
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The increasing order of acidity of the alcohols is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Acidity of a molecule is dependent on the value of
Answer to Problem 10.46AP
The increasing order of acidity of the alcohols is given below.
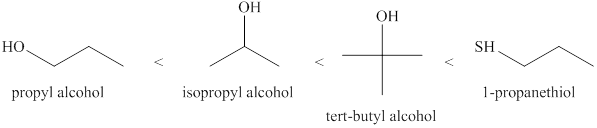
Explanation of Solution
Acidity of the molecules is dependent upon the stability of the ion formed after releasing hydrogen ion.
Sulfur atom present in
Order of the acidity is shown below in Figure 1.

Figure 1
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is
(b)
Interpretation:
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Acidity of a molecule is dependent on the value of
Answer to Problem 10.46AP
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is given below.
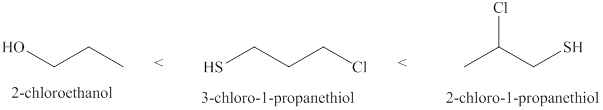
Explanation of Solution
Acidity of the molecules is dependent upon the stability of the ion formed after releasing hydrogen ion. Sulfur atom present in
Therefore, increasing order of the given molecules is shown below in Figure 2.
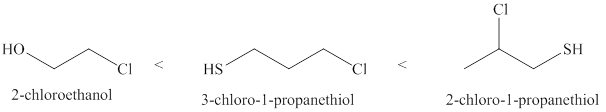
Figure 2
The increasing order of acidity of the given molecules is
(c)
Interpretation:
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Acidity of a molecule is dependent on the value of
Answer to Problem 10.46AP
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is stated below.
Explanation of Solution
Acidity of the molecules is dependent upon the stability of the ion formed after releasing hydrogen ion. Nitrogen atom which is positively charged, stabilizes the negative charge which is generated after releasing the hydrogen ion. Therefore, structure 3 is the most stable structure with most acidic character. Position of the electronegative atom also determines the strength of an acid. Closer the electronegative atom to the generated negative charge after releasing the hydrogen ion, more is the strength of the acid.
Therefore, increasing order of the given molecules is stated below.
The increasing order of acidity of the given molecules is
(d)
Interpretation:
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Acidity of a molecule is dependent on the value of
Answer to Problem 10.46AP
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is stated below.
Explanation of Solution
Acidity of the molecules is dependent upon the stability of the ion formed after releasing the hydrogen ion. In structure
Therefore, increasing order of acidity of the given molecules is stated below.
The increasing order of acidity of the given molecules is
(e)
Interpretation:
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Acidity of a molecule is dependent on the value of
Answer to Problem 10.46AP
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is stated below.
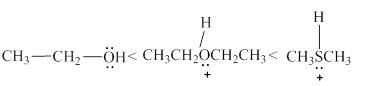
Explanation of Solution
Acidity of the molecules is dependent upon the stability of the ion formed after releasing the hydrogen ion. In structure
Therefore, increasing order of the given molecules is stated below in Figure 3.
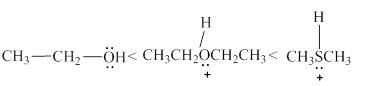
Figure 3
The increasing order of acidity of the given molecules is shown above in Figure 3.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





