
Concept explainers
A rigid, massless rod has three particles with equal masses attached to it as shown in Figure P11.37. The rod is free to rotate in a vertical plane about a frictionless axle perpendicular to the rod through the point P and is released from rest in the horizontal position at t = 0. Assuming m and d are known, find (a) the moment of inertia of the system of three particles about the pivot, (b) the torque acting on the system at t = 0, (c) the
Figure P11.37
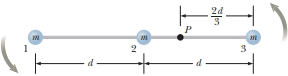
(a)
The moment of inertia of the system of three particles about the pivot.
Answer to Problem 11.49AP
The moment of inertia of the system of three particles about the pivot is
Explanation of Solution
The mass of three particles is
The formula to calculate moment of inertia is,
The distance of the particle 1 from point P is,
The distance of the particle 2 from point P is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the moment of inertia of the system of three particles about the pivot is
(b)
The torque acting on the system at
Answer to Problem 11.49AP
The torque acting on the system at
Explanation of Solution
Consider that the whole weight,
The formula to calculate torque is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the torque acting on the system at
(c)
The angular acceleration of the system at
Answer to Problem 11.49AP
The angular acceleration of the system at
Explanation of Solution
The formula to calculate angular acceleration is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angular acceleration of the system at
(d)
The linear acceleration of the particle 3 at
Answer to Problem 11.49AP
The linear acceleration of the particle 3 at
Explanation of Solution
The formula to calculate linear acceleration is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the linear acceleration of the particle 3 at
(e)
The maximum kinetic energy of the system.
Answer to Problem 11.49AP
The maximum kinetic energy of the system is
Explanation of Solution
Because the axle is fixed, no external work is performed on the system of the earth and three particles, so the total mechanical energy is conserved.
The rotation kinetic energy is maximum when rod has swung to a vertical orientation with the centre of gravity directly under the axle.
The expression for the energy is,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the maximum kinetic energy of the system is
(f)
The maximum angular speed reached by the rod.
Answer to Problem 11.49AP
The maximum angular speed reached by the rod is
Explanation of Solution
In the vertical orientation, the rod has the greatest rotational kinetic energy.
The expression for the kinetic energy is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the maximum angular speed reached by the rod is
(g)
The maximum angular momentum of the system.
Answer to Problem 11.49AP
The maximum angular momentum of the system is
Explanation of Solution
The expression for the angular momentum is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the maximum angular momentum of the system is
(h)
The maximum speed of particle 2.
Answer to Problem 11.49AP
The maximum speed of particle 2 is
Explanation of Solution
The expression for the speed is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the maximum speed of particle 2 is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Physics For Scientists And Engineers, Volume 2
- A long, uniform rod of length L and mass M is pivoted about a frictionless, horizontal pin through one end. The rod is released from rest in a vertical position as shown in Figure P10.65. At the instant the rod is horizontal, find (a) its angular speed, (b) the magnitude of its angular acceleration, (c) the x and y components of the acceleration of its center of mass, and (d) the components of the reaction force at the pivot. Figure P10.65arrow_forwardA rigid, massless rod has three particles with equal masses attached to it as shown in Figure P8.59. The rod is free to rotate in a vertical plane about a frictionless axle perpendicular to the rod through the point P and is released from rest in the horizontal position at t = 0. Assuming m and d are known, find (a) the moment of inertia of the system (rod plus particles) about the pivot, (b) the torque acting on the system at t = 0, (c) the angular acceleration of the system at t = 0, (d) the linear acceleration of the particle labeled 3 at t = 0, (e) the maximum kinetic energy of the system, (0 the maximum angular speed reached by the rod, (g) the maximum angular momentum of the system, and (h) the maximum translational speed reached by the particle labeled 2.arrow_forwardThe angular momentum vector of a precessing gyroscope sweeps out a cone as shown in Figure P11.31. The angular speed of the tip of the angular momentum vector, called its precessional frequency, is given by p=/I, where is the magnitude of the torque on the gyroscope and L is the magnitude of its angular momentum. In the motion called precession of the equinoxes, the Earths axis of rotation processes about the perpendicular to its orbital plane with a period of 2.58 104 yr. Model the Earth as a uniform sphere and calculate the torque on the Earth that is causing this precession. Figure P11.31 A precessing angular momentum vector sweeps out a cone in space.arrow_forward
