
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for ethylene oxide, ethylene glycol, and acrylonitrile has to be drawn and also the hybrid orbitals of the central atom have to be given along with the number of pi bonds present.
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structure is used for predicting the shape of molecules. From the steric number obtained in a Lewis structure, the molecular geometry can be predicted. VSEPR model can predict the shape of molecules considering their Lewis structure. Certain rules has to be followed in for the VSEPR model.
- The molecule will have a shape where there is minimal electrostatic repulsion between the valence‑shell electron pairs.
- The forces of repulsion between two lone pairs of electrons will be higher than the repulsion between lone pair and bond pair of electrons. This in turn will be higher than the bond pair‑bond pair of electrons.
The hybridized orbitals and the steric number can be related as shown below;
| Steric number | Hybridized orbital |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 |
Explanation of Solution
Ethylene oxide:
Formula for ethylene oxide is
The total number of valence electrons is calculated as shown below;
A total of
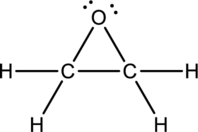
Hybrid orbitals of central carbon atoms:
The carbon atom has does not have a lone pair of electrons and it is bonded to four atoms. Therefore, the steric number is calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is four, the hybridization of carbon atom is
Hybrid orbitals of central oxygen atom:
The oxygen atom has two lone pair of electrons and it is bonded to two atoms. Therefore, the steric number is calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is four, the hybridization of oxygen atom is
There is no unhybridized orbital left out for the formation of pi bonds. Hence, there is no pi bonds in ethylene oxide.
Ethylene glycol:
Formula for ethylene glycol is
The total number of valence electrons is calculated as shown below;
A total of
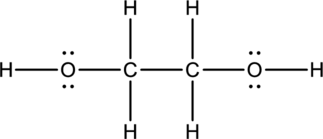
Hybrid orbitals of central carbon atoms:
The carbon atom has does not have a lone pair of electrons and it is bonded to four atoms. Therefore, the steric number is calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is four, the hybridization of carbon atom is
Hybrid orbitals of central oxygen atoms:
The oxygen atom has two lone pair of electrons and it is bonded to two atoms. Therefore, the steric number is calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is four, the hybridization of oxygen atom is
There is no unhybridized orbital left out for the formation of pi bonds. Hence, there is no pi bonds in ethylene glycol.
Acrylonitrile:
Formula for acrylonitrile is
The total number of valence electrons is calculated as shown below;
A total of
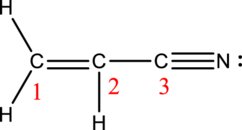
Hybrid orbitals of carbon atom C-1:
The carbon atom has does not have a lone pair of electrons and it is bonded to three atoms. Therefore, the steric number is calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is three, the hybridization of carbon atom is
Hybrid orbitals of carbon atom C-2:
The carbon atom has does not have a lone pair of electrons and it is bonded to three atoms. Therefore, the steric number is calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is three, the hybridization of carbon atom is
Hybrid orbitals of carbon atom C-3:
The carbon atom has does not have a lone pair of electrons and it is bonded to two atoms. Therefore, the steric number is calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is two, the hybridization of carbon atom is
There are one double bond and one triple bond present in the structure. As multiple bonds are present, acrylonitrile contains pi bonds.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Chemistry
- A toxic cloud covered Bhopal, India, in December 1984 when water leaked into a tank of methyl isocyanate, and the product escaped into the atmosphere. Methyl isocyanate is used in the production of many pesticides. Draw the Lewis structures for methyl isocyanate, CH3NCO, including resonance forms. The skeletal structure isarrow_forwardSulfuric acid is the industrial chemical produced in greatest quantity worldwide. About 90 billion pounds are produced each year in the United States alone. Write the Lewis structure for sulfuric acid, H2SO4, which has two oxygen atoms and two OH groups bonded to the sulfur.arrow_forwardA variety of chlorine oxide fluorides and related cations and anions are known. They tend to be powerful oxidizing and fluorinating agents. FClO3 is the most stable of this group of compounds and has been studied as an oxidizing component in rocket propellants. Draw a Lewis structure for F3ClO, F2ClO2+, and F3ClO2. What is the molecular structure for each species, and what is the expected hybridization of the central chlorine atom in each compound or ion?arrow_forward
- Cyanamide (H2NCN), an important industrial chemical, is produced by the following steps: Calcium cyanamide (CaNCN) is used as a direct-application fertilizer, weed killer, and cotton defoliant. It is also used to make cyanamide, dicyandiamide, and melamine plastics: a. Write Lewis structures for NCN2, H2NCN, dicyandiarnide, and melamine, including resonance structures where appropriate. b. Give the hybridization of the C and N atoms in each species. c. How many bonds and how many bonds are in each species? d. Is the ring in melamine planar? e. There are three different CN bond distances in dicyandiamide, NCNC(NH2)2, and the molecule is nonlinear. Of all the resonance structures you drew for this molecule, predict which should be the most important.arrow_forwardBest Lewis Formula and Molecular Geometry A student writes the Lewis electron-dot formula for the carbonate anion, CO32, as a Does this Lewis formula obey the octet rule? Explain. What are the formal charges on the atoms? Try describing the bonding for this formula in valence bond terms. Do you have any difficulty doing this? b Does this Lewis formula give a reasonable description of the electron structure, or is there a better one? If there is a better Lewis formula, write it down and explain why it is better. c The same student writes the following resonance description for CO2: Is there something wrong with this description? (What would you predict as the geometries of these formulas?) d Is one or the other formula a better description? Could a value for the dipole moment help you decide? e Can you write a Lewis formula that gives an even better description of CO2? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardConsider the following compounds: CO2, SO2, KrF2, SO3, NF3, IF3, CF4, SF4, XeF4, PF5, TF5, and SCl6. These 12 compounds are all examples of different molecular structures. Draw the Lewis structures for each and predict the molecular structures. Predict the bond angles and the polarity of each. (A polar molecule has a net dipole moment, while a nonpolar molecule does not.) See Exercises 25 and 26 for the molecular structures based on the trigonal bipyramid and the octahedral geometries.arrow_forward
- The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties is called organic chemistry. Besides carbon atoms, organic compounds also can contain hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms (as well as other types of atoms). A common trait of simple organic compounds is to have Lewis structures where all atoms have a formal charge of zero. Consider the following incomplete Lewis structure for an organic compound called histidine (an amino acid), which is one of the building blocks of proteins found in our bodies: Draw a complete Lewis structure for histidine in which all atoms have a formal charge of zero.arrow_forwardTwo compounds have the formula S2F2. Disulfur difluoride has the skeleton structure FSSF, whereas thiothionyl fluoride has the skeletal structure Determine Lewis structures for each compound.arrow_forwardSuccessive substitution of F atoms for H atoms in the molecule NH3 produces the molecules NH2F, NHF2, and NF3. a. Draw Lewis structures for each of the four molecules. b. Using VSEPR theory, predict the geometry of each of the four molecules. c. Specify the polarity (polar or nonpolar) for each of the four molecules.arrow_forward
- Nitrosyl azide, N4O, is a pale yellow solid first synthesized in 1993. Write the Lewis structure for nitrosyl azide.arrow_forwardWrite reasonable Lewis structures for the following species, none of which follow the octet rule. (a) BeCl2 (b) SeO2- (c) ClO3 (d) CH3arrow_forwardDraw a Lewis structure for chloromethane, CH 3Cl, a compound produced by giant kelp and a component of volcanic emissionsarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning





