful) DESC(successful flag indicator)- contains() that accepts a search string and it will return true if its variablename or the description contains that string (case-insensitive) and false otherwise.Show how this class being used to create objects and call all its methods and showhow they work.arrow_forward#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Player{private:int id;static int next_id;public:int getID() { return id; }Player() { id = next_id++; }};int Player::next_id = 1;int main(){Player p1;Player p2;Player p3;cout << p1.getID() << " ";cout << p2.getID() << " ";cout << p3.getID();return 0;} Run the program and give its output.arrow_forward
- C:/Users/r1821655/CLionProjects/untitled/sequence.cpp:48:5: error: return type specification for constructor invalidtemplate <class Item>class sequence{public:// TYPEDEFS and MEMBER SP2020typedef Item value_type;typedef std::size_t size_type;static const size_type CAPACITY = 10;// CONSTRUCTORsequence();// MODIFICATION MEMBER FUNCTIONSvoid start();void end();void advance();void move_back();void add(const value_type& entry);void remove_current();// CONSTANT MEMBER FUNCTIONSsize_type size() const;bool is_item() const;value_type current() const;private:value_type data[CAPACITY];size_type used;size_type current_index;};} 48 | void sequence<Item>::sequence() : used(0), current_index(0) { } | ^~~~ line 47 template<class Item> line 48 void sequence<Item>::sequence() : used(0), current_index(0) { }arrow_forward#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Player{private:int id;static int next_id;public:int getID() { return id; }Player() { id = next_id++; }};int Player::next_id = 1;int main(){Player p1;Player p2;Player p3;cout << p1.getID() << " ";cout << p2.getID() << " ";cout << p3.getID();return 0;} Run the program and give its output.arrow_forwardclass IndexItem { public: virtual int count() = 0; virtual void display()= 0; };class Book : public IndexItem { private: string title; string author; public: Book(string title, string author): title(title), author(author){} virtual int count(){ return 1; } virtual void display(){ /* YOU DO NOT NEED TO IMPLEMENT THIS FUNCTION */ } };class Category: public IndexItem { private: /* fill in the private member variables for the Category class below */ ? int count; public: Category(string name, string code): name(name), code(code){} /* Implement the count function below. Consider the use of the function as depicted in main() */ ? /* Implement the add function which fills the category with contents below. Consider the use of the function as depicted in main() */ ? virtualvoiddisplay(){ /* YOU DO NOT NEED TO IMPLEMENT THIS FUNCTION */ } };arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science
Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning
Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education
Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY
Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780124077263
Author:David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337569330
Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337093422
Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133750423
Author:VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781119368830
Author:FITZGERALD
Publisher:WILEY