
Activity-Based Costing of Customers
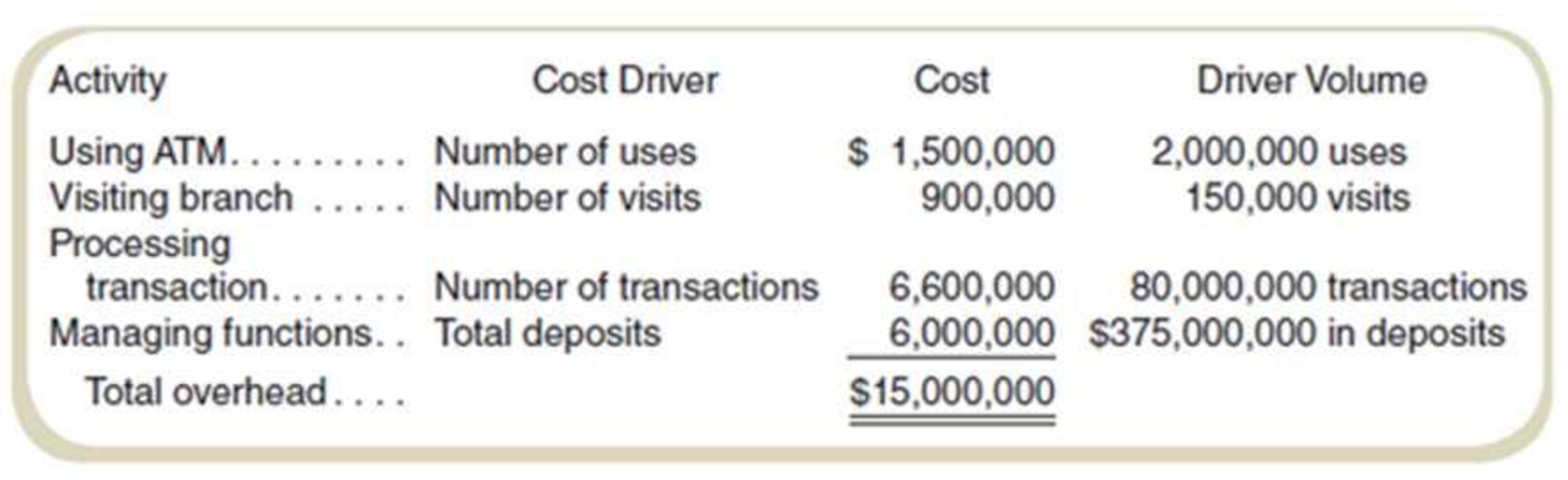
Rock Solid Bank and Trust (RSB&T) oilers only checking accounts. Customers can write checks and use a network of automated teller machines. RSB&T earns revenue by investing the money deposited; currently, it averages 5.2 percent annually on its investments of those deposits. To compete with larger banks. RSB&T pays depositors 0.5 percent on all deposits. A recent study classified the bank’s annual operating costs into four activities:
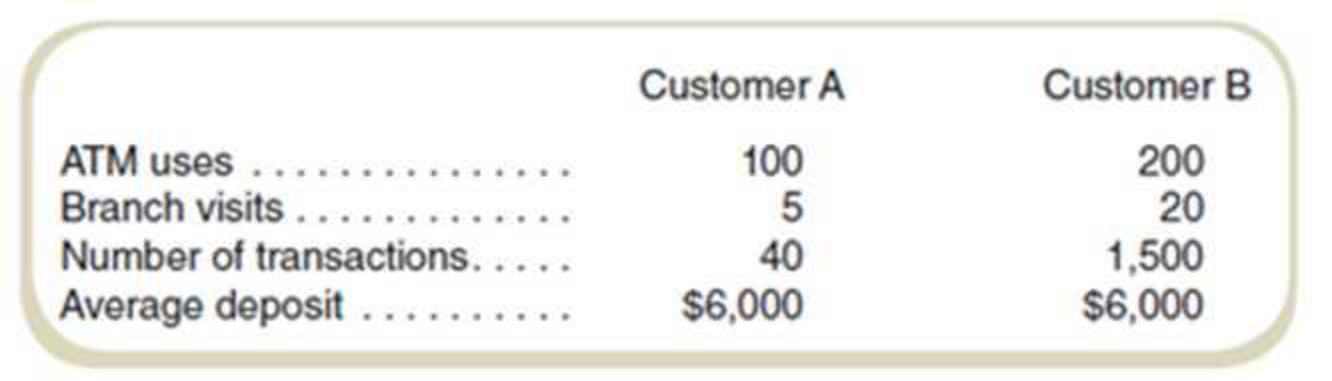
Data on two representative customers follow:
Required
- a. Compute RSB&T’s operating profits.
- b. Compute the profit from Customer A and Customer B, assuming that customer costs are based only on deposits. Interest costs = 0.5 percent of deposits; operating costs are 4 percent (= $15,000,000/$375,000,000) of deposits.
- c. Compute the profit from Customer A and Customer B, assuming that customer costs are computed using the information in the activity-based costing analysis.
a.
Compute the operating profit.
Explanation of Solution
Operating profit:
Operating profit is the amount retained by subtracting the total costs of operations occurred from the sales revenues earned.
Compute the operating profit:
| Particulars | Amount |
|
Sales revenue | $19,500,000 |
| Costs: | |
|
Interest on deposits | $1,875,000 |
| Operating costs | $15,000,000 |
|
Total costs | $16,875,000 |
|
Operating profit | $2,625,000 |
Table: (1)
b.
Compute the profit from customer A and customer B according to the information given in the question.
Explanation of Solution
Profit:
Profit is the amount retained by subtracting the total costs from the sales revenues earned.
Compute the customer profit of both the customers:
| Particulars | Customer A | Customer B |
|
Sales revenue | $312 | $312 |
|
Interest on deposits | $30 | $30 |
|
Operating costs | $240 | $240 |
|
Customer profit | $42 | $42 |
Table: (2)
Measures that are used for computation:
| Particulars | Details |
| Deposit of customer A | $6,000 |
| Deposit of customer B | $6,000 |
| Interest earned | 5.20% |
| Interests charged | 0.50% |
| Operating cost | 4.00% |
Table: (3)
c.
Compute the profit from customer A and customer B according to the information given in the question.
Explanation of Solution
Cost driver:
Cost driver refers to the factor that causes changes in the determination of the cost of the activity.
Compute the rates required for the computation of the customer profit:
| Activity | Cost driver |
Cost |
Driver volume |
Rate |
| Use ATM | Number of uses | $1,500,000 | 2,000,000 | 0.75 |
| Visit Branch | Number of visits | $900,000 | 150,000 | 6.00 |
| Process transaction | Number of transactions | $6,600,000 | 80,000,000 | 0.0825 |
| General bank overhead | Total deposits | $6,000,000 | 375,000,000 | 1.60% |
Table: (4)
| Customer A | Customer B | |
| Activity | Amount | Amount |
|
Sales revenue | $312 | $312 |
|
Interest on deposit | $30 | $30 |
| Account margin | $282 | $282 |
| Operating costs: | ||
|
Use ATM | $75 | $150 |
|
Add: Visit branch | $30 | $120 |
|
Add: Process transaction | $3 | $124 |
|
Add: General bank overhead | $96 | $69 |
| Total operating cost | $204 | $490 |
|
Customer profit | $78 | ($208) |
Table: (5)
| Particulars | Details |
| Deposit of customer A | $6,000 |
| Deposit of customer B | $6,000 |
| Interest earned | 5.20% |
| Interests charged | 0.50% |
Table: (6)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF COST ACCOUNTING BUNDLE
- CVP analysis, income taxes. The Home Style Eats has two restaurants that are open 24 hours a day. Fixed costs for the two restaurants together total $430,500 per year. Service varies from a cup of coffee to full meals. The average sales check per customer is $8.75. The average cost of food and other variable costs for each customer is $3.50. The income tax rate is 36%. Target net income is $117,600. Required: Compute the revenues needed to earn the target net income. How many customers are needed to break even? To earn net income of $117,600? Compute net income if the number of customers is 170,000.arrow_forwardNational Investor Group is opening an office in Portland, Oregon. Fixed monthly costs are office rent ($8,10), utilities ($2,000), special telephone lines ($1,500), a connection with an online brokerage service ($2,500), and the salary of a finanical planner ($5,200). Variable costs include payments to the financial planner (9% of revenue), advertising (11% of revenue), supplies and postage (4% of revenue), and usage fees for the telephone lines and computerized brokerage service (6% of revenue). REQUIREMENTS :Use the contribution margin ratio approach to compute National's breakeven revenue in dollars. If the average trade leads to $1,000 in revenue for National, how manhy trades must be made to break even? :Use the equation approach to compute the dollar revenues needed to earn a monthly target profit of $12,600. :Graph national's CVP relationships. Assume that an average trade leads to $1,000 in revenue for National. Show the breakeven point, the sales revenue line, the fixed cost…arrow_forwardClassifying Costs as Product or Period Costs Suppose that you have been given a summer job as an intern at Issac Aircams, a company that manufactures sophisticated spy cameras for remote-controlled military reconnaissance aircraft. The company, which is privately owned, has approached a bank for a loan to help finance its growth. The bank requires financial statements before approving the loan. Required: Classify each cost listed below as either a product cost or a period cost for the purpose of preparing financial statements for the bank. 1. Depreciation on salespersons’ cars. 2. Rent on equipment used in the factory. 3. Lubricants used for machine maintenance. 4. Salaries of personnel who work in the finished goods warehouse. 5. Soap and paper towels used by factory workers at the end of a shift. 6. Factory supervisors’ salaries. 7. Heat, water, and power consumed in the factory. 8. Materials used for boxing products for shipment overseas. (Units are not normally boxed.) 9.…arrow_forward
- CAN SOMEONE HELP ME WITH THIS QUESTION? Pretty Lady Cosmetic Products has an average production process time of 40 days. Finished goods are kept on hand for an average of 15 days before they are sold. Accounts receivable are outstanding an average of 35 days, and the firm receives 40 days of credit on its purchases from suppliers. Assume net sales of $1,200,000 and cost of goods sold of $900,000. Determine the average investment in accounts receivable, inventories, and accounts payable. What would be the net financing need considering only these three accounts? *Note: To solve this problem, you will need to first find the Inventory Period, the Receivables Period, and the Payment Period. A. $153,054.79 B. $154,054.79 C. $152,054.79 D. $152,154.80arrow_forwardAllocation of Administrative Costs Wical Rental Management Services manages four apartment buildings, each with a different owner. Wical’s CEO has observed that the apartment buildingswith more expensive rental rates tend to require more of her time and also the time of her staff. Thefour apartment buildings incur a total annual operating expense of $7,345,733, and these operatingexpenses are traced directly to the apartment buildings for the purpose of determining the profitearned by the building owners. The annual management fee that Wical earns is based on a percentageof total annual operating expenses and is negotiated each year. For the current year, the fee rate is 6%,and Wical has the following information for current-year average rental rates and occupancy rates:[LO 18-3]Apartment Complex Number of Units Average Occupancy Average RentCape Point 100 88.0% $1,895Whispering Woods 250 77.0 1,295Hanging Rock 200 72.0 995College Manor 350 82.0 895Total 900For the current year, Wical…arrow_forwardComputing breakeven sales and sales needed to earn a target profit; graphing CVP relationships; performing sensitivity analysis National Investor Group is opening an office in Portland, Oregon. Fixed monthly costs are office rent ($8,100), depreciation on office furniture ($1,700), utilities ($2,000), special telephone lines ($1,500), a connection with an online brokerage service ($2,500), and the salary of a financial planner ($5,200). Variable costs include payments to the financial planner (9% of revenue), advertising (11% of revenue), supplies and postage (4% of revenue), and usage fees for the telephone lines and computerized brokerage service (6% of revenue). Requirements Use the contribution margin ratio approach to compute Nationals breakeven revenue in dollars. If the average trade leads to $1,000 in revenue for National, how many trades must be made to break even? Use the equation approach to compute the dollar revenues needed to earn a monthly target profit of $12,600.…arrow_forward
- A company engaged high-end apparel sells for cash only. The marketing manager is contemplating of offering credit sales allowing 90 days to pay. Buyers understood the time value of money, so they would all wait and pay on the 90th day. As a result, the company has to carry big balances of receivable and the company would need to borrow funds from a bank at a nominal rate of 12% compounding daily based on approximate 360 days a year. The company wants to increase the base prices of its products by exactly enough to offset the bank’s interest charges. To the closest percentage point, by how much should the company raise the product’s prices?arrow_forwardSantana Rey’s two departments, Computer Consulting Services and Computer Workstation Furniture Manufacturing, have each been profitable for Business Solutions. Santana has heard of the cash conversion cycle and wants to use it as another performance measure for the workstation manufacturing department. Data below are for the most recent two quarters. 1st Quarter 2nd Quarter Days’ sales in accounts receivable . 19 days 21 days Days’ sales in inventory . 25 days 24 days Days’ payable outstanding 31 days 28 days Required 1. Compute the cash conversion cycle for the first quarter. 2. Compute the cash conversion cycle for the second quarter. 3. Did the cash conversion cycle increase or decrease from the first to the second quarter?arrow_forwardComputing margin of safety Robbie’s Repair Shop has a monthly target profit of $31,000. Variable costs are 20% of Sales, and monthly fixed costs are $19,000. Requirements Compute the monthly margin of Safety in dollars if the shop achieves its income goal. Express Robbie’s margin of safety, as a percentage of margin Sales. Why would Robbie’s management want to know the shop’s margin of safety?arrow_forward
- A CARDBOARD BOX FACTORY pays its suppliers 40 days after making the purchase and receiving the goods. The average collection period is 45 days, i.e. its customers settle their debt with the company in that time; and the average inventory age is based on the inventory turnover which is 10 times a year. The company spends about $1.23 million in operating cycle investments. With this data we need to calculate: The operating cycle.The cash conversion cycle.The cash turnover.The minimum cash balance.You plan to make modifications to your policies so that you can decrease your PPC by 10 days, and decrease your EPI by 2 times (before converting it to days). Negotiations with your supplier have been unsuccessful and the payment term has been reduced by 10 days. With these data you have to calculate: Re-calculate the Operating Cycle, the SCC, RC and SMC introducing the proposed changes.Calculate the opportunity cost that the changes will cause, if the company's interest rate is 8%.arrow_forwardBulldogs Inc. currently fills mail orders from all over the country and receipts were received in its head office. The company’s average accounts receivable is P3,125,000 and is financed by a bank loan with 10% interest. Bulldogs is considering a regional lockbox system to speed up collections. This system is projected to reduce the average accounts receivable by 15%. The annual cost of the lockbox system is P25,000. What is the estimated net annual savings in implementing the lockbox system? P22,985 P25,750 P28,455 P21,875arrow_forwardCruse Cleaning offers residential and small office cleaning services. An average cleaning service has the following price and costs. Sales price $ 128.00 per service Variable costs 90.00 per service Fixed costs 124,982 per year Cruse Cleaning is subject to an income tax rate of 22 percent. Required: How many cleaning services must Cruse Cleaning sell in a year to break even? How many cleaning services must Cruse Cleaning sell in a year to earn an annual operating profit of $34,086 after taxes?arrow_forward
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning





