
(a)
Interpretation: The galvanic cells based on given overall reaction needs to be sketched and the value of
Concept Introduction: A galvanic cell is an electro chemical cell that drives electrical energy from
In a galvanic cell the oxidation and the reduction half cells are separated by a connecting wire so that electrons can flow through the wire.
(a)
Answer to Problem 19E
Sketch of a galvanic cell is as follows:
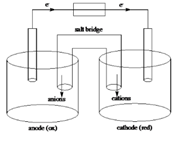
Values of
Explanation of Solution
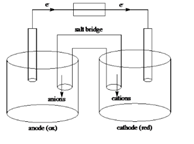
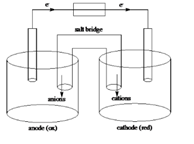
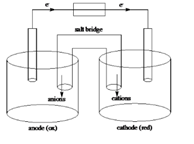
Below is a sketch of a galvanic cell where electrons flow from anode to cathode with a salt bridge between two to supply the required ions and complete the circuit. Cations will always flow to the anode and anions will always flow to the cathode.
By examining oxidation number of atoms in the reaction determine which compound is oxidized and which being reduced.
In above reaction Cr has +3 oxidation state and Cl has 0 oxidation state and in products Cr has +6 oxidation state and Cl has -1 oxidation state. Oxidation number increased for Cr, it is oxidized. This means that
Determine actual half reactions that have occurred.
Cr has lost three electrons because Cr atom has gone from +3 to +6. Add six electrons to the products. The half reaction is now change balanced as well.
It has been converted to
Each Cl atom required one electron because they have gone from 0 to -1, thus add two electrons in reactants for a change balance.
Add two half reactions together and cancel out the electrons to determine overall process. Because Cr half reaction has six electrons multiply Cl half reaction by three before adding two together.
Determine the standard reduction potential from reference table to calculate
Add these values together to give
(b)
Interpretation: The galvanic cells based on given overall reaction needs to be sketched and the value of
Concept Introduction: A galvanic cell is an electro chemical cell that drives electrical energy from chemical reactions taking place within a particular cell.
In a galvanic cell the oxidation and the reduction half cells are separated by a connecting wire so that electrons can flow through the wire.
(b)
Answer to Problem 19E
Sketch of a galvanic cell is as follows:
Values of
Explanation of Solution
By examining oxidation number of atoms in the reaction determine which compound is oxidized and which being reduced.
In above reaction Cu has +2 oxidation state and Mg has 0 oxidation state and in products Cu has 0 oxidation state and Mg has +2oxidation state. Oxidation number increased for Mg, it is oxidized. This means that Mg is at the anode. For Cu oxidation number decreased, it was reduced. This means that
Add two half reactions together and cancel out electrons determine overall process.
Determine the standard reduction potential from reference table to calculate
Add these values together to give
(c)
Interpretation: The galvanic cells based on given overall reaction needs to be sketched and the value of
Concept Introduction: A galvanic cell is an electro chemical cell that drives electrical energy from chemical reactions taking place within a particular cell.
In a galvanic cell the oxidation and the reduction half cells are separated by a connecting wire so that electrons can flow through the wire.
(c)
Answer to Problem 19E
Sketch of a galvanic cell is as follows:
Values of
Explanation of Solution
By examining oxidation number of atoms in the reaction determine which compound is oxidized and which being reduced.
In above reaction I has +5 oxidation state and Fe has +2 oxidation state and in products I has 0 oxidation state and Fe has +3oxidation state. Oxidation number increased for Fe, it is oxidized. This means that
Determine actual half reactions that have occurred
Each I atom has gone from +5 to 0 oxidation state, thus it has gained five electrons. Add ten electrons to reactants. Half-reaction is now charge balanced as well.
To determine overall process add two half reactions together and cancel out electrons. Because I half-reaction has ten electrons, multiply Fe half-reaction by ten before adding two together.
Determine standard reduction potentials from reference table to calculate
Add these values together to give
(d)
Interpretation: The galvanic cells based on given overall reaction needs to be sketched and the value of
Concept Introduction: A galvanic cell is an electro chemical cell that drives electrical energy from chemical reactions taking place within a particular cell.
In a galvanic cell the oxidation and the reduction half cells are separated by a connecting wire so that electrons can flow through the wire.
(d)
Answer to Problem 19E
Sketch of a galvanic cell is as follows:
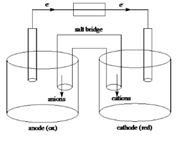
Values of
Explanation of Solution
By examining oxidation number of atoms in the reaction determines which compound is oxidized and which being reduced.
In above reaction Ag has +1 oxidation state and Zn has 0 oxidation state and in products Ag has 0 oxidation state and Zn has +2 oxidation state. This means Zn is at anode. Because oxidation number decrease for Ag. It is reduced. This means that
Determine actual-half reactions that have occurred. Zn has only been converted to
Zn loses two electrons so add two electrons to products to charge balance half-reaction.
Determine standard reduction potentials from reference table to calculate
Add these values together to give
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- Assume the following electrochemical cell simulates the galvanic cell formed by copper and zinc in seawater at pH 7.90 and 25 C. Zn | Zn(OH)2(s) | OH(aq) || Cu(OH)2(s) | Cu(s) a. Write a balanced equation for the reaction that occurs at the cathode. b. Write a balanced equation for the reaction that occurs at the anode. c. Write a balanced chemical equation for the overall reaction. d. Determine the potential (in volts) of the cell.arrow_forwardA galvanic cell is based on the following half-reactions: In this cell, the copper compartment contains a copper electrode and [Cu2+] = 1.00 M, and the vanadium compartment contains a vanadium electrode and V2+ at an unknown concentration. The compartment containing the vanadium (1.00 L of solution) was titrated with 0.0800 M H2EDTA2, resulting in the reaction H2EDTA2(aq)+V2+(aq)VEDTA2(aq)+2H+(aq)K=? The potential of the cell was monitored to determine the stoichiometric point for the process, which occurred at a volume of 500.0 mL H2EDTA2 solution added. At the stoichiometric point, was observed to be 1 .98 V. The solution was buffered at a pH of 10.00. a. Calculate before the titration was carried out. b. Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant, K, for the titration reaction. c. Calculate at the halfway point in the titration.arrow_forwardAn electrolysis experiment is performed to determine the value of the Faraday constant (number of coulombs per mole of electrons). In this experiment, 28.8 g of gold is plated out from a AuCN solution by running an electrolytic cell for two hours with a current of 2.00 A. What is the experimental value obtained for the Faraday Constant?arrow_forward
- A half-cell that consists of a copper wire in a 1.00 M Cu(NO3)2 solution is connected by a salt bridge to a solution that is 1.00 M in both Pu3+ and Pu4+, and contains an inert metal electrode. The voltage of the cell is 0.642 V, with the copper as the negative electrode. (a) Write the half-reactions and the overall equation for the spontaneous chemical reaction. (b) Use the standard potential of the copper half-reaction, with the voltage of the cell, to calculate the standard reduction potential for the plutonium half-reaction.arrow_forwardAn electrochemical cell consists of a silver metal electrode immersed in a solution with [Ag+] = 1.00 M separated by a porous disk from a compartment with a copper metal electrode immersed in a solution of 10.00 M NH3 that also contains 2.4 103 M Cu(NH3)42+. The equilibrium between Cu2+ and NH3 is: Cu2+(aq)+4NH3(aq)Cu(NH3)42+(aq)K=1.01013 and the two cell half-reactions are: Assuming Ag+ is reduced, what is the cell potential at 25C?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





