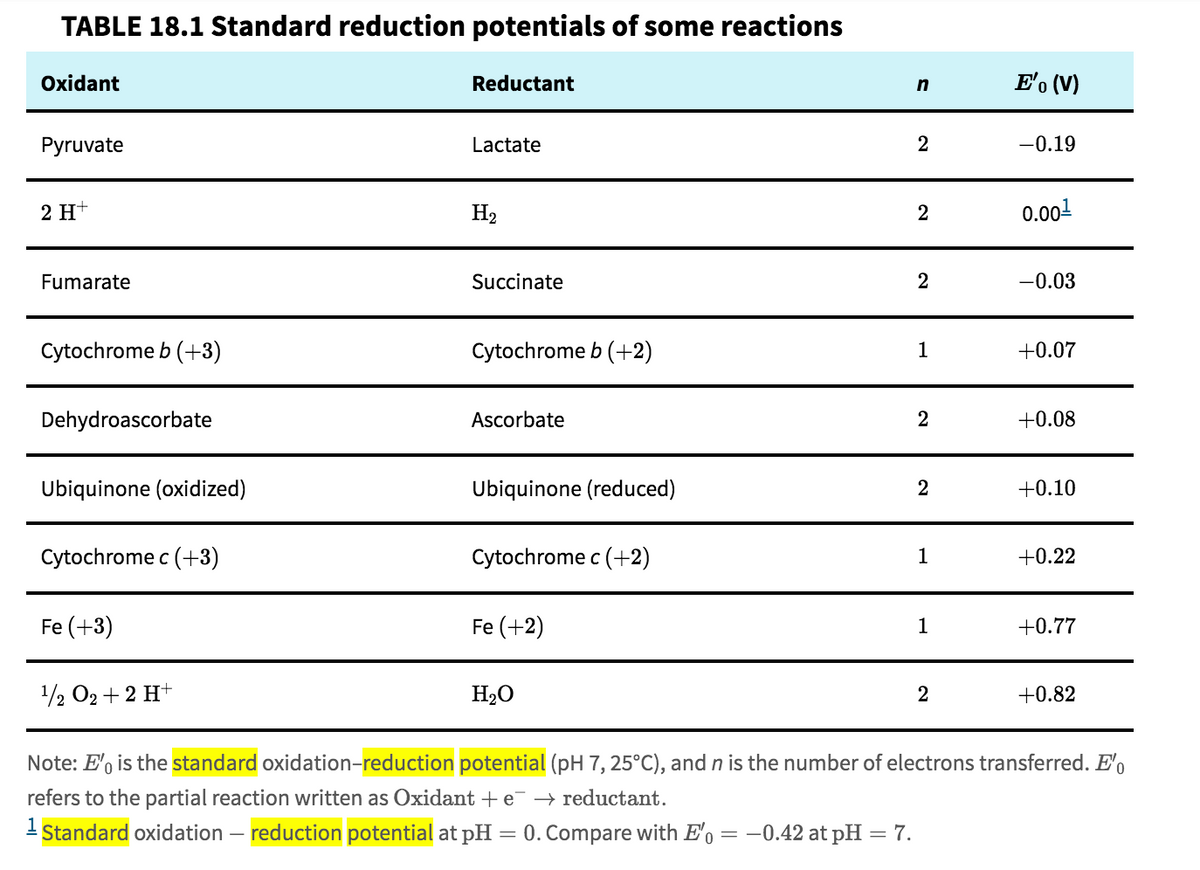
Question 1: The standard reduction potential for the the cytochrome c Fe3+/Fe2+ redox couple and for the dioxygen/water redox couple. Part a: Use these values, and the relevant equation, to compute the standard free energy change for the transfer of 4 electrons from cytochrome c to dioxygen. Part b: Next, compute the free energy needed to pump four protons across the mitochondrial membrane, using the relevant equation and values of -.14V for Δψ and 1.4 for ΔpH. Part c: If energy conservation by cytochrome c oxidase involved only the four pumped protons (and standard conditions applied), what would be the efficiency of energy conservation at this step? (what is the ratio [energy conserved in the gradient] / [redox energy used] ?)
Question 1: The standard reduction potential for the the cytochrome c Fe3+/Fe2+ redox couple and for the dioxygen/water redox couple.
Part a: Use these values, and the relevant equation, to compute the standard free energy change for the transfer of 4 electrons from cytochrome c to dioxygen.
Part b: Next, compute the free energy needed to pump four protons across the mitochondrial membrane, using the relevant equation and values of -.14V for Δψ and 1.4 for ΔpH.
Part c: If energy conservation by cytochrome c oxidase involved only the four pumped protons (and standard conditions applied), what would be the efficiency of energy conservation at this step? (what is the ratio [energy conserved in the gradient] / [redox energy used] ?)
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps


