
Concept explainers
C programming
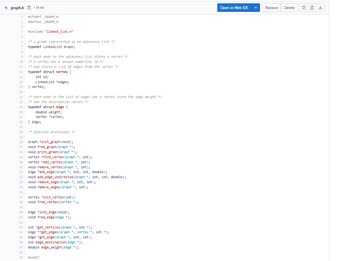
fill in the following code
#include "graph.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* initialise an empty graph */
/* return pointer to initialised graph */
Graph *init_graph(void)
{
}
/* release memory for graph */
void free_graph(Graph *graph)
{
}
/* initialise a vertex */
/* return pointer to initialised vertex */
Vertex *init_vertex(int id)
{
}
/* release memory for initialised vertex */
void free_vertex(Vertex *vertex)
{
}
/* initialise an edge. */
/* return pointer to initialised edge. */
Edge *init_edge(void)
{
}
/* release memory for initialised edge. */
void free_edge(Edge *edge)
{
}
/* remove all edges from vertex with id from to vertex with id to from graph. */
void remove_edge(Graph *graph, int from, int to)
{
}
/* remove all edges from vertex with specified id. */
void remove_edges(Graph *graph, int id)
{
}
/* output all vertices and edges in graph. */
/* each vertex in the graphs should be printed on a new line */
/* each vertex should be printed in the following format: */
/* vertex_id: edge_to_vertex[weight] edge_to_vertex[weight] ... */
/* for example: */
/* 1: 3[1.00] 5[2.00] */
/* indicating that vertex id 1 has edges to vertices 3 and 5 */
/* with weights 1.00 and 2.00 respectively */
/* weights should be output to two decimal places */
void print_graph(Graph *graph)
{
}
/* find vertex with specified id in graph. */
/* return pointer to vertex, or NULL if no vertex found. */
Vertex *find_vertex(Graph *graph, int id)
{
}
/* create and add vertex with specified id to graph. */
/* return pointer to vertex or NULL if an error occurs. */
/* if vertex with id already exists, return pointer to existing vertex. */
Vertex *add_vertex(Graph *graph, int id)
{
}
/* remove vertex with specified id from graph. */
/* remove all edges between specified vertex and any other vertices in graph. */
void remove_vertex(Graph *graph, int id)
{
}
/* add directed edge with specified weight between vertex with id from */
/* to vertex with id to. */
/* if no vertices with specified ids (from or to) exist */
/* then the vertices will be created. */
/* multiple edges between the same pair of vertices are allowed. */
/* return pointer to edge, or NULL if an error occurs found. */
Edge *add_edge(Graph *graph, int from, int to, double weight)
{
}
/* add two edges to graph, one from vertex with id from to vertex with id to, */
/* and one from vertex with id to to vertex with id from. */
/* both edges should have the same weight */
/* if no vertices with specified ids (from or to) exist */
/* then the vertices will be created. */
/* multiple vertices between the same pair of vertices are allowed. */
void add_edge_undirected(Graph *graph, int from, int to, double weight)
{
}
/* return array of node ids in graph. */
/* array of node ids should be dynamically allocated */
/* set count to be the number of nodes in graph */
/* return NULL if no vertices in graph */
int *get_vertices(Graph *graph, int *count)
{
}
/* return array of pointers to edges for a given vertex. */
/* array of edges should be dynamically allocated */
/* set count to be number of edges of vertex */
/* return NULL if no edges from/to vertex */
Edge **get_edges(Graph *graph, Vertex *vertex, int *count)
{
}
/* return pointer to edge from vertex with id from, to vertex with id to. */
/* return NULL if no edge */
Edge *get_edge(Graph *graph, int from, int to)
{
}
/* return id of destination node of edge. */
int edge_destination(Edge *edge)
{
}
/* return weight of edge. */
double edge_weight(Edge *edge)
{
}
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

- #ifndef LLCP_INT_H#define LLCP_INT_H #include <iostream> struct Node{ int data; Node *link;};void DelOddCopEven(Node*& headPtr);int FindListLength(Node* headPtr);bool IsSortedUp(Node* headPtr);void InsertAsHead(Node*& headPtr, int value);void InsertAsTail(Node*& headPtr, int value);void InsertSortedUp(Node*& headPtr, int value);bool DelFirstTargetNode(Node*& headPtr, int target);bool DelNodeBefore1stMatch(Node*& headPtr, int target);void ShowAll(std::ostream& outs, Node* headPtr);void FindMinMax(Node* headPtr, int& minValue, int& maxValue);double FindAverage(Node* headPtr);void ListClear(Node*& headPtr, int noMsg = 0); // prototype of DelOddCopEven of Assignment 5 Part 1 #endifarrow_forward// FILE: DPQueue.h// CLASS PROVIDED: p_queue (priority queue ADT)//// TYPEDEFS and MEMBER CONSTANTS for the p_queue class:// typedef _____ value_type// p_queue::value_type is the data type of the items in// the p_queue. It may be any of the C++ built-in types// (int, char, etc.), or a class with a default constructor, a// copy constructor, an assignment operator, and a less-than// operator forming a strict weak ordering.//// typedef _____ size_type// p_queue::size_type is the data type considered best-suited// for any variable meant for counting and sizing (as well as// array-indexing) purposes; e.g.: it is the data type for a// variable representing how many items are in the p_queue.// It is also the data type of the priority associated with// each item in the p_queue//// static const size_type DEFAULT_CAPACITY = _____// p_queue::DEFAULT_CAPACITY is the default initial capacity of a// p_queue that is created by the default…arrow_forward// FILL IN THE BLANKS (LINKED-LISTS CODE) (C++)#include<iostream>using namespace std; struct ________ {int data ;struct node *next; }; node *head = ________;node *createNode() { // allocate a memorynode __________;temp = new node ;return _______ ;} void insertNode(){node *temp, *traverse;int n;cout<< "Enter -1 to end "<<endl;cout<< "Enter the values to be added in list"<<endl;cin>>n; while(n!=-1){temp = createNode(); // allocate memorytemp->data = ________;temp->next = ________;if ( ___________ == NULL){head = _________;} else {traverse = ( );while (traverse->next != ________{traverse = traverse-> ___________;} traverse->next= temp;} cout<<"Enter the value to be added in the list"<<endl;cin>>n; }} void printlist(){node *traverse = head; // if head == NULLwhile (traverse != NULL) { cout<<traverse->data<<" ";traverse = traverse->next;}} int main(){int option; do{cout<<"\n =============== MAIN…arrow_forward
- C++ Data Structure:Create an AVL Tree C++ class that works similarly to std::map, but does NOT use std::map. In the PRIVATE section, any members or methods may be modified in any way. Standard pointers or unique pointers may be used.** MUST use given Template below: #ifndef avltree_h#define avltree_h #include <memory> template <typename Key, typename Value=Key> class AVL_Tree { public: classNode { private: Key k; Value v; int bf; //balace factor std::unique_ptr<Node> left_, right_; Node(const Key& key) : k(key), bf(0) {} Node(const Key& key, const Value& value) : k(key), v(value), bf(0) {} public: Node *left() { return left_.get(); } Node *right() { return right_.get(); } const Key& key() const { return k; } const Value& value() const { return v; } const int balance_factor() const {…arrow_forwardC++ Given code #include <iostream>using namespace std; class Node {public:int data;Node *pNext;}; void displayNumberValues( Node *pHead){while( pHead != NULL) {cout << pHead->data << " ";pHead = pHead->pNext;}cout << endl;} //Option 1: Search the list// TODO: complete the function below to search for a given value in linked lsit// return true if value exists in the list, return false otherwise. ?? linkedlistSearch( ???){ } //Option 2: get sum of all values// TODO: complete the function below to return the sum of all elements in the linked list. ??? getSumOfAllNumbers( ???){ } int main(){int userInput;Node *pHead = NULL;Node *pTemp;cout<<"Enter list numbers separated by space, followed by -1: "; cin >> userInput;// Keep looping until end of input flag of -1 is givenwhile( userInput != -1) {// Store this number on the listpTemp = new Node;pTemp->data = userInput;pTemp->pNext = pHead;pHead = pTemp;cin >> userInput;}cout <<"…arrow_forward
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