- Rigid rods of negligible mass lying along the y axis connect three particles (Fig. P10.18). The system rotates about the x axis with an angular speed of 2.00 rad/s. Find (a) the moment of inertia about the x axis, (b) the total rotational kinetic energy evaluated from 12I2, (c) the tangential speed of each particle, and (d) the total kinetic energy evaluated from 12mivi2. (e) Compare the answers for kinetic energy in parts (b) and (d). Figure P10.18arrow_forwardA uniform, hollow, cylindrical spool has inside radius R/2, outside radius R, and mass M (Fig. P10.47). It is mounted so that it rotates on a fixed, horizontal axle. A counterweight of mass m is connected to the end of a string wound around the spool. The counterweight falls from rest at t = 0 to a position y at time t. Show that the torque due to the friction forces between spool and axle is f=R[m(g2yt2)M5y4t2] Figure P10.47arrow_forwardA square plate with sides 2.0 m in length can rotatearound an axle passingthrough its center of mass(CM) and perpendicular toits surface (Fig. P12.53). There are four forces acting on the plate at differentpoints. The rotational inertia of the plate is 24 kg m2. Use the values given in the figure to answer the following questions. a. Whatis the net torque acting onthe plate? b. What is theangular acceleration of the plate? FIGURE P12.53 Problems 53 and 54.arrow_forward
- Two astronauts (Fig. P10.67), each having a mass M, are connected by a rope of length d having negligible mass. They are isolated in space, orbiting their center of mass at speeds v. Treating the astronauts as particles, calculate (a) the magnitude of the angular momentum of the two-astronaut system and (b) the rotational energy of the system. By pulling on the rope, one of the astronauts shortens the distance between them to d/2. (c) What is the new angular momentum of the system? (d) What are the astronauts new speeds? (e) What is the new rotational energy of the system? (f) How much chemical potential energy in the body of the astronaut was converted to mechanical energy in the system when he shortened the rope? Figure P10.67 Problems 67 and 68.arrow_forwardA uniform beam resting on two pivots has a length L = 6.00 m and mass M = 90.0 kg. The pivot under the left end exerts a normal force n1 on the beam, and the second pivot located a distance = 4.00 m from the left end exerts a normal force n2. A woman of mass m = 55.0 kg steps onto the left end of the beam and begins walking to the right as in Figure P10.28. The goal is to find the womans position when the beam begins to tip. (a) What is the appropriate analysis model for the beam before it begins to tip? (b) Sketch a force diagram for the beam, labeling the gravitational and normal forces acting on the beam and placing the woman a distance x to the right of the first pivot, which is the origin. (c) Where is the woman when the normal force n1 is the greatest? (d) What is n1 when the beam is about to tip? (e) Use Equation 10.27 to find the value of n2 when the beam is about to tip. (f) Using the result of part (d) and Equation 10.28, with torques computed around the second pivot, find the womans position x when the beam is about to tip. (g) Check the answer to part (e) by computing torques around the first pivot point. Figure P10.28arrow_forwardIn Figure P10.40, the hanging object has a mass of m1 = 0.420 kg; the sliding block has a mass of m2 = 0.850 kg; and the pulley is a hollow cylinder with a mass of M = 0.350 kg, an inner radius of R1 = 0.020 0 m, and an outer radius of R2 = 0.030 0 m. Assume the mass of the spokes is negligible. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is k = 0.250. The pulley turns without friction on its axle. The light cord does not stretch and does not slip on the pulley. The block has a velocity of vi = 0.820 m/s toward the pulley when it passes a reference point on the table. (a) Use energy methods to predict its speed after it has moved to a second point, 0.700 m away. (b) Find the angular speed of the pulley at the same moment. Figure P10.40arrow_forward
- A uniform disk of mass m = 10.0 kg and radius r = 34.0 cm mounted on a frictionlessaxle through its center, and initially at rest, isacted upon by two tangential forces of equalmagnitude F, acting on opposite sides of itsrim until a point on the rim experiences acentripetal acceleration of 4.00 m/s2 (Fig.P13.73). a. What is the angular momentumof the disk at this time? b. If F = 2.00 N, howlong do the forces have to be applied to thedisk to achieve this centripetal acceleration? FIGURE P13.73arrow_forwardConsider the disk in Problem 71. The disks outer rim hasradius R = 4.20 m, and F1 = 10.5 N. Find the magnitude ofeach torque exerted around the center of the disk. FIGURE P12.71 Problems 71-75arrow_forwardA student sits on a freely rotating stool holding two dumbbells, each of mass 3.00 kg (Fig. P10.56). When his arms are extended horizontally (Fig. P10.56a), the dumbbells are 1.00 m from the axis of rotation and the student rotates with an angular speed of 0.750 rad/s. The moment of inertia of the student plus stool is 3.00 kg m2 and is assumed to be constant. The student pulls the dumbbells inward horizontally to a position 0.300 m from the rotation axis (Fig. P10.56b). (a) Find the new angular speed of the student. (b) Find the kinetic energy of the rotating system before and after he pulls the dumbbells inward. Figure P10.56arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning





