Given that volume of base,
KOH
and it is denoted by
Vb.
Given the strength (
M1
) and volume of formic acid
HCOOH
solution (
V1
) and strength of
KOH
(
M2
), the volume of
KOH
at equivalence point (
V2
)is calculated as,
V1M1 = V2M250.0 mL× 0.0500 M = V2×0.0500MV2 = 50 mL× 0.0500 M0.0500M = 50.0 mL
The reaction occurring in titration of formic acid with
KOH
is represented as,
HCOOH+OH−→HCOO−+H2O
When volume of base added is
0.00mL
, that is in absence of base, the
pH
depends upon the dissociation of formic acid. Since it is a weak acid it doesn’t dissociate completely into individual ions.
HA⇌H++A−
[H+]=[A−]=x, [HA]=0.0500−x
and
Ka of HCOOH is 1.8×10−4
Ka
for the above reaction is,
Ka = x20.0500−x1.8×10−4 = x20.0500−x
Solving for ‘x’,
x=2.91×10−3M=[H+]
pH
is determined as,
pH = - log[H+] = -log[2.91×10−3] = 2.54
When volume of
KOH
added is
10.0mL
, the base begins to react with acid. Upon reaction with base the acid forms conjugate base. The titrating mixture then becomes buffer. The concentration of conjugate base formed increases with addition of base at each step. Using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
pH
can be determined.
The titration reaction at this instant is,
HA + OH−→ A−+H2O
Their respective concentration is,
HA + OH− → A−+ H2O_______________________________________________________Initial: 50 mL 10 mL - -Final: 50-10 mL - 10 mL -
Substitute the values known to determine
pH
,
pH = pKa+ log[A−][HA] = 3.744 +log(1040) = 3.14
When volume of
KOH
added is
20.0mL
, the base begins to react with acid. Upon reaction with base the acid forms conjugate base. The titrating mixture then becomes buffer. The concentration of conjugate base formed. Using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
pH
can be determined.
The titration reaction at this instant is,
HA + OH−→ A−+H2O
Their respective concentration is,
HA + OH− → A−+ H2O_______________________________________________________Initial: 50 mL 20 mL - -Final: 50-20 mL - 20 mL -
Substitute the values known to determine
pH
,
pH = pKa+ log[A−][HA] = 3.744 +log(2030) = 3.57
When volume of
KOH
added is
25.0mL
, the base begins to react with acid. Upon reaction with base the acid forms conjugate base. The titrating mixture then becomes buffer. The concentration of conjugate base formed. Using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
pH
can be determined.
The titration reaction at this instant is,
HA + OH−→ A−+H2O
Their respective concentration is,
HA + OH− → A−+ H2O_______________________________________________________Initial: 50 mL 25 mL - -Final: 50-25 mL - 25 mL -
Substitute the values known to determine
pH
,
pH = pKa+ log[A−][HA] = 3.744 +log(2525) = 3.74
When volume of
KOH
added is
30.0mL
, the base begins to react with acid. Upon reaction with base the acid forms conjugate base. The titrating mixture then becomes buffer. The concentration of conjugate base formed. Using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
pH
can be determined.
The titration reaction at this instant is,
HA + OH−→ A−+H2O
Their respective concentration is,
HA + OH− → A−+ H2O_______________________________________________________Initial: 50 mL 30 mL - -Final: 50-30 mL - 30 mL -
Substitute the values known to determine
pH
,
pH = pKa+ log[A−][HA] = 3.744 +log(3020) = 3.92
When volume of
KOH
added is
40.0mL
, the base begins to react with acid. Upon reaction with base the acid forms conjugate base. The titrating mixture then becomes buffer. The concentration of conjugate base formed. Using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
pH
can be determined.
The titration reaction at this instant is,
HA + OH−→ A−+H2O
Their respective concentration is,
HA + OH− → A−+ H2O_______________________________________________________Initial: 50 mL 40 mL - -Final: 50-40 mL - 40 mL -
Substitute the values known to determine
pH
,
pH = pKa+ log[A−][HA] = 3.744 +log(4010) = 4.35
When volume of
KOH
added is
45.0mL
, the base begins to react with acid. Upon reaction with base the acid forms conjugate base. The titrating mixture then becomes buffer. The concentration of conjugate base formed. Using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
pH
can be determined.
The titration reaction at this instant is,
HA + OH−→ A−+H2O
Their respective concentration is,
HA + OH− → A−+ H2O_______________________________________________________Initial: 50 mL 45 mL - -Final: 50-45 mL - 45 mL -
Substitute the values known to determine
pH
,
pH = pKa+ log[A−][HA] = 3.744 +log(455) = 4.70
When volume of
KOH
added is
48.0mL
, the base begins to react with acid. Upon reaction with base the acid forms conjugate base. The titrating mixture then becomes buffer. The concentration of conjugate base formed. Using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
pH
can be determined.
The titration reaction at this instant is,
HA + OH−→ A−+H2O
Their respective concentration is,
HA + OH− → A−+ H2O_______________________________________________________Initial: 50 mL 48 mL - -Final: 50-48 mL - 2 mL -
Substitute the values known to determine
pH
,
pH = pKa+ log[A−][HA] = 3.744 +log(482) = 5.12
When volume of
KOH
added is
50.0mL
, all of the acid has been converted to its conjugate base as the equivalence point is reached. Hydrolysis of conjugate base determines the
pH.
The titration reaction at this instant is,
A− + H2O→ HA+OH−
formal concentration of formic acid at this instant is,
F = (50mL50mL+50mL)×0.05M=0.025M
After reaction of Hydrolysis of conjugate base,
[HA]=[OH−]=x, [A−]=0.025−x
Kb
for the above reaction is known to be
5.56×10−11
and hence,
Kb = x20.025−x5.56×10−11 = x20.025−x
Solving for ‘x’,
x=[OH−]=1.18×10−6M
Substitute the values known to determine
pH
,
pH = -logKw[OH−] = -log(1×10−141.18×10−6) = 8.07
After reaching the equivalence point, continual addition of base increases the concentration of base so that we need to calculate
[OH−]
to determine
pH.
As the concentration of
[OH−]
increases upon each addition of acid,
pH
of the reaction medium increases.
When volume of base added is
50.5mL
,
[OH−] =(50.5−50 mL100.5 mL)×0.0500M = 2.5×10−4M
Substitute the values known to determine
pH
,
pH+pOH = 14pH = 14 - pOH = 14-(-log [OH−]) = 14-(-log(2.5×10−4)) = 14 - 3.60 = 10.4
When volume of base added is
51mL
,
[OH−] =(51−50 mL101 mL)×0.0500M = 4.95×10−4M
Substitute the values known to determine
pH
,
pH+pOH = 14pH = 14 - pOH = 14-(-log [OH−]) = 14-(-log(4.95×10−4)) = 14 - 3.31 = 10.69
When volume of acid added is
52mL
,
[OH−] =(52−50 mL102 mL)×0.0500M = 9.80×10−4M
Substitute the values known to determine
pH
,
pH+pOH = 14pH = 14 - pOH = 14-(-log [OH−]) = 14-(-log(9.80×10−4)) = 14 - 3.009 = 10.99
When volume of acid added is
55mL
,
[OH−] =(55−50 mL105 mL)×0.0500M = 0.0024M
Substitute the values known to determine
pH
,
pH+pOH = 14pH = 14 - pOH = 14-(-log [OH−]) = 14-(-log(0.0024)) = 14 - 2.62 = 11.38
When volume of acid added is
60mL
,
[OH−] =(60−50 mL110 mL)×0.0500M = 0.0045M
Substitute the values known to determine
pH
,
pH+pOH = 14pH = 14 - pOH = 14-(-log [OH−]) = 14-(-log(0.0045)) = 14 - 2.35 = 11.65
The graph of
pH
versus volume of
KOH
is plotted as,
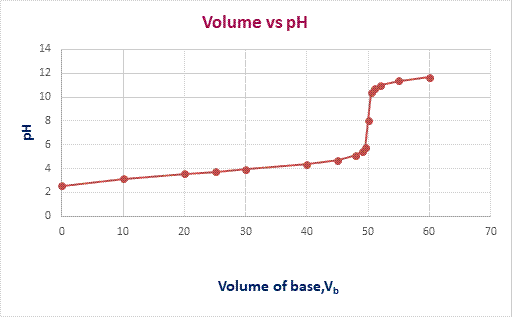

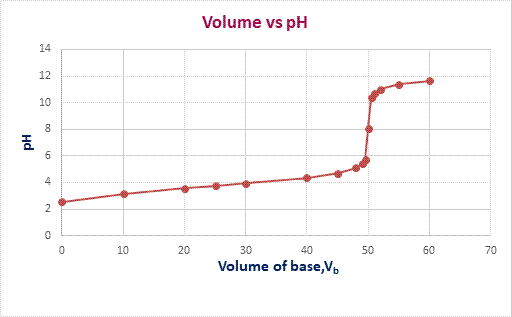

 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY




