
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:M
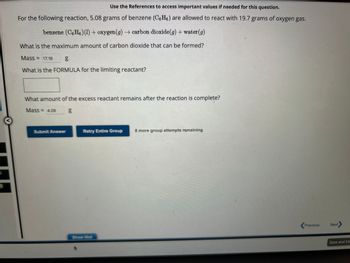
Use the References to access important values if needed for this question.
For the following reaction, 5.08 grams of benzene (C6H6) are allowed to react with 19.7 grams of oxygen gas.
benzene (C6H6) (1) + oxygen (g) → carbon dioxide(g) + water (g)
What is the maximum amount of carbon dioxide that can be formed?
Mass = 17.16
g
What is the FORMULA for the limiting reactant?
What amount of the excess reactant remains after the reaction is complete?
Mass = 4.08
Submit Answer
6.0
g
Retry Entire Group 8 more group attempts remaining
Show Hint
Previous
Next>
Save and Exi
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the mass of the initial sample burned?arrow_forwardImagine that you perform a combination reaction between 60.0 g of sodium metal (Na) with 10.0 g of nitrogen gas (N2). Write the balanced chemical equationarrow_forwardFor the reaction Ca(s)+Cl2(g)→CaCl2(s) calculate how many grams of the product form when 21.4 gg of Ca completely reacts. Assume that there is more than enough of the other reactant.arrow_forward
- [Tutorial: Limiting reactant stoichiometry] This question will walk you through the steps of calculating the mass of products produced based on your determination of the limiting reactant. b) Step 2a: Use dimensional analysis to determine the theoretical yield of the product. Calculate the theoretical yield in grams Al₂O₃ from the complete reaction of 64.7 grams Al according to the following balanced chemical equation: 2 Al(s) + Fe₂O₃(s) → Al₂O₃(s) + 2 Fe(s) c) Calculate the theoretical yield in grams Al₂O₃ from the complete reaction of 201 grams Fe₂O₃ according to the following balanced chemical equation: 2 Al(s) + Fe₂O₃(s) → Al₂O₃(s) + 2 Fe(s) d) Which of the following substances is the limiting reactant? e) What is the mass in grams of the excess Fe₂O₃ remaining after the partial reaction of 201 g Fe₂O₃ with 64.7 g Al? Give your answer to three significant figures.arrow_forwardUse the References to access important values if needed for this question. For the following reaction, 5.08 grams of benzene (C6H6) are allowed to react with 19.7 grams of oxygen gas. benzene (C6H6) (1) + oxygen (g) → carbon dioxide(g) + water (g) What is the maximum amount of carbon dioxide that can be formed? Mass= g What is the FORMULA for the limiting reactant? What amount of the excess reactant remains after the reaction is complete? Mass= g Submit Answer b.0 Retry Entire Group Show Hint 8 more group attempts remaining Previousarrow_forwardUse the References to access important values if needed for this question. For the following reaction, 26.8 grams of sulfur dioxide are allowed to react with 6.14 grams of water. sulfur dioxide(g) + water (1)→ sulfurous acid (H₂SO3)(g) What is the maximum mass of sulfurous acid (H₂SO3) that can be formed? g What is the FORMULA for the limiting reactant? Mass= What mass of the excess reagent remains after the reaction is complete? Mass= Submit Answer b.0 g Retry Entire Group Show Hint 8 more group attempts remaining Previous Next> Save and Exitarrow_forward
- Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. An element X has a tribromide with the empirical formula XBr3 and a trichloride with the empirical formula XCl3. The tribromide is converted to the trichloride according to the equation XBr3+ Cl₂ → XCl3 + Br₂ If the complete conversion of 1.329 g of XBr3 results in the formation of 0.719 g of XCl3, what is the atomic mass of the element X? Atomic mass X = g/molarrow_forwardFor the following reaction, 26.9 grams of bromine are allowed to react with 15.2 grams of chlorine gas. bromine(g)+ chlorine(g) bromine monochloride(g) What is the maximum mass of bromine monochloride that can be formed? grams What is the FORMULA for the limiting reagent? What mass of the excess reagent remains after the reaction is complete? gramsarrow_forwardNitrogen dioxide is produced by combustion in an automobile engine. For the following reaction, 0.197 moles of nitrogen monoxide are mixed with 0.171 moles of oxygen gas. Nitrogen monoxide (G) + Oxygen (G) = Nitrogen dioxide (G) What is the formula for the limiting reactant? What is the maximum amount of nitrogen dioxide that can be produced? Amount = molarrow_forward
- References Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. For the following reaction, 24.3 grams of iron are allowed to react with 27.8 grams of hydrochloric acid. iron(s) + hydrochloric acid (aq) → iron (II) chloride (aq) + hydrogen (g) What is the maximum amount of iron(II) chloride that can be formed? Mass= g What is the FORMULA for the limiting reactant? What amount of the excess reactant remains after the reaction is complete? Mass= g Submit Answerarrow_forwardFor the following reaction, 4.70 grams of benzene (C6H6) are allowed to react with 18.1 grams of oxygen gas . benzene (C6H6) (1) + oxygen ( g) → carbon dioxide (g) + water (g) What is the maximum amount of carbon dioxide that can be formed? grams What is the FORMULA for the limiting reagent? What amount of the excess reagent remains after the reaction is complete? gramsarrow_forwardFor the following reaction, 11.2 grams of glucose (C6H1206) are allowed to react with 15.5 grams of oxygen gas. glucose (C6H1206) + oxygen---> carbon dioxide + water What is the maximum amount of carbon dioxide that can be formed? Mass= __ g What is the FORMULA for the limiting reactant? What amount of the excess reactant remains after the reaction is complete? Mass= garrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY