
1 to 7.
Prepare payroll register for Company M from the information given.
1 to 7.
Explanation of Solution
Payroll: The total payment that a company is required to pay to its employee for the services received is called as payroll.
Payroll withholding deduction: The amounts which the employer withheld from employees’ gross pay to deduct taxes such as federal income tax, state income tax, social security tax, and Medicare tax are called payroll withholding deduction.
Payroll register: A schedule which is maintained by the company to record the earnings, earnings withholdings, and net pay of each employee is referred to as payroll register.
The purpose of payroll register is used to record the following:
- Earnings of each employee.
- Taxes (Social security tax, Medicare tax, and federal income tax) and other withholdings (health insurance, and other) of each employee.
- Net pay of each employee.
Prepare payroll register for Company M as below:
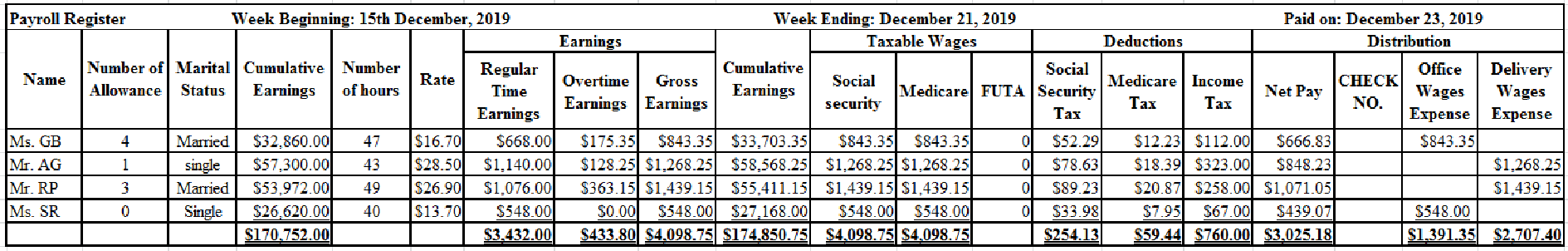
Table (1)
Working notes:
Calculate regular time earnings for Ms. GB.
Calculate regular time earnings for Mr. AG.
Calculate regular time earnings for Mr. RP.
Calculate regular time earnings for Ms. SR.
Calculate overtime earnings for Ms. GB.
Calculate overtime earnings for Mr. AG.
Calculate overtime earnings for Mr. RP.
Calculate social security tax for Ms. GB.
Calculate social security tax for Mr. AG.
Calculate social security tax for Mr. RP.
Calculate social security tax for Ms. SR.
Calculate Medicare tax for Ms. GB.
Calculate Medicare tax for Mr. AG.
Calculate Medicare tax for Mr. RP.
Calculate Medicare tax for Ms. SR.
Calculate the amount of Federal income tax for Ms. SR.
Mr. AA is single, claims zero withholding allowances, and earned weekly salary of $548.00. Hence, by using withholding table (Refer figure 10.2A) his Federal income tax amount would be $67.
Notes:
- Gross earnings are calculated by using the following formula:
- Net pay is calculated by using the following formula:
8.
Journalize the entry to record the payroll on December 21, 2019.
8.
Explanation of Solution
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in
stockholders’ equity accounts. - Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Prepare general journal entry to record the payroll on December 21, 2019.
| General Journal | Page 32 | |||||||
| Date | Accounts and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||
| 2019 | Office Wages Expense | 1,391.35 | ||||||
| December | 21 | Delivery Wages Expense | 2,707.40 | |||||
| Social Security Taxes Payable | 254.13 | |||||||
| Medicare Taxes Payable | 59.44 | |||||||
| Employees Income Taxes Payable | 760.00 | |||||||
| Wages Payable | 3,025.18 | |||||||
| (To record wages expense and payroll withholdings) | ||||||||
Table (2)
- Office Wages expense is an expense and it decreases equity value. So, debit it by $1,391.35.
- Delivery Wages expense is an expense and it decreases equity value. So, debit it by $2,707.40.
- Social security taxes payable is a liability and it is increased. So, credit it by $254.13.
- Medicare taxes payable is a liability and it is increased. So, credit it by $59.44.
- Employee income taxes payable is a liability and it is increased. So, credit it by $760.00.
- Wages payable is a liability and it is increased. So, credit it by $3,025.18.
9.
Journalize the entry to record the payment of weekly payroll on December 23, 2019.
9.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare general journal entry to record payment of weekly payroll on December 23, 2019.
| General Journal | Page 32 | ||||||
| Date | Accounts and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2019 | Wages Payable | 3,025.18 | |||||
| December | 23 | Cash | 3,025.18 | ||||
| (To record the payment of weekly payroll) | |||||||
Table (3)
- Wages payable is a liability and it is decreased. So, debit it by $3,025.18.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased. So, credit it by $3,025.18.
Analyze: The percentage of delivery wages was 66.05%
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
COLLEGE ACCOUNTING: CONTEMP APPROACH
- Audrey Martin and Beth James are partners in the Country Gift Shop, which employs the individuals listed below. Paychecks are distributed every Friday to all employees. Based on the information given, compute the amounts listed below for a weekly payroll period. Employers OASDI Tax ________ Employers HI Tax ________arrow_forwardAmanda Autry and Carley Wilson are partners in A W Gift Shop, which employs the individuals listed below. Paychecks are distributed every Friday to all employees. Based on the information given, compute the amounts listed below for a weekly payroll period. Employers OASDI Tax ________ Employers HI Tax ________arrow_forwardAdams, Inc., pays its employees weekly wages in cash. A supplementary payroll sheet that lists the employees names and their earnings for a certain week is shown below. Complete the payroll sheet by calculating the total amount of payroll and indicating the least possible number of denominations that can be used in paying each employee. However, no employees are to be given bills in denominations greater than 20.arrow_forward

 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning





