The standard free energy of formation, AG? , of a substance is the free energy change for the formation of one mole of the substance from the component elements in their standard states. These values are applicable at 25 °C and are found in thermodynamic tables. When propanol (CH3CH2CH2OH) is combusted, such as when in a gasoline blend, the following reaction occurs: 2CH3 CH2 CH2OH(1) + 902 (g)→6CO2(g)+8H2O(g) Based on the standard free energies of formation given in the table below, what is the standard free energy change for this reaction? The value of AG; for a substance gives a measure of the thermodynamic stability with respect to the component elements. Negative values for a formation reaction indicate thermodynamic stability of the product. In other words, the compound formed does not spontaneously decompose back into the component elements. Positive values for a formation reaction indicate thermodynamic instability of the product. Thus, the compound will spontaneously decompose, though the rate may be slow. AG Substance kJ/mol) СH3 CHCH2OН()| — 360.5 O2 (g) The sign of AG can be used to predict the feasibility of CO2 (8) -394.4 synthesizing a substance from its component elements. The standard free energy change for a reaction, AG°, is a state function and can be calculated from the standard free energies H2O(g) -228.6 of formation as follows: Express your answer to one decimal place and include the appropriate units. ΔG Σn, ΔG; (products) -Ση, ΔG (reactants) μΑ ? where np and ny represent the stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced chemical equation for the reactants and products respectively. AG° = Value Units
The standard free energy of formation, AG? , of a substance is the free energy change for the formation of one mole of the substance from the component elements in their standard states. These values are applicable at 25 °C and are found in thermodynamic tables. When propanol (CH3CH2CH2OH) is combusted, such as when in a gasoline blend, the following reaction occurs: 2CH3 CH2 CH2OH(1) + 902 (g)→6CO2(g)+8H2O(g) Based on the standard free energies of formation given in the table below, what is the standard free energy change for this reaction? The value of AG; for a substance gives a measure of the thermodynamic stability with respect to the component elements. Negative values for a formation reaction indicate thermodynamic stability of the product. In other words, the compound formed does not spontaneously decompose back into the component elements. Positive values for a formation reaction indicate thermodynamic instability of the product. Thus, the compound will spontaneously decompose, though the rate may be slow. AG Substance kJ/mol) СH3 CHCH2OН()| — 360.5 O2 (g) The sign of AG can be used to predict the feasibility of CO2 (8) -394.4 synthesizing a substance from its component elements. The standard free energy change for a reaction, AG°, is a state function and can be calculated from the standard free energies H2O(g) -228.6 of formation as follows: Express your answer to one decimal place and include the appropriate units. ΔG Σn, ΔG; (products) -Ση, ΔG (reactants) μΑ ? where np and ny represent the stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced chemical equation for the reactants and products respectively. AG° = Value Units
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter10: Entropy And The Second Law Of Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10.84PAE: Methane can be produced from CO and H2.The process might be done in two steps, as shown below, with...
Related questions
Question
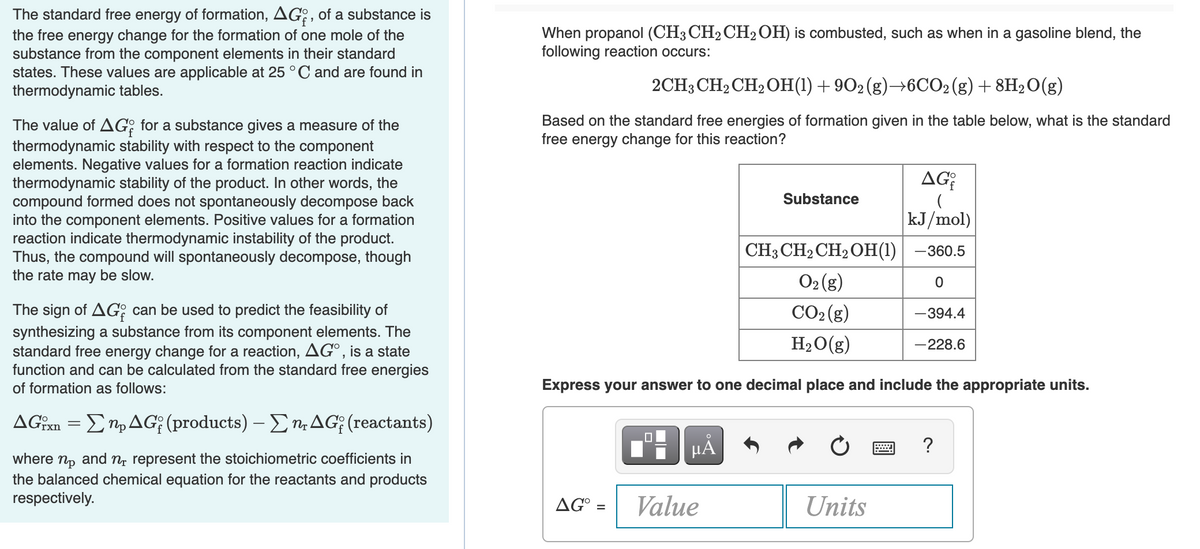
Transcribed Image Text:The standard free energy of formation, AG:, of a substance is
the free energy change for the formation of one mole of the
substance from the component elements in their standard
states. These values are applicable at 25°C and are found in
thermodynamic tables.
When propanol (CH3 CH2CH2 OH) is combusted, such as when in a gasoline blend, the
following reaction occurs:
2CH3 CH2 CH2OH(1) + 902 (g)→6CO2(g) + 8H2O(g)
Based on the standard free energies of formation given in the table below, what is the standard
free energy change for this reaction?
The value of AG: for a substance gives a measure of the
thermodynamic stability with respect to the component
elements. Negative values for a formation reaction indicate
thermodynamic stability of the product. In other words, the
compound formed does not spontaneously decompose back
into the component elements. Positive values for a formation
reaction indicate thermodynamic instability of the product.
Thus, the compound will spontaneously decompose, though
the rate may be slow.
AG
Substance
kJ/mol)
CH3 CH2CH2 OH(1)| –360.5
O2 (g)
CO2 (g)
The sign of AG; can be used to predict the feasibility of
synthesizing a substance from its component elements. The
standard free energy change for a reaction, AG°, is a state
function and can be calculated from the standard free energies
of formation as follows:
-394.4
H2O(g)
-228.6
Express your answer to one decimal place and include the appropriate units.
ΔG Σn, ΔG; (products)-Ση ΔG; (reactants)
μΑ
?
where np and n, represent the stoichiometric coefficients in
the balanced chemical equation for the reactants and products
respectively.
AG° =
Value
Units
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning