
Concept explainers
Using the terms origin, insertion, and belly, describe how skeletal muscles produce body movements by pulling on bones.
To review:
The way in which the skeletal muscles move the body parts, considering the terms belly, insertion, and origin.
Introduction:
The muscle system helps in the movement of body in a uniform manner. The skeletal muscles are the basic components of body, which leads to accurate maintenance of posture. Their function can be controlled in a remarkable manner as they are voluntary muscles.
Explanation of Solution
The bones are connected with each other through tendons and muscles, which work together to bring movement of the body parts. Contraction of the skeletal muscle leads to articulation of the bones, in which one bone remains stationary and the other one moves in an opposite direction.
When muscle tendon gets attached to a stationary bone present in the muscular system, it is called origin. It is generally proximal in position. On the other hand, when muscle tendon gets attached to movable bone, it is called as insertion. It is usually distal in position. The fleshy fragment of muscle present between the tendons is called belly. The figure given below shows the three points of the muscle's tendon attachment on the bones.
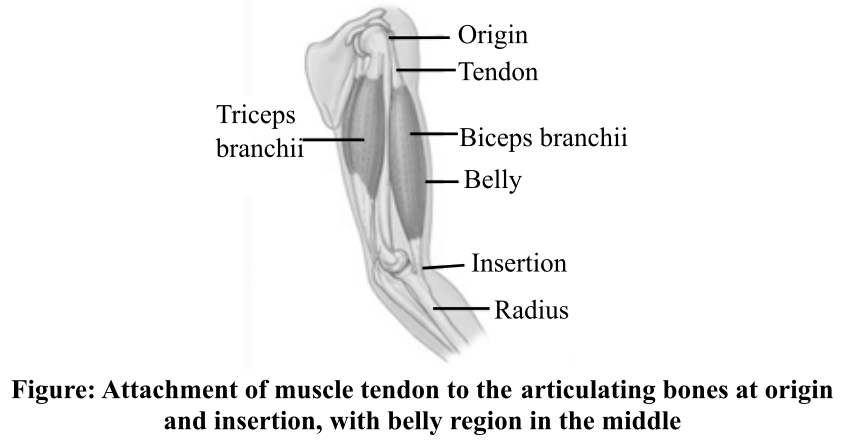
Thus, the attachment of the muscle's tendon with the stationary and movable articulating bones is known as origin and insertion, respectively. The middle portion of the connecting muscle is called belly.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
PRIN.OF ANAT.+PHYSIO.-WILEYPLUS+BB
- Describe how muscles generate different levels of contractive forcearrow_forwardHow are muscles formed? Explain.arrow_forwarda. Explain why the muscles of the legs of a childwith Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy appearlarge.b. Explain why only boys are affected byDuchenne’s muscular dystrophy.c. Explain why a child with muscular dystrophypulls himself up a flight of stairs.arrow_forward
- Do you think flexibility exercises work to make tendons or ligaments more flexible? Why would flexibility be so important to musculoskeletal health?arrow_forwardDescribe three types of musculoskeletal levers and their respective advantages?arrow_forwardDetermine the muscles involved in common movements Lists the joints used Discuss the physiology of the movement Movements: Jumping (search spring actuated models) Frog Muscles involved: quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes Joints: hip joint, knee joint, and ankle joint Physiology of the movement: The moment when the frog jumps, such as a catapult or archer’s bow, the tendons which wrap around the ankle release energy, which causes a rapid extension of the ankle that drives the frog forward. Grasshopper Muscles involved: Joints: Physiology of the movement: Dolphin Muscles involved: peduncle (in the tail section) Joints: Physiology of the movement: Running Elephant Muscles involved: Joints: Physiology of the movement: Cheetah Muscles involved: Joints: Physiology of the movement: Iguana (or any lizard with a tail) Muscles involved: Joints: Physiology of the movement: Flying/Gliding/Swimming Hummingbird Muscles involved: Joints: Physiology of the…arrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning
Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning



