
Concept explainers
Chemical/Bio Engineering
An irreversible, first-order reaction takes place in four well mixed reactors (Fig. P12.10),
Thus, the rate at which A is transformed to B can be represented as
The reactors have different volumes, and because they are operated at different temperatures, each has a different reaction rate:
| Reactor | V, L |
|
| 1 | 25 | 0.05 |
| 2 | 75 | 0.1 |
| 3 | 100 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 25 | 0.1 |
Determine the concentration of A and B in each of the reactors at steady state.
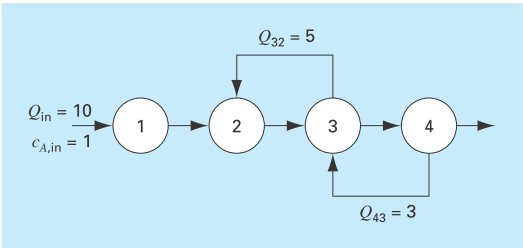
FIGURE P12.10
To calculate:
Answer to Problem 10P
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Write the provided values of the volume and rate of reaction.
Formula used:
Write system of linear equations in matrix form.
And,
The term
Calculation:
Consider the provided diagram for an irreversible first order reaction takes place in four will-mixed reactors.
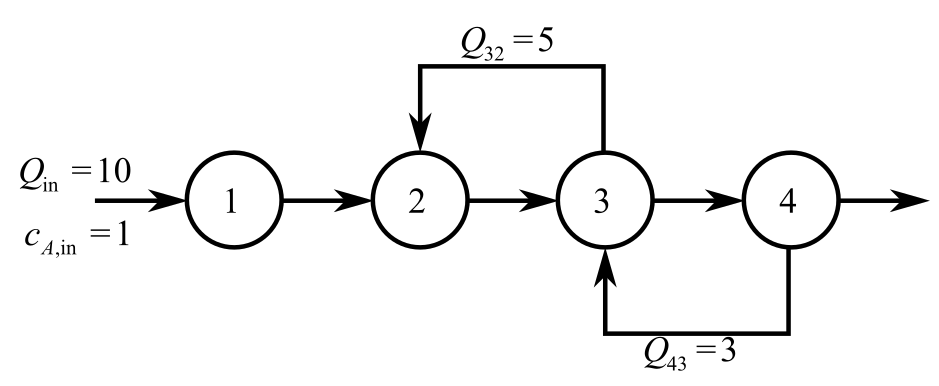
Balance the mass for A in reactor 1 at steady-state.
Substitute
Further solve.
Balance the mass for A in reactor 2 at steady-state.
Substitute
Further solve.
Balance the mass for A in reactor 3 at steady-state.
Substitute
Further solve.
Balance the mass for A in reactor 4 at steady-state.
Substitute
Further solve.
Balance the mass for B in reactor 1 at steady-state.
Substitute
Further solve.
Balance the mass for B in reactor 2 at steady-state.
Substitute
Further solve.
Balance the mass for B in reactor 3 at steady-state.
Substitute
Further solve.
Balance the mass for B in reactor 4 at steady-state.
Substitute
Further solve.
Now, write all the equations, to find linear system of equations.
Write the above linear equations in matrix form as written in symbolized form.
Here, coefficient matrix A is,
Column matrix
Column matrix B is,
Substitute the values in the matrix equation form.
Solve for
Code:
Type the above code into MATLAB command window and press enter to find the result.
Result is obtained as follows:
Hence,
Hence, the concentration of A and B is,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Numerical Methods for Engineers
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Basic Technical Mathematics
Fundamentals of Differential Equations (9th Edition)
Calculus: Single And Multivariable
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
- Investment Portfolio: In Exercise 57 and 58, you invest in AAA-rated bonds, A-rated bonds, and B-rated bonds. The average yields are 4.5 on AAA bonds, 5 on A bonds, and 9 on B bonds. You invest twice as much in B bonds as in A bonds. Let x, y, and z represent the amounts invested in AAA, A, and B bonds, respectively. { x+y+z=(totalinvestment)0.045x+0.05y+0.09z=(annualreturn)2yz=0 Use the inverse of the coefficient matrix of this system to find the amount invested in each type of bond for the given total investment and annual return. TotalInvestmentAnnualReturn$10,000$650arrow_forwardOptimal Cost A public aquarium is adding coral nutrients to a large reef tank. The minimum amounts of nutrients A, B, and C that need to be added to the tank are 30 units, 16 units, and 24 units, respectively. Information about each bottle of brand X and brand Y additives is shown below. How many bottles of each brand must be added to satisfy the needs of the reef tank at the minimum possible cost? CostNutrientANutrientBNutrientCBrandX$253units3unit7unitsBrandY$159units2unit2unitsarrow_forward
 Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning


