TABLE 17.1 The Reactions of Glycolysis and Their Standard Free-Energy Changes AG* AG** Step k) mol- kcal mol- kJ mol- Reaction Enzyme 1 Glucose + ATP → Glucose-6-phosphate + ADP Hexokinase/Glucokinase -16.7 -4.0 -33,9 Glucose-6-phosphate → Fructose-6-phosphate Glucose phosphate isomerase +1.67 +0.4 -2.92 -3.4 Fructose-6-phosphate + ATP → Fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate + ADP Phosphofructokinase -14.2 -18.8 4 +5.7 Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate → Dihydroxyacetone phosphate + Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Aldolase +23.9 -0.23 +7.56 Dihydroxyacetone phosphate → Glyceraldehyde- 3-phosphate Triose phosphate isomerase +1.8 +2.41 2(Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate + NAD* + P, → 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate + NADH + H*) 2(-1.29) Glyceraldehyde-3-P dehydrogenase 2(+6.20) 2(+1.5) 7 2(+0.1) 2(1,3-bisphosphoglycerate + ADP → 3-Phosphoglycerate + ATP) Phosphoglycerate kinase 2(-18.8) 2(-4.5) 2(3-Phosphoglycerate → 2-Phosphoglycerate) Phosphoglyceromutase 2(+4.4) 2(+1.1) 2(+0.83) 2(2-Phosphoglycerate → Phosphoenolpyruvate + H,O) Enolase 2(+1.8) 2(+0.4) 2(+1.1) 10 2(Phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP → Ругuvate + ATP) Pyruvate kinase 2(-31.4) 2(-7.5) 2(-23.0) -73.3 2(-25.1) Overall -17.5 Glucose + 2ADP + 2P, + NAD+ → 2 Pyruvate 2ATP + NADH + H* 2(Pyruvate + NADH + H* →Lactate + NAD*) Glucose + 2ADP + 2P, →2 Lactate + 2ATP Lactate dehydrogenase -98.0 2(-6.0) -29.5 2(-14.8) -127.6 -123.5 AG" values are assumed to be the same at 25°Cand 37°C and are calculated for standard-state conditions (1 Mconcentration of reactants and products pH 7.0). AG values are calculated at 310 K (37°C) using steady-state concentrations of these metabolites found in erythrocytes.
TABLE 17.1 The Reactions of Glycolysis and Their Standard Free-Energy Changes AG* AG** Step k) mol- kcal mol- kJ mol- Reaction Enzyme 1 Glucose + ATP → Glucose-6-phosphate + ADP Hexokinase/Glucokinase -16.7 -4.0 -33,9 Glucose-6-phosphate → Fructose-6-phosphate Glucose phosphate isomerase +1.67 +0.4 -2.92 -3.4 Fructose-6-phosphate + ATP → Fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate + ADP Phosphofructokinase -14.2 -18.8 4 +5.7 Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate → Dihydroxyacetone phosphate + Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Aldolase +23.9 -0.23 +7.56 Dihydroxyacetone phosphate → Glyceraldehyde- 3-phosphate Triose phosphate isomerase +1.8 +2.41 2(Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate + NAD* + P, → 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate + NADH + H*) 2(-1.29) Glyceraldehyde-3-P dehydrogenase 2(+6.20) 2(+1.5) 7 2(+0.1) 2(1,3-bisphosphoglycerate + ADP → 3-Phosphoglycerate + ATP) Phosphoglycerate kinase 2(-18.8) 2(-4.5) 2(3-Phosphoglycerate → 2-Phosphoglycerate) Phosphoglyceromutase 2(+4.4) 2(+1.1) 2(+0.83) 2(2-Phosphoglycerate → Phosphoenolpyruvate + H,O) Enolase 2(+1.8) 2(+0.4) 2(+1.1) 10 2(Phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP → Ругuvate + ATP) Pyruvate kinase 2(-31.4) 2(-7.5) 2(-23.0) -73.3 2(-25.1) Overall -17.5 Glucose + 2ADP + 2P, + NAD+ → 2 Pyruvate 2ATP + NADH + H* 2(Pyruvate + NADH + H* →Lactate + NAD*) Glucose + 2ADP + 2P, →2 Lactate + 2ATP Lactate dehydrogenase -98.0 2(-6.0) -29.5 2(-14.8) -127.6 -123.5 AG" values are assumed to be the same at 25°Cand 37°C and are calculated for standard-state conditions (1 Mconcentration of reactants and products pH 7.0). AG values are calculated at 310 K (37°C) using steady-state concentrations of these metabolites found in erythrocytes.
Biochemistry
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Chapter27: Metabolic Integration And Organ Specialization
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20P: Figure 27.3 illustrates the response of R (ATP-regenerating) and U (ATP-utilizing) enzymes to energy...
Related questions
Question
According to Table 17.1, four reactions have positive ΔG values. How can this be explained?
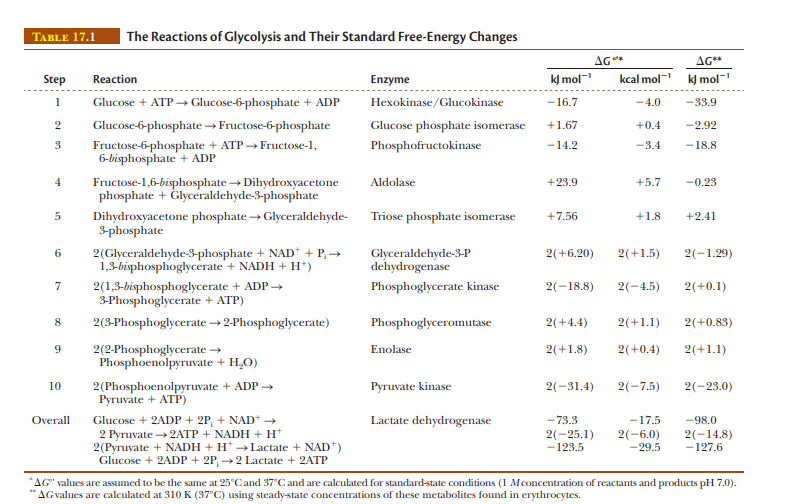
Transcribed Image Text:TABLE 17.1
The Reactions of Glycolysis and Their Standard Free-Energy Changes
AG*
AG**
Step
k) mol-
kcal mol- kJ mol-
Reaction
Enzyme
1
Glucose + ATP → Glucose-6-phosphate + ADP
Hexokinase/Glucokinase
-16.7
-4.0
-33,9
Glucose-6-phosphate → Fructose-6-phosphate
Glucose phosphate isomerase
+1.67
+0.4
-2.92
-3.4
Fructose-6-phosphate + ATP → Fructose-1,
6-bisphosphate + ADP
Phosphofructokinase
-14.2
-18.8
4
+5.7
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate → Dihydroxyacetone
phosphate + Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Aldolase
+23.9
-0.23
+7.56
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate → Glyceraldehyde-
3-phosphate
Triose phosphate isomerase
+1.8
+2.41
2(Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate + NAD* + P, →
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate + NADH + H*)
2(-1.29)
Glyceraldehyde-3-P
dehydrogenase
2(+6.20)
2(+1.5)
7
2(+0.1)
2(1,3-bisphosphoglycerate + ADP →
3-Phosphoglycerate + ATP)
Phosphoglycerate kinase
2(-18.8)
2(-4.5)
2(3-Phosphoglycerate → 2-Phosphoglycerate)
Phosphoglyceromutase
2(+4.4)
2(+1.1)
2(+0.83)
2(2-Phosphoglycerate →
Phosphoenolpyruvate + H,O)
Enolase
2(+1.8)
2(+0.4)
2(+1.1)
10
2(Phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP →
Ругuvate + ATP)
Pyruvate kinase
2(-31.4)
2(-7.5)
2(-23.0)
-73.3
2(-25.1)
Overall
-17.5
Glucose + 2ADP + 2P, + NAD+ →
2 Pyruvate 2ATP + NADH + H*
2(Pyruvate + NADH + H* →Lactate + NAD*)
Glucose + 2ADP + 2P, →2 Lactate + 2ATP
Lactate dehydrogenase
-98.0
2(-6.0)
-29.5
2(-14.8)
-127.6
-123.5
AG" values are assumed to be the same at 25°Cand 37°C and are calculated for standard-state conditions (1 Mconcentration of reactants and products pH 7.0).
AG values are calculated at 310 K (37°C) using steady-state concentrations of these metabolites found in erythrocytes.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning