
Concept explainers
• LO11–2
For each of the following depreciable assets, determine the missing amount (?). Abbreviations for depreciation methods are SL for straight line, SYD for sum-of-the-years’-digits, and DDB for double-declining balance.
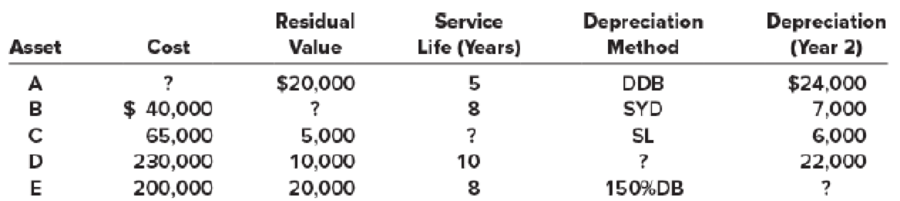
Depreciation:
Depreciation refers to the reduction in the monetary value of a fixed asset due to its wear and tear or obsolescence. It is a method of distributing the cost of the fixed assets over its estimated useful life. The following is the formula to calculate the depreciation.
To determine: The missing amounts.
Explanation of Solution
Asset A:
In the given case cost of the asset is missing. Given information is residual value $20,000; service life 5 years, depreciation method: double declining balance method and depreciation in year 2 is $24,000.
Double declining balance (DDB) method:
In this method of depreciation, the depreciation is calculated by multiply beginning of year book value, not depreciable base, by an annual rate that is a multiple of the straight line rate.
Determine cost of the asset.
Beginning value of the asset A at year 1 is calculated as follows:
Hence, cost at year 1 is $100,000.
Asset B:
In given case residual value is missing. Given information is cost of the asset B is $40,000; service life is 8 years; depreciation method is sum of the year’s digit method; depreciation in year 2 is $7,000.
Sum-of- the-years’ digits (SYD) method:
Sum-of-the years’ digits method determines the depreciation expense by multiplying the depreciable base and declining fraction.
Determine the residual value of asset B
Working note:
Conclusion:
Hence, the residual value of the asset B is $4,000.
Asset C:
In the given case for asset C, estimated life is missing. Given information is as follows cost of the asset is $65,000; residual value of the asset is $5,000; depreciation method is straight line method and year 2 depreciation is $6,000.
Straight line method:
Under the straight-line method of depreciation, the same amount of depreciation is allocated every year over the estimated useful life of an asset.
Determine estimated life of the asset C
Hence, estimated life or service life of the asset C is 10 Years.
Asset D:
In the given case, method of depreciation is missing. Given information is as follows: cost of the asset D is $230,000; residual value of the asset D is $10,000; service life is 10 years; depreciation for year 2 is $22,000.
Determine the method of depreciation.
Hence, straight line method of depreciation is used to determine the depreciation of asset D.
Asset E:
In the given situation depreciation for year 2 is missing. Given information is as follows: cost of the asset E $200,000; residual value of the asset E is $20,000; service life is 8 years; depreciation method is 150% declining method.
One hundred fifty percent declining balance:
In this method of depreciation, the depreciation is calculated by multiply beginning of year book value, not depreciable base, by an annual rate that is a 150% or 1.5 of the straight line rate.
Determine the depreciation on asset E for year 2.
Depreciation on asset E for year 1 is $37,500
For year 2 depreciation expense is calculated as follows
Hence, depreciation expense for year 2 is $30,469.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting
- LO1 The purpose of depreciation is to (a) spread the cost of an asset over its useful life. (b) show the current market value of an asset. (c) set up a reserve fund to purchase a new asset. (d) expense the asset in the year it was purchased.arrow_forwardLO1 The purpose of depreciation is to record the assets market value in the accounting records.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements are true about the revaluation model perIAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipment?1) Excess depreciation as a result of a revaluation exercise can betransferred between reserves2) Depreciation must be charged based on the historical cost of theasset3) All assets of the same class must be revalued4) Valuations must be independent and carried out regularly Which is correct ?a) 1, 3 and 4b) All of the abovec) 1 and 3d) 2, 3 and 4arrow_forward
- Which statement is INCORRECT about subsequent measurement of intangible assets? Q7 Select one: a. When using the cost model an entity should estimate the estimated useful life as well as the estimated residual value if the asset is determined to have an indefinite useful life b. When using the cost model an entity should estimate the estimated useful life as well as the estimated residual value if the asset is determined to have a definite useful life. c. The same model chosen by an entity should be used for all intangible assets in the same class. d. Intangible assets may be measured using either the cost model or the revalued cost model.arrow_forward46. Evaluate the following statements: S1. In the sum-of-the-years'-digits method, residual value is not used in the computations of depreciation expense. S2. Straight-line depreciation assumes equal usefulness in each time period, and the periodic charge is not affected by asset productivity or efficiency variations. S3. The residual value of an asset is deducted from the depreciable base when calculating double-declining-balance depreciation. a. True, False, True b. False, True, False c. False, False, True d. False, False, False e. True, True, False f. True, True, True g. False, True, Truearrow_forward34a 34 - Which of the following statements about depreciation is false? a) The asset to be depreciated should be among the assets of the enterprise. B) Proportional depreciation method can be applied for all tangible fixed assets. NS) For a property, plant and equipment to be depreciated, its economic life must be more than one year. D) As a result of use, wear, tear, depreciation or obsolescence must be experienced in the tangible asset. TO) Depreciation is a type of expense that does not require a cash outflow.arrow_forward
- Question 36: Match each depreciation function with its best description. SLN SYD DDB Results in the same depreciation expense each period Bases depreciation on the number of years in the asset's useful life Accelerated depreciation method that doesn't consider salvage value in the initial calculationsarrow_forwardquestion 10 A change in salvage value or estimated life of an asset should 1) be handled in future periods only. 2) result in restatement of prior period statements. 3) be handled in current and future periods. 4) be handled retroactively.arrow_forwardPQ16.03 Equipment with a cost of $450,000 has an estimated salvage value of $30,000 and an estimated life of 4 years or 10,000 hours. It is to be depreciated by the declining balance method. What is the amount of depreciation for the first full year, during which the equipment was used 2,700 hours?arrow_forward
- 26. haracteristics of Depreciation Methods In each dropdown below is a list of common depreciation methods and characteristics related to depreciation. Required: Select one or more of the depreciation methods with each characteristic. 1. Results in depreciation expense that decreases over the life of the asset 2. Results in depreciation expense that increases over the life of the asset 3. Allocates the same amount of cost to each period of a depreciable asset's life 4. Calculated by multiplying a constant depreciation rate by depreciable cost 5. Calculated by applying a constant depreciation rate to the asset's book value at the beginning of the period 6. Results in lowest income tax expense in early years of the asset's life 7. Consistent with the matching process Options: Straight-line depreciation method Declining balance depreciation method Units-of-production depreciation method when actual units produced increases over the life of the asset All of these…arrow_forwardBLOCK C/2018/2 Why is there a transition to straight-line depreciation when applying the planar declining balance depreciation?arrow_forwardQ1 Which of the following statement (s) is (are) true? (i) When no future economic benefits are no longer expected to flow from an intangible asset, such asset should be derecognized the financial statements of an organization. (ii) When an intangible asset is derecognized, the carrying amount should be written off as a loss in the profit or loss statement at the date of retirement of the asset. (iii) When an intangible asset is sold, the difference between the carrying amount and consideration received is recognized in the profit or loss statement at the date of the sale. (iv) Consideration to be received in the event of sale of an intangible asset should only be cash Select one: a. (ii) and (iv) only b. (i) and (ii) only c. (i) and (iv) only d. (i), (ii) and (iii) onlyarrow_forward
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,

