
(a)
Interpretation:
A multi-step synthesis has to be designed for the given conversion.
Concept Introduction:
Target molecule is nothing but the desired product.
Adding
The elimination reaction should be carried out under SN2 condition i.e. with strong nucleophile. So there will be no compensating substitution reaction.
The bulky base is used in the elimination reaction to maximize the amount of elimination product.
To prepare cyclic ether, the
Addition of water to the given starting material creates bifunctional compound.
(b)
Interpretation:
A multi-step synthesis has to be designed for the given conversion.
Concept Introduction:
Target molecule is nothing but the desired product.
Adding
The elimination reaction should be carried out under SN2 condition i.e. with strong nucleophile. So there will be no compensating substitution reaction.
The bulky base is used in the elimination reaction to maximize the amount of elimination product.
To prepare cyclic ether, the alkyl halide and alcohol must be a part of the same molecule.
Addition of water to the given starting material creates bifunctional compound.
(c)
Interpretation:
A multi-step synthesis has to be designed for the given conversion.
Concept Introduction:
Target molecule is nothing but the desired product.
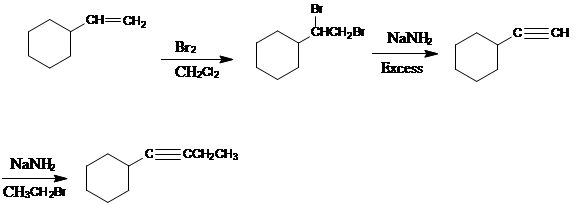 Adding
Adding
The elimination reaction should be carried out under SN2 condition i.e. with strong nucleophile. So there will be no compensating substitution reaction.
The bulky base is used in the elimination reaction to maximize the amount of elimination product.
To prepare cyclic ether, the alkyl halide and alcohol must be a part of the same molecule.
Addition of water to the given starting material creates bifunctional compound.
(d)
Interpretation:
A multi-step synthesis has to be designed for the given conversion.
Concept Introduction:
Target molecule is nothing but the desired product.
Adding
The elimination reaction should be carried out under SN2 condition i.e. with strong nucleophile. So there will be no compensating substitution reaction.
The bulky base is used in the elimination reaction to maximize the amount of elimination product.
To prepare cyclic ether, the alkyl halide and alcohol must be a part of the same molecule.
Addition of water to the given starting material creates bifunctional compound.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM(PKG) TEXT+MASTERING+SOL M
- provide an efficient synthesis for the following transformation. Please answer fast i give you upvote.arrow_forwardDraw out the complete synthesis for the target molecule below using only compounds containing three or fewer carbon atoms as the starting materials, be sure to indicate all reagents for each reaction (may require more than one step).arrow_forwardDesign a route for the synthesis of the following compounds from the starting materials shown in the left. Please answer fast I give you upvote.arrow_forward
- Complete the following synthesis by selecting from the list of 10 reagents below. Each reagent (or set of reagents) is labeled as a letter. In the answer box, simply place the order of reagents used as uppercase letters. For example, if your synthesis involves using reagent A followed by B,followed by C, and then D, your answer would be: ABCD.arrow_forwardUsing any reagent/reactant you wish and the following reactants, propose synthesis for the target products shown belowarrow_forwardPropose a multistep synthesis of the following target. All carbon atoms in the target must come from two molecules of propane. You can use any other reagents as needed. You do not have to draw any curved-arrow mechanism but are strongly encouraged to provide the products of each synthetic step.arrow_forward
- Propose a multi-step synthesis of the target molecule shown at the right, using the starting materials on the left and any other reagents you need. Show the reagents needed for each step and the product of each step. You will need 4 reaction arrows.arrow_forwardPlease help with the following: Propose a synthesis of the following molecule from the given starting material. If more than one step is necessary, be sure to number separate steps.arrow_forward4.Draw all of the target products for the reactions below. Identify the major productarrow_forward
- identify the reagents necessary to complete this synthesis. be sure to draw the product(s) for each step of your synthesisarrow_forwardDesign a multistep synthesis to show how the following compounds can be prepared from the given starting material:arrow_forwardShow how each of the following compounds can be synthesized from the given starting materials:arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
