
Concept explainers
(Complex Class) Consider class Complex shown in Figs. 10.14-10.16. The class enables operations on so-called complex numbers. These are numbers of the form real Part + imaginaryPart * i. where i has the value
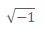
- Modify the class to enable input and output of complex numbers via overloaded >> and << operators, respectively (you should remove the toString function from the class)
- Overload the multiplication operator to enable multiplication of two complex numbers as in algebra.
- Overload the == and t = operators to allow comparisons of complex numbers.
After doing this exercise, you might want to read about the Standard Library’s complex class (from) header <comp1ex>)
- // Fig. 10.14 : Complex.h
- // Complex class definition.
- #include <string>
- #ifndef COMPLEX_H
- #define COMPLEX_H
- Class Complex {
- Public :
- Explicit Complex (double = 0.0, double = 0.0) ; // constructor
- Complex operator+(const Complex&) const; // addition
- Complex operator-(const Complex&) const; // subtraction
- Std:: string toString () const:
- Private:
- Double real : // real part
- Double imaginary ; // imaginary part
- };
- #endif
Fig. 10.14 Complex class deginition.
- // Fig. 10.15 : Complex.cpp
- // Complex class member-function definitions.
- #include <string>
- #include “Complex.h” // Complex class definition
- Using namespace std;
- // Constructor
- Complex: : Complex (double realPart, double imaginaryPart)
- : reak {real Part}, imaginary {imaginaryPart} { }
- // addition operator
- Complex Complex : : operator+ (const Complex& operand2) const {
- Return Complex {real +operand2. Real, imaginary+ operand2. Imaginary};
- }
- // subtraction operator
- Complex Complex : : operator-(const Complex& opetand2) const {
- Return Complex { real − operand 2.real, imaginary − operand2. Imaginary } :
- }
- // return string representation of a complex object in the form: (a, b)
- String Complex : : to String () const {
- Return “(“s +to_string(real) + “, “s + to_string(imaginary) + “)”s;
- }
Fig.10.15 Complex class member-function definition
25 // Fig. 10.16; fig10_16.cpp
26 // Complex class test program.
27 #include <iostream>
28 #include “Complex.h”
29 using namespace std;
30
31 int main () {
32 Complex x:
33 Complex y {4.3, 8,2}:
34 Complex z {3,3, 1,1}:
35
36 count << “x: “ << x.toString () << :\ny: “<<y.to string ()
37 << “\nz: “ <<z:
38
39 x=y+z;
40 count << “\n\nx = y+z:\n” << x.toString () << “= “ << y.toString()
41 << “ + ” <<z.toString ():
42
43 x = y - z :
44 count << “\n\nx = y-z:\n” << x. to String () << “ = “ << y. to String ()
45 << “ - “ << z. toString () << end}:
X: (0, 0)
Y: (4,3, 8,2)
Z: (3,3, 1.1)
X = y+z:
(7.6, 9.3) = (4.3, 8.2) + (3.3, 1.1)
X= y-z :
(1, 7.1) = (4.3, 8.2 ) −(3.3, 1.1)
Fig. 10.16 Complex class test program (Part 2 of 2)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Mylab Programming With Pearson Etext -- Access Code Card -- For C++ How To Program (early Objects Version)
- 7. using c++, Write a void function that accepts an integer array a and a integer SizeA, and an integer n, and adds n to every element in that array. Be sure to develop an appropriate name for your function.arrow_forwardUse P, L or E to answer whether the line of code being presented isPrototype (P),Function call (L), orFunction Header (E).arrow_forwardState whether each of the following is true or false. If false, explain why.a) Function printf always begins printing at the beginning of a new linearrow_forward
- Define Inline Functions.arrow_forwardI need the answer quickly What is the meaning of the following declaration? int(*p[5])(); a) p is pointer to functionb) p is array of pointer to functionc) p is pointer to such function which return type is the arrayd) p is pointer to array of functionarrow_forwardWhen should you prefer the use of inline function over not inline function? Explain friend function and the situation in which you should use this concept? Explain with example program.arrow_forward
 C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr

