
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Use this mRNA coding sequence as your starting point. This sequence begins with a start codon and ends with a stop codon, so it is only looking at the region of DNA that directly encodes a protein sequence.
5’-AUGCACAAAUUAGAGUACCCCCCAGGAAGGUAG-3’
Make the following mutation in this sequence by changing/adding/removing only one
A missense mutation that is also a transversion
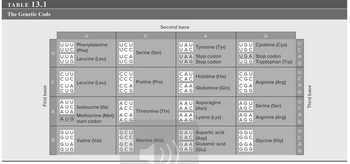
Transcribed Image Text:**Table 13.1: The Genetic Code**
The chart illustrates the genetic code used in translating mRNA sequences into amino acids. The genetic code is presented in a table format, consisting of triplet codons, which represent sequences of three nucleotides (bases). These triplet codons correspond to specific amino acids or signaling instructions (such as the start or stop of protein synthesis).
**Layout and Explanation:**
- **Rows and Columns:**
- The table is arranged based on combinations of three nucleotide bases, denoted as U (Uracil), C (Cytosine), A (Adenine), and G (Guanine).
- The first column on the left represents the first base.
- The top row represents the second base.
- The right column represents the third base.
- **Codons and Amino Acids:**
- Each cell within the table contains a group of triplet codons that code for the same amino acid or function.
- Amino acids, along with their three-letter and one-letter codes, are listed next to their corresponding codons.
**Content Details:**
- **First Base = U:**
- Second Base U:
- Phenylalanine (Phe) - UUU, UUC
- Leucine (Leu) - UUA, UUG
- Second Base C:
- Serine (Ser) - UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG
- Second Base A:
- Tyrosine (Tyr) - UAU, UAC
- Stop codons - UAA, UAG
- Second Base G:
- Cysteine (Cys) - UGU, UGC
- Stop codon - UGA
- Tryptophan (Trp) - UGG
- **First Base = C:**
- Second Base U:
- Leucine (Leu) - CUU, CUC, CUA, CUG
- Second Base C:
- Proline (Pro) - CCU, CCC, CCA, CCG
- Second Base A:
- Histidine (His) - CAU, CAC
- Glutamine (Gln) - CAA, CAG
- Second Base G:
- Arginine (Arg) - CGU
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For each mutant, state what change has occurred in the DNA, whether it was a substitution by transition or transversion, sense mutation, nonsense or reading frame change. It must present the codon sequence. Normal nucleotide sequence starting from the third codon: CCC-ACG-GUG-ACG-ACA-CGG-UGG Please show the codon and nucleotide sequence of the mutation.arrow_forwardmRNA Codon Chart: Second letter с บบบ UCU UAU Phe UUC UCC U Ser UAC Tyr UGU UGC Cys UUA UCA Leu UAA Stop UGA Stop A UUG UCG UAG Stop UGG Trp CUU CCU CAU CGU CUC CCC His CAC Leu Pro CUA CCA CAA CGA Arg Gin CUG CCG CAG CGG AUU ACU AAU AUC lle ACC AAC AGU ]Asn Ser AGC A Thr AUA ACA AAA Lys AGA Arg AUG Met ACG AGG GUU GCU GAU GUC GCC Val GAC Asp GGU GGC Ala GUA GCA GUG GCG GAG GGG GAA Glu GGA Gly Amino Acid 3-Letter Codes Name of Amino Name of Amino 3-Letter Code 3-Letter Code Acid Acid Alanine Ala Leucine Leu Arginine Arg Lysine Lys Asparagine sex Methionine Met (start) Aspartic Acid Asp Phenylalanine ebe Cysteine Cve Proline Pro Glutamic Acid Glu Serine Ser Glutamine Gln Threonine Glycine GLK Tryptophan JAR Histidine His Tyrosine Tyr Isoleucine lle Valine Val Exercise: Transcription & Translation 1. Choose 3 DNA Templates. 2. Write the mRNA sequence divided into 3 letter codons. 3. Write the sequence of amino acids. 4. Find the corresponding amino acid sequence and include the letter of…arrow_forwardWhich of the triplets below is a possible anticodon for a tRNA that transports Leucine (Leu) to a ribosome? Second letter C UGU cys UCU1 UCC UCA UCG UAU Tyr UACS Ser UAA Stop UGA Stop A UAG Stop UGG Trp UUU UGCS Phe UUC U UUA UUG FLeu CAU HiS CGU] CUU CUC Leu CCU ССС CCA CCGJ CACS CGC Arg CGA CAA GIn Pro C CUA CUG J CAG S CGG AUU AUC lle AUA AAU Asn AGU ser ACU АСС Thr ACA AAC AAA ys AGA Arg AAG J AGC AUG Met ACG Lys AGG J GUU GUC CUA Val GAU ASP GCU GACJ GCC FAla GGU] GGC CGA Gly CCA C CAA M UCAG Third letter UCAG UCAG First letterarrow_forward
- Can you help me solve this sequence question and identifty the mutation?arrow_forwardUse this mRNA coding sequence as your starting point. This sequence begins with a start codon and ends with a stop codon, so it is only looking at the region of DNA that directly encodes a protein sequence. 5’-AUGCACAAAUUAGAGUACCCCCCAGGAAGGUAG-3’ Make the following mutation in this sequence by changing/adding/removing only one nucleotide. Make the mutation easy to see (a different color, circled, something like that) A frameshift mutationarrow_forwardListed below are five amino acids. Use the genetic code to determine the exact codon for each amino acid. A point mutation at the genetic level in each codon results in the change indicated. For each mutation, indicate whether it is due to a transition or a transversion, and then indicate the effect of each mutation at the protein (amino acid level) (i.e. silent, nonsense, missense). In addition, Please note, each of the three lines above an amino acid represents a single RNA base. For example, when you look at the codon chart AUG would stand for Met (methionine) Lys 1 Glu Ile 3 Stop Ile 4.arrow_forward
- Transcribe and translate the mutated sequence #3. Determine the consequence, if any, for each mutation. You will need to use your codon charts in your ISN. Practice with both charts.arrow_forwardPlease answer all parts of this questionarrow_forwardIf the template strand of DNA carries the code: GGT-AAT-ACT, then what is the corresponding mRNA code? Recall that DNA does not use "U" as a base. Enter your answer below using the same format as shown here (three capital letters for each codon, separated by a single dash, no spaces, repeat for each codon). Table 26-1 The Genetic Code First Third Position Position (5'-end) Second Position (3'-end) U C A G Phe UAU UCU UCC Тyr Тyr Stop Stop UGU UGC Cys Cys Stop Trp UUU Ser U UUC Phe Ser UAC C UUA Leu UCA Ser UAA UGA A UUG Leu UCG Ser UAG UGG G Leu Leu Leu Leu CAU САС CAA CAG CUU CCU Pro Pro Pro Pro His His CGU Arg Arg Arg Arg U CỤC CỦA CUG CCC CCA CGC CGA C Gln Gln CCG CGG G Пе Thr ACU АСС ACA ACG AUU AAU Asn AGU Ser U AAC AAA AAG AUC Пе Thr Asn AGC Ser C AUA Ile Thr Lys Lys AGA AGG Arg Arg A A AUG* Met Thr GUU Val Val Val Val GCU GCC GCA GCG Ala GGU GGC GGA Gly Gly Gly Gly U C A GAU GỤC GUA GUG Asp Asp Glu Glu Ala GAC G Ala Ala GAA GAG GGG *AUG also serves as the principal initiation…arrow_forward
- c) Based on your answer to part b above, determine the polypeptide sequence produced by the ribosome from the mRNA which you transcribedarrow_forwardSARS E You have generated several random mutations in this region. One of them is - 5'-AAUUACCUAUAGAUUGUUU-3' What may be the mutant protein sequence Enter the single letter code for the amino acids. For a stop codon (if any) enter: STOP And fill subsequent blanks with: N/A For example: if you the sequence you need to enter is: M*, enter M N/A N/A N/A N/Aarrow_forwardGive the sequence of the LEFT (5'-end) region of this RNA strand that would participate in forming the stem of a stem-loop with this bit of RNA. DRAW this stem-loop in your scratch work! 5’-UGGUGGAUCUCUGCAACUGAUCCAUUG-3’arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education