
Concept explainers
A uniform beam resting on two pivots has a length L = 6.00 m and mass M = 90.0 kg. The pivot under the left end exerts a normal force n1 on the beam, and the second pivot located a distance ℓ = 4.00 m from the left end exerts a normal force n2. A woman of mass m = 55.0 kg steps onto the left end of the beam and begins walking to the right as in Figure P10.28. The goal is to find the woman’s position when the beam begins to tip. (a) What is the appropriate analysis model for the beam before it begins to tip? (b) Sketch a force diagram for the beam, labeling the gravitational and normal forces acting on the beam and placing the woman a distance x to the right of the first pivot, which is the origin. (c) Where is the woman when the normal force n1 is the greatest? (d) What is n1 when the beam is about to tip? (e) Use Equation 10.27 to find the value of n2 when the beam is about to tip. (f) Using the result of part (d) and Equation 10.28, with torques computed around the second pivot, find the woman’s position x when the beam is about to tip. (g) Check the answer to part (e) by computing torques around the first pivot point.
Figure P10.28
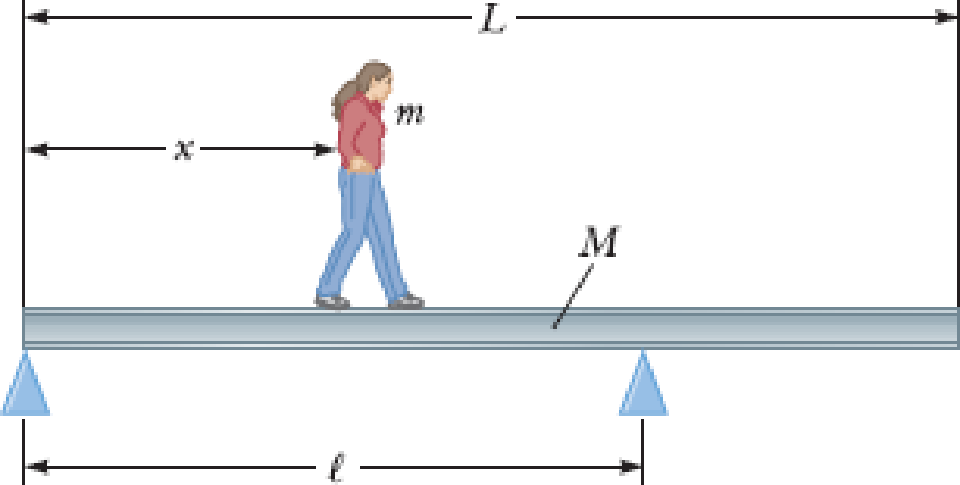
(a)
The model of beam used for analysis before it begins to tip.
Answer to Problem 28P
The object is in static equilibrium before it begins to tip.
Explanation of Solution
Initially the beam is balanced. When an object is at rest the equilibrium maintained by the object is called static equilibrium.
Hence the object is in static equilibrium before it begins to tip.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the object is in static equilibrium before it begins to tip.
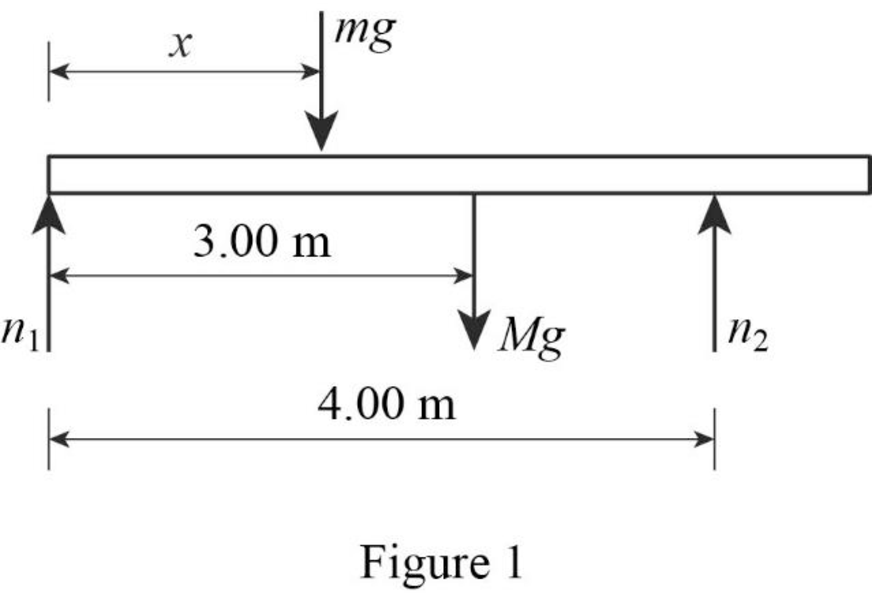
(b)
Sketch the force diagram for the beam.
Answer to Problem 28P
The force diagram of the beam is given below.
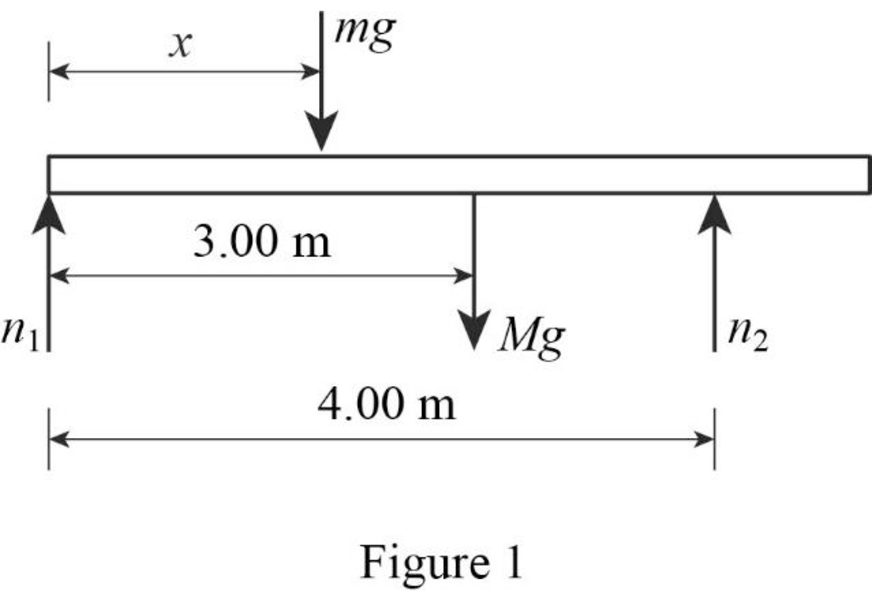
Explanation of Solution
Force diagram represents all the different kinds of forces acting on the given system. Weight of the women,
Conclusion:
The weight of the women is.
Here,
The weight of the beam corresponding to center of mass is.
Substitute,
Substitute,
The force diagram of the beam is given below.
(c)
The position of the women when the normal force is greatest.
Answer to Problem 28P
When the women is at
Explanation of Solution
The normal force
The normal force
Conclusion:
Therefore, the normal force
(d)
The value of
Answer to Problem 28P
The value of
Explanation of Solution
When the women walk from left end to right end she will reach at a point so that the beam start to rotate in clockwise direction about the right pivot. So the beam starts to lift up about the leftmost pivot, thus the normal force exerted by the pivot will be zero.
Thus the normal force
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value of
(e)
The value of
Answer to Problem 28P
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the total force acting on
Since the force exerted on beam, and normal force
Rearrange equation (IV) to obtain an expression for
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, value of
(f)
The position of women when the beam is about to tip.
Answer to Problem 28P
The position of women when the beam is about to tip is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for total torque in the beam.
When the beam is about to the tip, the torque
Substitute,
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, the position of women when the beam is about to tip is
(g)
To check the answer in part (f) computing the torque around the first pivot point.
Answer to Problem 28P
The position of the women is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the net torque about the left pivot.
Conclusion:
The net torque about the left pivot is zero.
Substitute,
The position obtained in part (f) is
Therefore, the position of the women is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Principles of Physics
- A stepladder of negligible weight is constructed as shown in Figure P12.40, with AC = BC = = 4.00 m. A painter of mass m = 70.0 kg stands on the ladder d = 3.00 m from the bottom. Assuming the floor is frictionless, find (a) the tension in the horizontal bar DE connecting the two halves of the ladder, (b) the normal forces at A and B, and (c) the components of the reaction force at the single hinge C that the left half of the ladder exerts on the right half. Suggestion: Treat the ladder as a single object, but also treat each half of the ladder separately. Figure P12.40 Problems 40 and 41.arrow_forwardA rod 7.0 in long is pivoted at a point 2.0 m from the left end. A downward force of 50 N acts at the left end, and a downward force of 200 N acts at the right end. At what distance to the right of the pivot can a third force of 300 N acting upward be placed to produce rotational equilibrium? Sole: Neglect the weight of the rod. (a) 1.0 m (b) 2.0 m (c) 3.0 m (d) 4.0 m (e) 3.5 marrow_forwardA disk with a radius of 4.5 m has a 100-N force applied to its outer edge at two different angles (Fig. P12.55). The disk has arotational inertia of 165 kg m2. a. What is the magnitude of the torque applied to the disk incase 1? b. What is the magnitude of the torque applied to the disk incase 2? c. Assuming the force on the disk is constant in each case,what is the magnitude of the angular acceleration applied tothe disk in each case? d. Which case is a more effective way of spinning the disk?Describe which quantity you are using to determine effectiveness and why you chose that quantity. FIGURE P12.55arrow_forward
- A stepladder of negligible weight is constructed as shown in Figure P10.73, with AC = BC = = 4.00 m. A painter of mass m = 70.0 kg stands on the ladder d = 3.00 m from the bottom. Assuming the floor is frictionless, find (a) the tension in the horizontal bar DE connecting the two halves of the ladder, (b) the normal forces at A and B, and (c) the components of the reaction force at the single hinge C that the left half of the ladder exerts on the right half. Suggestion: Treat the ladder as a single object, but also treat each half of the ladder separately.arrow_forwardA horizontal plank 4.00 m long and having mass 20.0 kg rests on two pivots, one at the left end and a second 1.00 m from the right end. Find the magnitude of the force exerted on the plank by the second pivot. (See Section 8.4.)arrow_forwardA bridge of length 50.0 m and mass 8.00 104 kg is supported on a smooth pier at each end as shown in Figure P12.25. A truck of mass 3.00 104 kg is located 15.0 m from one end. What are the forces on the bridge at the points of support? Figure P12.25arrow_forward
- A square plate with sides 2.0 m in length can rotatearound an axle passingthrough its center of mass(CM) and perpendicular toits surface (Fig. P12.53). There are four forces acting on the plate at differentpoints. The rotational inertia of the plate is 24 kg m2. Use the values given in the figure to answer the following questions. a. Whatis the net torque acting onthe plate? b. What is theangular acceleration of the plate? FIGURE P12.53 Problems 53 and 54.arrow_forwardA stepladder of negligible weight is constructed as shown in Figure P10.73, with AC = BC = ℓ. A painter of mass m stands on the ladder a distance d from the bottom. Assuming the floor is frictionless, find (a) the tension in the horizontal bar DE connecting the two halves of the ladder, (b) the normal forces at A and B, and (c) the components of the reaction force at the single hinge C that the left half of the ladder exerts on the right half. Suggestion: Treat the ladder as a single object, but also treat each half of the ladder separately. Figure P10.73 Problems 73 and 74.arrow_forwardA wooden door 2.1 m high and 0.90 m wide is hung by two hinges 1.8 m apart. The lower hinge is 15 cm above the bottom of the door. The center of mass of the door is at its geometric center, and the weight of the door is 260 N, which is supported equally by both hinges. Find the horizontal force exerted by each hinge on the door.arrow_forward
- A person carries a plank of wood 2.00 m long with one hand pushing down on it at one end with a force F1 and the other hand holding it up at .500 m from the end of the plank with force F2. If the plank has a mass of 20.0 kg and its center of gravity is at the middle of the plank, what are the magnitudes of the forces F1 and F2?arrow_forwardA long, uniform rod of length L and mass M is pivoted about a frictionless, horizontal pin through one end. The rod is released from rest in a vertical position as shown in Figure P10.65. At the instant the rod is horizontal, find (a) its angular speed, (b) the magnitude of its angular acceleration, (c) the x and y components of the acceleration of its center of mass, and (d) the components of the reaction force at the pivot. Figure P10.65arrow_forwardA 10.0-kg monkey climbs a uniform ladder with weight 1.20 102 N and length L = 3.00 m as shown in Figure P12.14. The ladder rests against the wall and makes an angle of = 60.0 with the ground. The upper and lower ends of the ladder rest on frictionless surfaces. The lower end is connected to the wall by a horizontal rope that is frayed and can support a maximum tension of only 80.0 N. (a) Draw a force diagram for the ladder. (b) Find the normal force exerted on the bottom of the ladder. (c) Find the tension in the rope when the monkey is two-thirds of the way up the ladder. (d) Find the maximum distance d that the monkey can climb up the ladder before the rope breaks. (e) If the horizontal surface were rough and the rope were removed, how would your analysis of the problem change? What other information would you need to answer parts (c) and (d)? Figure P12.14arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill





