
(a)
Interpretation:
The equations for formation constants
Concept Introduction:
Formation Constant:
In the reaction of metal with ligand, the equilibrium constant is called as formation constant or the stability constant.
The formation constant for above complex reaction is,
Where,
(a)
Answer to Problem 12.18P
The equations for formation constants
The equations for formation constants
Explanation of Solution
To give the equations for formation constants
Given,
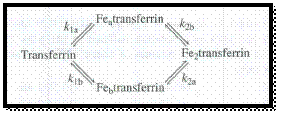
Figure 1
We know the formation constant for forward reaction is,
Apply the respective reactant and product in above equation to gives the equations for formation constants
The equations for formation constants
The equations for formation constants
The equations for formation constants
(b)
Interpretation:
The given respected equations should be explained.
Concept Introduction:
Formation Constant:
In the reaction of metal with ligand, the equilibrium constant is called as formation constant or the stability constant.
The formation constant for above complex reaction is,
Where,
(b)
Answer to Problem 12.18P
The equations for formation constants
The equations for formation constants
Explanation of Solution
To give the equations for formation constants
Given,

Figure 1
We know the formation constant for forward reaction is,
Apply the respective reactant and product in above equation to gives the equations for formation constants
The equations for formation constants
The equations for formation constants
The above equations are combined to give,
The reciprocal of
From the above derivation s the given equations are derived and they are shown correct relationship with corresponding reactions.
The given respected equations should be explained.
(c)
Interpretation:
Respect with the given reaction, the given expression should be explained.
Concept Introduction:
Formation Constant:
In the reaction of metal with ligand, the equilibrium constant is called as formation constant or the stability constant.
The formation constant for above complex reaction is,
Where,
(c)
Explanation of Solution
To give the equations for formation constants
Given,

Figure 1
The given equation is,
We know the formation constant for forward reaction is,
Apply the respective reactant and product in above equation to gives the equations for formation constants
The equations for formation constants
The equations for formation constants
The above equations are combined to give,
To cancel the common the terms,
Respect with the given reaction, the given expression was explained.
(d)
Interpretation:
From the given equations, the three unknown values are should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Formation Constant:
In the reaction of metal with ligand, the equilibrium constant is called as formation constant or the stability constant.
The formation constant for above complex reaction is,
Where,
(d)
Answer to Problem 12.18P
Three unknown values are,
Explanation of Solution
To give the equations for formation constants
Given,

Figure 1
The given equation is,
We know the formation constant for forward reaction is,
Apply the respective reactant and product in above equation to gives the equations for formation constants
The equations for formation constants
The equations for formation constants
The above equations are combined to give,
Plugged the equation 1 and in 3 and equation 2 in 4,
To solve the quadratic equation to give the
The given value of
Using the calculated
From the above calculations three unknown values are,
From the given equations, the three unknown values are determined.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
QUAN. CHEM. ANALYSIS. W/ACCESS>LLF< >I
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





