
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
There are primarily four types of acid-base titrations –
- Strong base vs strong acid
- Strong base vs weak acid
- Weak base vs strong acid
- Weak base vs weak acid
The term
Answer to Problem 11.6P
The
| S.No | Volume of
|
|
| 1. |
|
|
| 2. |
|
|
| 3. |
|
|
| 4. |
|
|
| 5. |
|
|
| 6. |
|
|
| 7. |
|
|
| 8. |
|
|
The graph of
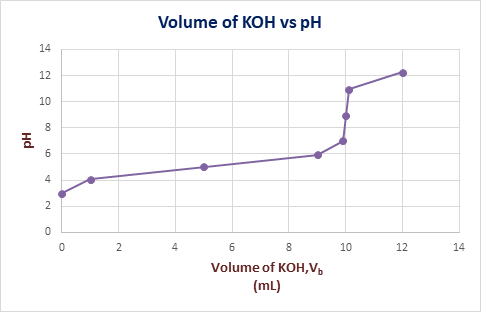
Explanation of Solution
Given that volume of base,
When volume of base added is
Solving for ‘x’,
When volume of
The titration reaction at this instant is,
Their respective concentration is,
Substitute the values known to determine
When volume of
The titration reaction at this instant is,
Their respective concentration is,
Substitute the values known to determine
When volume of
The titration reaction at this instant is,
Their respective concentration is,
Substitute the values known to determine
When volume of
The titration reaction at this instant is,
Their respective concentration is,
Substitute the values known to determine
When volume of
The titration reaction at this instant is,
Formal concentration of weak acid at this instant is,
After reaction of Hydrolysis of conjugate base,
Solving for ‘x’,
Substitute the values known to determine
After reaching the equivalence point, continual addition of base increases the concentration of base so that we need to calculate
When volume of base added is
Substitute the values known to determine
When volume of base added is
Substitute the values known to determine
The graph of

The
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
QUAN. CHEM. ANALYSIS. W/ACCESS>LLF< >I
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





