
(a)
The market demand curve, price, and output under the monopolist.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The market demand curve for Otters is given as
The marginal revenue of the market can be derived as follows:
The market marginal revenue is
By substituting the value of Q in the demand equation, the
Thus, the market demand curve can be illustrated as follows:
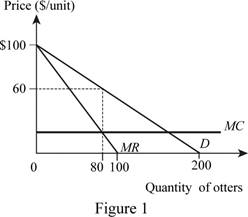
The monopoly output and price are 80 units and $60 per unit.
Imperfect competition: The imperfect competition is the market structure where there are many sellers selling the differentiated products and there will be information asymmetry in the market which provides some market control to the producers.
(b)
The output in the market by A.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
When firm J announces that half of the monopoly output would be brought by J, firm J would bring 40 units. By knowing this, the residual demand for A can be calculated as follows:
Inverse demand equation (Price) for firm A can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the marginal revenue curve of A will be
Thus, A's profit maximizing output would be 60 units.
(c)
Industrial output, price, and each seller's profit.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The output by J is 40 units and the output by A is 60 units, which means that the total industrial output would be the summation of these two which is equal to 100 units. The price can be calculated by substituting the values of the two quantities in the demand function as follows:
Thus, the price of the market would be $50 per unit. Thus, the profit of each seller can be calculated as follows:
Similarly, the profit of A can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the profit of A is $1,800 and that of J is $1,200.
(d)
Industrial output, price, and each seller's profit.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
When firm J knows that the output brought by A is 60 units, the residual demand for the J can be calculated as follows:
Inverse demand equation (Price) for firm J can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the marginal revenue curve of J will be
Thus, J's profit maximizing output would be 50 units. The output by J is 50 units and the output by A is 60 units, which means that the total industrial output would be the summation of these two which is equal to 110 units. The price can be calculated by substituting the values of the two quantities in the demand function as follows:
Thus, the price of the market would be $45 per unit. Thus, the profit of each seller can be calculated as follows:
Similarly, the profit of A can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the profit of A is $1,500 and that of J is $1,250.
(e)
Cournot equilibrium in the economy.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The market demand curve is
The marginal revenue of firm J can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the marginal revenue curve for J will be
The marginal revenue of firm A can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the marginal revenue curve for J will be
Similarly, A can be calculated as follows:
Thus, by substituting the reaction function of A in J the equilibrium output can be provided as follows:
Since A also faces the identical problem, the output of A will also be 53.33. Thus, the total output is 106.66 and this can be substituted in the market demand in order to calculate the market price as follows:
Thus, the Cournot equilibrium price is $46.67 and the output is 53.33. Since part d calculated the outputs and prices that are different, they are not Cournot equilibrium prices and outputs.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
LaunchPad for Goolsbee's Microeconomics (Six Month Access)

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





