Question
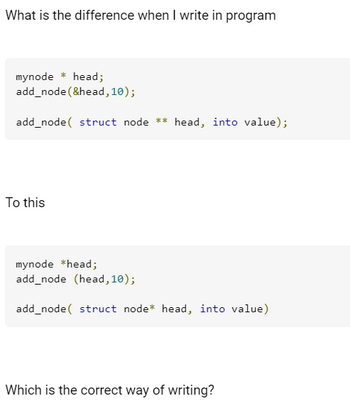
Transcribed Image Text:What is the difference when I write in program
mynode * head;
add_node (&head, 10);
add_node struct node ** head, into value);
To this
mynode *head;
add_node (head, 10);
add_node struct node* head, into value)
Which is the correct way of writing?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- please go in to the detail and explain in detail the purpose and function to each line & function of code listed below. #include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h> struct node{int data;struct node *next;}; struct node *head, *tail = NULL; void addNode(int data) {struct node *newNode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));newNode->data = data;newNode->next = NULL; if(head == NULL) {head = newNode;tail = newNode;}else {tail->next = newNode;tail = newNode;}} void removeDuplicate() {struct node *current = head, *index = NULL, *temp = NULL; if(head == NULL) {return;}else {while(current != NULL){temp = current;index = current->next; while(index != NULL) {if(current->data == index->data) {temp->next = index->next;}else {temp = index;}index = index->next;}current = current->next;}}} void display() {struct node *current = head;if(head == NULL) {printf("List is empty \n");return;}while(current != NULL) {printf("%d ", current->data);current =…arrow_forwardhello. This is my code: #include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h> typedef struct HuffmanNode { int character; float frequency; struct HuffmanNode* left; struct HuffmanNode* right;} HuffmanNode; typedef struct HeapNode { HuffmanNode* node; struct HeapNode* next;} HeapNode; HuffmanNode* create_huffman_node(int character, float frequency) { HuffmanNode* node = (HuffmanNode*)malloc(sizeof(HuffmanNode)); node->character = character; node->frequency = frequency; node->left = NULL; node->right = NULL; return node;} HeapNode* create_heap_node(HuffmanNode* node) { HeapNode* heap_node = (HeapNode*)malloc(sizeof(HeapNode)); heap_node->node = node; heap_node->next = NULL; return heap_node;} HeapNode* insert_into_heap(HeapNode* heap, HuffmanNode* node) { HeapNode* heap_node = create_heap_node(node); if (heap == NULL) { return heap_node; } // Compare nodes based on probability and…arrow_forward{JAVA data structure set} Suppose you have a list of numbers: numbers = [1, 2, 13, 4, 4, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7, 7, 12] Convert this list into a set and assign it to a new variable called unique_numbers. Print unique_numbers to see the result.arrow_forward
- #include <iostream>using namespace std;double median(int *, int);int get_mode(int *, int);int *create_array(int);void getinfo(int *, int);void sort(int [], int);double average(int *, int);int getrange(int *,int);int main(){ int *dyn_array; int students; int mode,i,range;float avrg;do{cout << "How many students will you enter? ";cin >> students;}while ( students <= 0 );dyn_array = create_array( students );getinfo(dyn_array, students);cout<<"\nThe array is:\n";for(i=0;i<students;i++)cout<<"student "<<i+1<<" saw "<<*(dyn_array+i)<<" movies.\n";sort(dyn_array, students);cout << "\nthe median is "<<median(dyn_array, students) << endl;cout << "the average is "<<average(dyn_array, students) << endl;mode = get_mode(dyn_array, students);if (mode == -1)cout << "no mode.\n";elsecout << "The mode is " << mode << endl;cout<<"The range of movies seen is…arrow_forward#include <iostream>using namespace std;double median(int *, int);int get_mode(int *, int);int *create_array(int);void getinfo(int *, int);void sort(int [], int);double average(int *, int);int getrange(int *,int);int main(){ int *dyn_array; int students; int mode,i,range;float avrg;do{cout << "How many students will you enter? ";cin >> students;}while ( students <= 0 );dyn_array = create_array( students );getinfo(dyn_array, students);cout<<"\nThe array is:\n";for(i=0;i<students;i++)cout<<"student "<<i+1<<" saw "<<*(dyn_array+i)<<" movies.\n";sort(dyn_array, students);cout << "\nthe median is "<<median(dyn_array, students) << endl;cout << "the average is "<<average(dyn_array, students) << endl;mode = get_mode(dyn_array, students);if (mode == -1)cout << "no mode.\n";elsecout << "The mode is " << mode << endl;cout<<"The range of movies seen is…arrow_forward// FILL IN THE BLANKS (LINKED-LISTS CODE) (C++)#include<iostream>using namespace std; struct ________ {int data ;struct node *next; }; node *head = ________;node *createNode() { // allocate a memorynode __________;temp = new node ;return _______ ;} void insertNode(){node *temp, *traverse;int n;cout<< "Enter -1 to end "<<endl;cout<< "Enter the values to be added in list"<<endl;cin>>n; while(n!=-1){temp = createNode(); // allocate memorytemp->data = ________;temp->next = ________;if ( ___________ == NULL){head = _________;} else {traverse = ( );while (traverse->next != ________{traverse = traverse-> ___________;} traverse->next= temp;} cout<<"Enter the value to be added in the list"<<endl;cin>>n; }} void printlist(){node *traverse = head; // if head == NULLwhile (traverse != NULL) { cout<<traverse->data<<" ";traverse = traverse->next;}} int main(){int option; do{cout<<"\n =============== MAIN…arrow_forward
- #include <iostream>#include <vector>using namespace std; void PrintVectors(vector<int> numsList) { unsigned int i; for (i = 0; i < numsList.size(); ++i) { cout << numsList.at(i) << " "; } cout << endl;} int main() { vector<int> numsList; int userInput; int i; for (i = 0; i < 3; ++i) { cin >> userInput; numsList.push_back(userInput); } numsList.erase(numsList.begin()+1); numsList.insert(numsList.begin()+1, 102); numsList.insert(numsList.begin()+1, 100); PrintVectors(numsList); return 0;} Not all tests passed clearTesting with inputs: 33 200 10 Output differs. See highlights below. Special character legend Your output 33 100 102 10 Expected output 100 33 102 10 clearTesting with inputs: 6 7 8 Output differs. See highlights below. Special character legend Your output 6 100 102 8 Expected output 100 6 102 8 Not sure what I did wrong but the the 33…arrow_forwarduse code below in part with bts #include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <time.h> typedef struct node_struct {int item;struct node_struct *next;} node; /*** 10->NULL* We want to insert 20* First call ([10], 20) [not complete]* {10, {20, NULL}} To compute the conditional probabilities you need to determine unigram andbigram counts first (you can do this in a single pass through a file if you do thingscarefully) and store them in a Binary Search Tree (BST). After that, you can computethe conditional probabilities.Input filesTest files can be found on (http://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/). For example,search for “Mark Twain.” Then click on any of his books. Next download the “PlainText UTF-8” format.In addition, you should test your program on other input files as well, for which youcan hand-compute the correct answer.Output filesYour program must accept the name of an input file as a command line argument.Let's call the file name of this file fn. Your program must…arrow_forwardIn c++ you have two Nodes A and B, both Nodes contain two numbers, how will you calculate and find which Node has the smallest numbers.arrow_forward
- #include #include using namespace std; void PrintSize(vector numsList) { cout intList (3); PrintSize(intList); cin >> currval; while (currval >= 0) { } Type the program's output intList.push_back(currval); cin >> currVal; PrintSize(intList); intList.clear(); PrintSize(intList); return 0; 1 se mice with camScanner Check Next Input 1234-1 Outputarrow_forwardC programming fill in the following code #include "graph.h" #include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h> /* initialise an empty graph *//* return pointer to initialised graph */Graph *init_graph(void){} /* release memory for graph */void free_graph(Graph *graph){} /* initialise a vertex *//* return pointer to initialised vertex */Vertex *init_vertex(int id){} /* release memory for initialised vertex */void free_vertex(Vertex *vertex){} /* initialise an edge. *//* return pointer to initialised edge. */Edge *init_edge(void){} /* release memory for initialised edge. */void free_edge(Edge *edge){} /* remove all edges from vertex with id from to vertex with id to from graph. */void remove_edge(Graph *graph, int from, int to){} /* remove all edges from vertex with specified id. */void remove_edges(Graph *graph, int id){} /* output all vertices and edges in graph. *//* each vertex in the graphs should be printed on a new line *//* each vertex should be printed in the following format:…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios